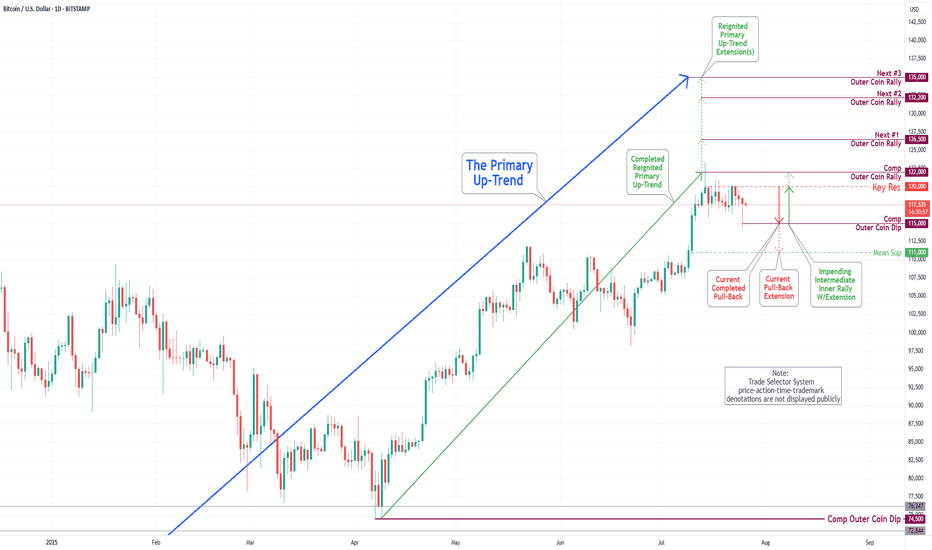
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of July 25, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
In the trading session of the previous week, the Bitcoin market exhibited considerable volatility as it retested the Key Resistance level at 120000. On the lower end of the spectrum, the market engaged with the Mean Support levels at 117500 and 115900, culminating in the completion of the Outer Coin Dip at 115000. Currently, the coin is poised to retest the Key Resistance at 120000 once again. This anticipated rebound will necessitate a retest of the completed Outer Coin Rally at 122000. The additional target levels for the renewed Primary Up-Trend are 126500, 132200, and 135000.
Macroeconomic Analysis And Trading Ideas
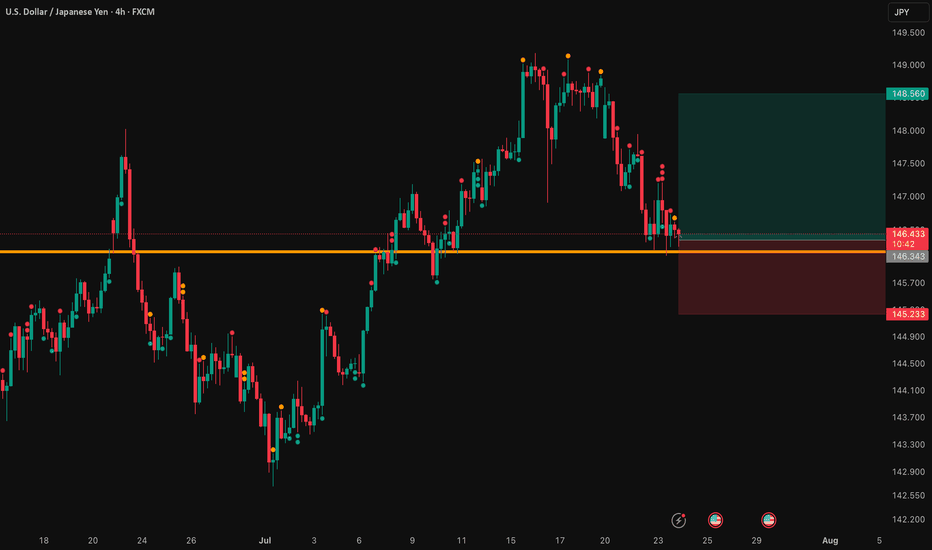
USD/JPY: A Bullish Thesis for Trend ContinuationThis analysis outlines a data-driven, bullish thesis for USD/JPY, identifying a strategic long entry within an established market trend. The setup is supported by a combination of fundamental catalysts and a clear technical structure.
📰 The Fundamental Picture
The primary driver for this trade will be the high-impact US economic data scheduled for release. This release is expected to inject significant volatility into the market. Fundamentally, this trade is a play on the deep policy differences between the US Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan. While the Fed's future steps are a topic of debate, the Bank of Japan's policy remains one of the most accommodative in the world, creating a long-term headwind for the Japanese Yen. This dynamic provides a strong fundamental basis for relative US Dollar strength against the Yen.
📊 The Technical Structure
Chart analysis reveals that USD/JPY is in a confirmed and healthy uptrend. The current price action indicates a constructive pullback, presenting a strategic opportunity to join the dominant trend at a favorable price. The proposed entry point is positioned at a key technical level that offers a low-risk entry. Technical indicators support the continuation of the trend, suggesting that momentum remains with the bulls.
✅ The Trade Plan
This trade is structured with a clear and favorable risk-to-reward profile, aiming to capitalize on the established trend.
👉 Entry: 146.343
⛔️ Stop Loss: 145.233
🎯 Take Profit: 148.560
⚖️ Risk/Reward Ratio: 1:2
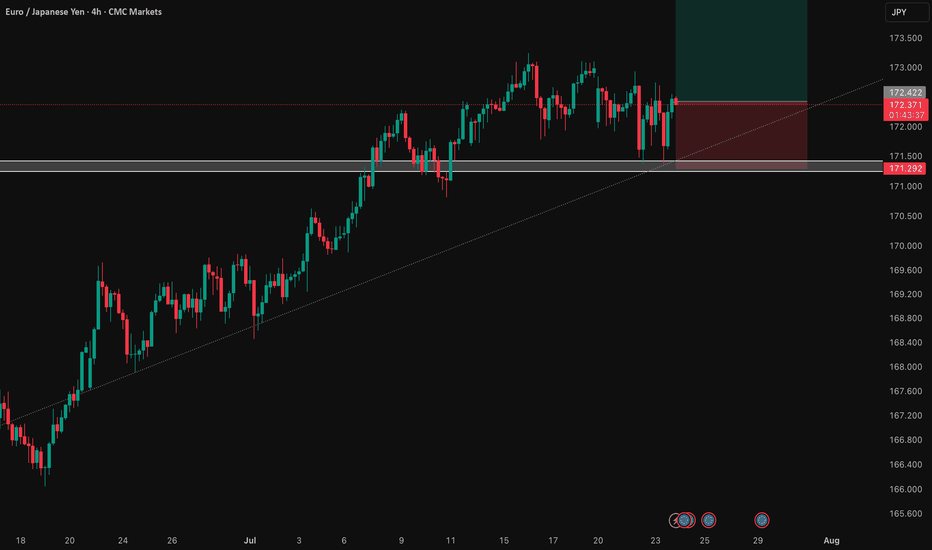
EUR/JPY: Bullish Thesis on Policy DivergenceOur primary thesis is built on a powerful confluence of compelling fundamental drivers and a clear technical structure. We are taking a long position in EUR/JPY with high conviction, anticipating significant upside fueled by a stark monetary policy divergence confirmed by a constructive chart formation.
📰 Fundamental Analysis: The core of this trade is the widening policy gap between the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Bank of Japan (BoJ). While the BoJ is only just beginning to exit its ultra-loose monetary policy, the global environment points toward continued JPY weakness. The upcoming high-impact US news will act as a major catalyst. A "risk-on" reaction to the data would significantly weaken the JPY, providing a strong tailwind for this trade.
📊 Technical Analysis: The chart structure for EUR/JPY is decidedly bullish. The pair has established a clear uptrend, and recent price action indicates a period of healthy consolidation above key support levels. This presents a strategic entry point, as the market appears to be gathering momentum for the next leg higher. The current setup suggests a low-risk entry into a well-defined upward trend.
🧠 The Trade Plan: Based on this synthesis, we are executing a precise trade with a favorable risk profile.
👉 Entry: 172.422
⛔️ Stop Loss: 171.292
🎯 Take Profit: 174.684
⚖️ Risk/Reward: 1:2
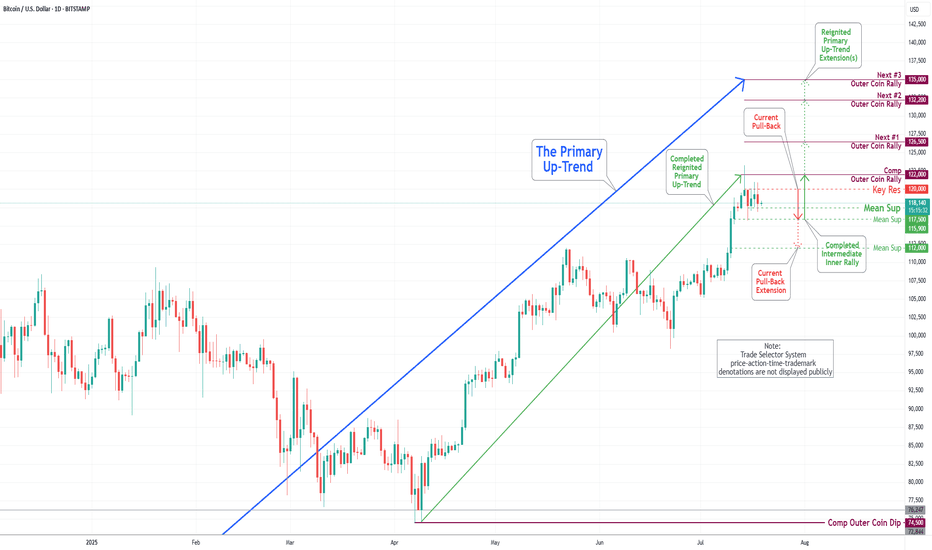
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of July 18, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
In last week's trading session, we achieved a new historical high by completing our Outer Coin Rally at 122000. Following this milestone, the coin retraced, as expected, to the newly established Mean Support at 115900 and is currently trading at the Intermediate Mean Support at 117500. Presently, the coin is set to retest the Mean Support at 115900, with the potential for a further pullback to the Mean Support at 112000. This anticipated decline will necessitate a retest for the completed Outer Coin Rally at 122000. The designated targets for the renewed Primary Up-Trend are 126500, 132200, and 135000.
Weekly Macro Brief: Chinese Economic Data, US Inflation, Tariff CME_MINI:ES1! CME_MINI:NQ1! COMEX:GC1! CME:BTC1! CME_MINI:RTY1! COMEX:SI1! CME_MINI:MNQ1! NYMEX:CL1! CME_MINI:M6E1! CBOT:ZN1! CME_MINI:MES1!
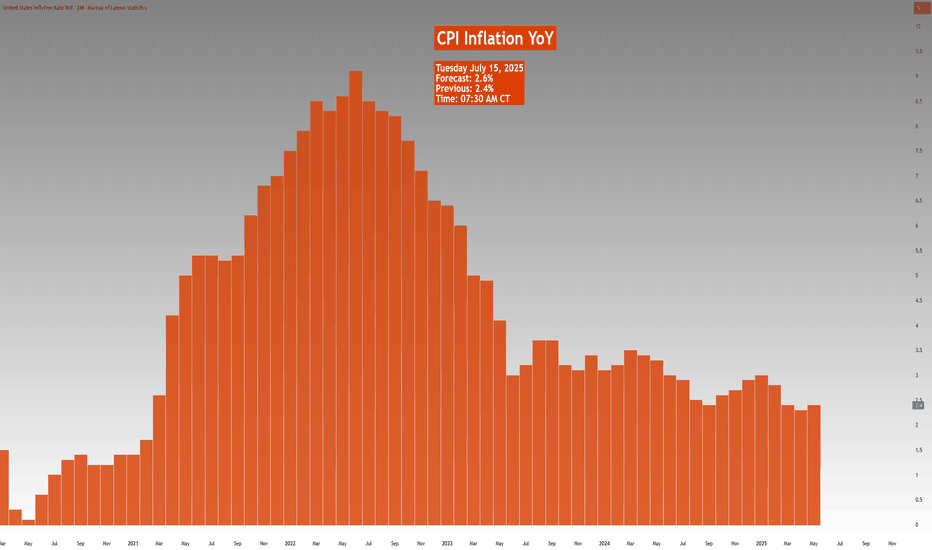
Highlights this week include Chinese economic data points, UK CPI, US CPI, PPI, and Retail Sales. Inflation data is key, as it comes ahead of the Fed's meeting on July 30th, 2025.
Market participants, including institutional investors and futures brokers like EdgeClear, will be scrutinizing these data points closely to monitor global growth and underlying inflation pressures.
Fed speakers are scheduled throughout the week. With increasing calls for Fed Chair Powell voluntary resignation and impeachment, the US administration desiring lower rates, the Fed’s independence and credibility to carry out its dual mandate is at risk. It will be interesting to monitor who folds first. Last week’s FOMC minutes revealed a divided Fed on the interest rate outlook, affirming its June dot plot.
On the fiscal policy front, we are already witnessing a shift in global trade policies, with many nations making concessions to negotiate trade deals with the world’s largest economy. In our analysis, the inflation impact of tariffs may not show up until Q4 2025 or early 2026, as tariff threats are mostly used as a lever to negotiate deals. While effective tariff rates have increased, as Trump reshapes how tariffs are viewed, cost pass-through to consumers will be limited in Q3 2025, as companies’ front-loaded inventory helps mitigate the risks of increased tariff exposure.
So, what we have is an interesting development shaping up where, while inflation may rise and remain sticky, it is yet to be seen whether slowing consumer spending will weaken enough to the point where companies have to start offering discounts, which would nullify the tariff risk to the end consumer and result in companies absorbing all tariffs. This scenario will see reduced earnings margins leading into the last quarter and early 2026. However, it will materially reduce risks of higher inflation.
In summary, the complex interplay between tariffs, inflation, and consumer behavior presents critical considerations for traders. EdgeClear, as a dedicated futures broker, remains focused on equipping clients with the insights needed to help navigate this evolving macroeconomic environment.
Overnight Data Recap:
• Chinese Trade Balance (CNY)(Jun) 826.0B (Prev. 743.6B)
• Chinese Trade Balance USD* (Jun) 114.77B vs. Exp. 109.0B (Prev. 103.22B)
• Chinese Imports YY* (Jun) 1.1% vs. Exp. 1.3% (Prev. -3.4%)
• Chinese Exports YY* (Jun) 5.8% vs. Exp. 5.0% (Prev. 4.8%)
Key Economic Releases:
• MON: EU 90-Day Retaliatory Pause Ends
• TUE: OPEC MOMR, Chinese House Prices (Jun), Retail Sales (Jun), GDP (Q2), EZ Industrial Production (May), German ZEW (Jun), US CPI (Jun), NY Fed Manufacturing (Jul), Canadian CPI (Jun)
• WED: UK CPI (Jun), EZ Trade (May), US PPI (Jun), Industrial Production (Jun)
• THU: Japanese Trade Balance (Jun), EZ Final HICP (Jun), US Export/Import Prices (Jun), Weekly Claims, Philadelphia Fed (Jul), Retail Sales (Jun)
• FRI: Japanese CPI (Jun), German Producer Prices (Jun), US Building Permits/Housing Starts (Jun), Uni. of Michigan Prelim. (Jul)
China GDP / Retail Sales/ Housing (TUE):
• Q2 GDP is expected to slow to 5.1% Y/Y (vs 5.4% in Q1) and 0.9% Q/Q.
• Retail sales have been resilient, but industrial production and investment show signs of weakness; deflation and labor market concerns persist.
• Property prices continue to decline, fueling stimulus speculation; policymakers remain cautious, with only modest easing expected (LPR and RRR cuts in Q4).
US CPI (TUE)
• June CPI expected at +0.3% M/M headline and core, suggesting a modest rebound from May’s subdued figures.
• Inflation impact from tariffs seen as temporary; Fed officials maintain a cautious stance with possible rate cuts only if price pressures stay benign.
• Markets are pricing near-zero odds for a July rate cut, but still expect two 25bps cuts by year-end in line with Fed guidance.
US Retail Sales (THU):
• Headline June retail sales expected flat M/M; ex-autos expected to rise +0.3%, showing signs of consumer stabilization.
• BofA data shows mild spending rebound, though discretionary service spending continues to weaken, especially among lower-income households.
• Spending strength remains concentrated in higher-income cohorts; weakness in wage growth limits broader consumption momentum.
US Trade Tensions – Tariffs & Negotiations:
• Trump announced 30% tariffs on EU and Mexican goods effective August 1st, separate from sector-specific tariffs.
• Trump stated the EU is engaging in talks and South Korea is also pursuing a trade deal.
Mexico Response:
• President Sheinbaum expects a deal before August 1st but reaffirmed Mexican sovereignty is non-negotiable.
• Mexico’s Economy Ministry is negotiating to protect domestic firms and workers, aiming for an alternative resolution.
EU Response:
• European Commission President von der Leyen warned that 30% tariffs would disrupt key transatlantic supply chains.
• The EU will extend suspension of countermeasures until early August but is prepared to respond proportionally if needed.
• The EU prefers a negotiated solution and dropped plans for a digital tax, seen as a concession to US tech interests.
• Separately, the EU is drafting a broad corporate tax on firms with turnover above EUR 50 million to support its budget.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of July 11, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
In the last week's trading session, Bitcoin has demonstrated a significant surge, achieving historical prices as anticipated by TSS for an extended period. The cryptocurrency has successfully completed both the Outer Coin Rally 114500 and the Inner Coin Rally 118200. Presently, Bitcoin is poised to celebrate this notable accomplishment with a victory lap, but it may face a potential downward trajectory, targeting the Mean Support level of 112000. This anticipated decline will necessitate the resilience to a retest of Inner Coin Rally 118200. The designated targets for the Outer Coin Rally at this juncture are 122000, 126500, 132200, and 135000.
DXY (USD Basket) - 3 Month - Short Squeeze In Play?Technicals:
The last 3-month candle closed above the major resistance that tends to hold according to historic levels going back to the year 1967.
Golden Cross is almost complete (50 MA crossing the 200 MA).
Fundamentals:
The dollar has only been more shorted once in history (2018), setting things up for a potential "Short Squeeze" and triggering a "Risk Off" scenario. Tends to hurt risk assets quite hard—for example, tech stocks, crypto, and other leverage plays.
A rise in the DXY could potentially trigger a "Short Squeeze" for foreign countries, companies, and investors that borrow in USD, creating "economic panic" in other countries that get their currency devalued relative to their obligations.
Countries that need USD to service their debt. With the current tariffs, the flow of dollars in the world will change. The question is: what will the effect look like in August when these tariffs start to go live? Like I mentioned before, other countries need the dollars in order to service their debt. If it gets more expensive for US consumers to import (caused by the tariffs), the exporting countries won’t get those dollars—setting it up for a buying cycle that could potentially drive the USD (DXY) higher, even to all-time highs.
Current narrative:
The narrative right now is that the USD will get "worthless," setting the stage to take more risk and use more leverage, maybe without even hedging. A surprise variable to this narrative could be devastating to the financial markets—not just in the US, but even to the world. IF/When this happens, everyone will hunt the USD once again, creating a new bullish narrative for the USD, and everyone will be forced to return to the reserve currency.
Nothing in this post should be considered financial advice. Always do your own research and analysis before investing.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of July 4, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
During this week's trading session, Bitcoin rebounded from our Mean Support level of 104900 and, with significant momentum, subsequently completing the Mean Resistance level of 110300. Currently, the cryptocurrency is poised for a continuation of its downward trajectory, with a target set at the Mean Support level of 105500. This downward trend may necessitate heightened resilience to address the Key Resistance point at 111700 and the emerging historical price action of the Outer Coin Rally at 114500 and beyond. Nonetheless, it remains essential to acknowledge the possibility that current prices may experience an uptick from this juncture, bolstering the rally mentioned above.
NZDCAD: High-Conviction Long - Fundamental Strength & TechnicalThis analysis identifies an extremely high-conviction long opportunity in the NZDCAD currency pair 📈🇨🇦🇳🇿. Our conviction is primarily driven by a significant divergence in monetary policy outlooks and economic fundamentals between New Zealand and Canada. New Zealand's economic resilience, underpinned by robust dairy prices and a less dovish central bank stance, contrasts sharply with Canada's decelerating growth, rising unemployment, and a central bank poised for further rate cuts amidst trade policy uncertainties. Technically, NZDCAD appears poised for an upward move from key support levels, supported by bullish momentum indicators on the 4-hour chart. This is a medium-term trade expected to play out over days to weeks. 🗓️
I. Fundamental Rationale: Diverging Economic Trajectories 📊🌍
The core of this trade lies in the starkly different economic paths New Zealand and Canada are currently on, creating a compelling fundamental case for NZD appreciation against CAD:
Monetary Policy Divergence:
New Zealand (NZD): The Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) maintained its Official Cash Rate (OCR) at 3.25% in June 2025. Analysts anticipate a hold at the upcoming July 9 meeting, balancing growth concerns with an "uncomfortably high near-term inflation outlook". This signals a less aggressive easing path. 🏦🇳🇿
Canada (CAD): In contrast, the Bank of Canada (BoC) held its policy rate steady at 2.75% in June 2025, after nine consecutive 0.25% cuts since June 2024. Market expectations for the upcoming July 30, 2025 meeting indicate a 33% chance of a further 25 basis point cut, with economists anticipating gradual cuts to 2.25% by mid-2025. This clear easing bias is driven by consistently below-target inflation (1.73% in May 2025). 📉🇨🇦
Impact: This creates a clear and widening interest rate differential fundamentally favoring the NZD. 💰
Inflation Outlook:
New Zealand: Annual inflation accelerated to 2.5% in Q1 2025, exceeding market expectations and marking the highest rate since June 2024. This reinforces the RBNZ's cautious stance. ⬆️
Canada: Canada's CPI registered 1.73% in May 2025, notably below the BoC's 2.0% target, providing ample justification for further monetary easing. ⬇️
Economic Performance & Labor Market:
New Zealand: GDP is projected to grow by 1.9% in 2025. The unemployment rate remained unchanged at 5.1% in March 2025, with average hourly earnings increasing by 4.5% annually. 💼✨
Canada: Real GDP contracted by 0.1% in April 2025, with a flash estimate pointing to another 0.1% decline in May, implying an annualized loss of 0.3% in Q2 2025. The unemployment rate rose to 7.0% in May 2025, its highest since September 2016 (excluding pandemic years). 📉🏭
Impact: New Zealand demonstrates greater economic resilience and a more stable labor market. 💪
Commodity & Trade Dynamics:
New Zealand: Benefits significantly from surging dairy prices, its top export commodity, which saw a substantial 10% increase in Q1 2025, with Fonterra forecasting record milk prices and production volumes. This contributed to a robust monthly trade surplus of $1.2 billion in May 2025. 🥛🧀💰
Canada: While the CAD maintains a strong positive correlation with oil prices, energy exports decreased by 5.6% in May, with crude oil exports falling 4.0%. Furthermore, Canadian exports to the US have declined for four consecutive months due to ongoing US tariffs. 🛢️📉
Impact: Strong commodity tailwinds and a healthy trade surplus for NZD, versus tariff-induced headwinds and declining energy exports for CAD. 🌬️
Yield Differential: The New Zealand 10-year government bond yield (4.57% as of June 30, 2025) is notably higher than Canada's (3.38% as of July 3, 2025). This provides a positive carry for holding NZD over CAD. 📊
II. Technical Rationale: Chart Insights (4-Hour Timeframe) 📈🔍
The technical picture on the 4-hour chart supports a bullish reversal from current levels, complementing the fundamental outlook:
Current Price Action & Long-Term Trend: NZDCAD is currently approximately 0.8277 (as of July 1, 2025). While short-term analyses may show a "sharp bearish trend," the pair is described as "trading in an uptrend and currently is in a correction phase" as it approaches a key support area. The 1-month change for NZDCAD is +0.13%, and year-to-date is +2.45%, indicating a longer-term bullish bias despite recent fluctuations. This corrective dip presents a favorable entry point. 📉➡️📈
Key Support & Resistance Levels:
Entry Point (0.8270) is strategically chosen near the immediate support cluster, specifically around the Pivot Point 1st Support of 0.8276 and an identified buying opportunity zone around 0.82700. ✅
Take Profit (TP) of 0.8350 is positioned just below the Pivot Point 3rd Level Resistance of 0.8356. 🎯
Stop Loss (SL) of 0.8220) is carefully placed below the key support levels of 0.8240 (Pivot Point 3rd Support) and 0.8236 (Pivot Point 3rd Support). A sustained break below this level would invalidate the bullish thesis. 🛑
Momentum Indicators:
RSI (14): The 14-day RSI for NZDCAD is around 41.78 to 54.33, suggesting a neutral to slightly bullish sentiment, with room for upward movement. 📊
MACD (12, 26, 9): A "bullish divergence" has been identified on the hourly timeframe, often signaling a return of buying interest. The MACD line is also observed to be slightly above its signal line, hinting at a potential bullish crossover. ⬆️
Moving Averages: The 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) is positioned slightly above the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA). This configuration suggests a potential bullish crossover of longer-term moving averages, generally considered a positive long-term signal. 📈
III. Trade Setup: 📋✨
Currency Pair: NZDCAD 🇳🇿🇨🇦
Direction: Long (Buy) ⬆️
Entry Point: 0.8270
Take Profit (TP): 0.8350
Stop Loss (SL): 0.8220
Calculated Risk (in pips): 50 pips
Calculated Reward (in pips): 80 pips
Risk-Reward Ratio: Approximately 1.6:1 (A favorable ratio for a high-probability setup!) ✅
Key Considerations: Always adhere to strict risk management principles, risking no more than 1-2% of your total trading capital on this single trade. Be mindful of potential volatility around upcoming high-impact economic events in July, particularly the RBNZ and Bank of Canada interest rate decisions, and inflation data. 🗓️🔔
Sintra Signals: Central Banks Stay Cautious The ECB Forum in Sintra brought together the heads of the world’s most influential central banks—Lagarde (ECB), Powell (Fed), Bailey (BOE), Ueda (BOJ), and Rhee (BOK).
Across the board, central banks are remaining cautious and data-driven, with no firm commitments on timing for rate changes.
Fed Chair Powell said the U.S. economy is strong, with inflation manageable despite expected summer upticks. He noted tariffs have delayed potential rate cuts and confirmed the Fed is proceeding meeting by meeting.
BOE’s Bailey highlighted signs of softening in the UK economy and said policy remains restrictive but will ease over time. He sees the path of rates continuing downward.
BOJ’s Ueda noted headline inflation is above 2%. Any hikes will depend on underlying core inflation which remains below target.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of June 27, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
Throughout this week’s trading session, Bitcoin has demonstrated an upward trajectory and is positioned to achieve the specified targets of Mean Resistance 110300 and Key Resistance 111700. This progression may ultimately culminate in the realization of the Outer Coin Rally 114500 and beyond. Nevertheless, it is crucial to recognize the possibility of a subsequent decline from the current price to the Mean Support level of 104900 before a definitive upward rebound.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of June 20, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
In the recent trading session, Bitcoin exhibited an upward trend; however, it subsequently experienced a significant decline from the established Mean Resistance level at 110300. On Friday, Bitcoin exhibited notable price action, characterized by a pump-and-dump scenario. At this juncture, Bitcoin is retracing downwards as it seeks to approach the Mean Support level at 101500 and the ultimate Inner Coin Dip at 96500. It is essential to acknowledge the potential for an upward rally from the Mean Support levels of $101500 and/or the Inner Coin Dip at $96500. Such a rally could culminate in a retest of the Mean Resistance level at $107000.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of June 13, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
Throughout the past week, Bitcoin has exhibited considerable volatility. After reaching a peak at the first Mean Resistance level of 109500, the cryptocurrency experienced a significant decline. Nevertheless, on Friday, Bitcoin demonstrated a notable recovery, ascending to a newly established resistance now designated as the new Mean Resistance level marked at 110300.
At this juncture, Bitcoin is retracing downward as it retests the initial Mean Support level of 104000 while aiming to target the Mean Support at 101500 and the ultimate Inner Coin Dip at 96500. It is essential to recognize the potential for an upward rally from the Mean Support levels of $ 104,000 and/or $ 101,500, which could culminate in a retest of the Mean Resistance level of $ 110,300.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of June 6, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
Bitcoin has experienced a notable downturn throughout the week; however, on Friday, it made a substantial upward movement, effectively recovering all previous losses. It is currently positioned to establish a temporary pause at the Mean Resistance level of $106,000, which may facilitate the development of upward momentum from this point. This situation may pose challenges to achieving the Inner Coin Rally target of $ 114,500, which is contingent upon the Mean Resistance at $ 109,500 and Key Resistance at $ 111,700. It is essential to acknowledge the possibility of a downward pullback from the Mean Resistance level of $106,000, which could result in a decline toward the Mean Support level of $101500.
Macro Gold vs Stocks - Is it finally the Gold Bug's turn?When you zoom out things become more clear.
Has it always been that easy? Easy to see in hindsight difficult to execute over years and hold strong.
Trust the trends and when they break, you best be on your toes. It will never be the same but similar.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of May 30, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
Bitcoin has undergone a significant decline during the current week's trading session and is presently situated at the Mean Support level of $103,000. This downward trajectory has the potential to establish a temporary pause, which may facilitate the emergence of upward momentum from this level, and it could pose a challenge to the Key Resistance level at 109500. A successful breach of this resistance may lead to the completion of the Inner Coin Rally target at $114500. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the possibility of renewed downward momentum from the current level, as this could result in a decline toward the Mean Support of 99000.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of May 23, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
In the course of this week's trading session, Bitcoin demonstrated significant upward movement, surpassing both Mean Resistance at 105000 and Key Resistance at 106100. This progression also facilitated the surpassing completed Inner Coin Rally at 108,000, and the highly anticipated Outer Coin Rally marked at 110000. As a result, the cryptocurrency experienced a substantial decline, currently aiming toward Mean Support at 105600, with a potential further decline toward an additional Mean Support target at 101500.
It is essential to acknowledge the possibility of an upward momentum emerging from the current level, which may enable a challenge to Key Resistance at 111700. Success in this regard could result in reaching the Inner Coin Rally at $114500 and, subsequently, the Outer Coin Rally at 122000.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of May 16, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
During this week's trading session, Bitcoin has remained tightly bound within our Mean Resistance level of 104000 and is positioned to retest the lower target identified as Mean Support at 99300. There exists a possibility of a further decline toward an additional Mean Support target at 94000. Nonetheless, it is crucial to recognize the potential for upward momentum from the current level, which may lead to a challenge of the Key Resistance at 106100. This could culminate in a retest of the previously established Inner Coin Rally at $108,000.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of May 9, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
Bitcoin leapfrogged our Interim Coin Rally 100000 via Key Res 97500 in this week's trading session and is clearly aiming to retest the next target of completed Inner Coin Rally 108000. Nevertheless, current price movements indicate a potential retracement from Mean Resistance 104000 toward the Mean Support level at 99300, with a further possible decline likely toward an additional Mean Support target at 94000. However, it is imperative to recognize the potential for upward momentum from the current level, as this could facilitate a trajectory toward the Key Res 106100 and the next Interim Coin Rally at $108,000 and beyond.
Taiwan Dollar Weakens Past 30 per USD Amid Trade Rumors and CentThe Taiwanese dollar weakened past 30 per USD on Tuesday, reversing a two-day rally and retreating from its strongest level in nearly three years.
📉 Recent gains in Asian currencies like the TWD and MYR were fueled by speculation over regional support for U.S. trade talks. However, Taiwan’s central bank denied any such coordination, stating the U.S. made no formal request. President Lai Ching-te also warned against spreading misinformation.
🔧 As a key player in global chip production, Taiwan remains highly exposed to shifts in trade dynamics and geopolitical risks.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of May 2, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
Bitcoin prices have significantly exceeded our previously completed Interim Rally 95000, thereby positioning the cryptocurrency to aim for the forthcoming Interim Coin Rally marked at 100000. Nevertheless, current price movements indicate a potential retracement toward the Mean Support level at 94000, with a further possible decline likely toward an additional Mean Support target at 91800. It is imperative to recognize the potential for upward momentum to develop from a retest of either support level, as this could facilitate a trajectory toward the next Interim Coin Rally at $100,000 and beyond.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of April 25, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
Bitcoin experienced a significant rally in this week's trading session, breaking through all identified Mean Resistance levels: 86400, 90600, and 94500. This breakout led to the completion of the Interim Coin Rally at 88400. As a result, the newest identified Interim Coin Rally at 95000 has also been completed, indicating a possible pullback to the Mean Support at 92000 and a further decline potential toward an additional Mean Support target at 88500. However, it's important to recognize the chance of upward momentum emerging from a retest of the completed Interim Coin Rally at 95000, which could advance toward the next Interim Coin Rally at 100000.
Bitcoin(BTC/USD) Daily Chart Analysis For Week of April 18, 2025Technical Analysis and Outlook:
During the price movements observed throughout the week, Bitcoin has remained close to the previous Mean Support level of 85200 and appears poised to initiate an upward breakout, targeting the newly developed Mean Resistance level of 86400. This breakout may facilitate a retest of the completed Interim Coin rally at 88400, with additional expansions of targets also being a possibility. It is critical to acknowledge that potential for downward momentum may arise from a rechallenge of either the Interim Coin Rally at 88400 or the Mean Resistance at 86400.