Semiconductors & SOXL: A Bull ThesisWhy Semiconductors?
Virtually every single electronic device contains some form of a semiconductor unit within its components. The entire Bull theory on semiconductors as an industry could be reduced to this one sentence. The following, however, will introduce concepts contingent to the understanding of what is shaping the market for semiconductors. The weight of intra-industry, political, macroeconomic, and physical factors discerning an inconceivable upside potential for certain investments carrying maximum exposure to the sector, such as AMEX:SOXL . The last section contains my technical approach to trading SOXL.
We begin with the fundamental, and by fundamental, I refer to the simplest reasons for what is happening in the market up until now; [ Early morning Monday, 7/28 ].
Macroeconomic Context
Like essentially the rest of the market, SOXL hit its 1 year low of 7.23 USD on Monday, 4/7, following the announcement (and soon postponement) of global tariffs at levels not observed since the early 30's. This of course sparked a panic spiral in the entire market, leading to outflows from the S&P 500 of approximately 70 billion USD during the month of April. During this time we also saw a new, but familiar narrative emerge. Asset Managers, Such as J.P. Morgan set historically low price targets on the S&P 500, going as low as 5,200 USD. They reinforced their PTs with publications warning investors across the world that the risk of recession in the United States was raised to 80%, and this message was relayed across all media in parabolic fashion. While it does not seem too outward to assume an increased risk of recession due to tariffs by looking back on what we learned of the consequences from the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930. There exists a widely overlooked, fundamental , reason as to why I can claim that the REAL risk of recession at the time that J.P. Morgan assigned an 80% risk of recession, was in actuality, 0% (I assume J.P. Morgan knew this but pushed the narrative anyways in order to acquire massive equity at a discount). If anyone has taken introductory macroeconomics in their lifetime, they may be familiar with the function for calculating GDP via the expenditure approach: GDP = C + I + G - NX. Now, why am I referencing high school/college economics basics, the answer to that lies in how we determine our rate of economic growth in the context of tariffs. The part of this formula that we must focus on is NX or Net Exports, the negative factor to GDP. Tariffs, if implemented would effectively decrease import volume, resulting in a smaller Net Exports, and ultimately a higher GDP calculation. Now, what makes this scenario unique, the tariffs having been postponed shortly after their inception, allowed US retailers to engage in front running, or the accelerated purchasing of foreign goods in advance of tariffs. During the month of April, we saw a 5.4% increase in import volume in US west coast ports. This increase in imports effectively caused the inverse impact on GDP growth that import tariffs themselves would have caused: front-running lead to import uptick, leading to a greater Net Exports, which results in lower (negative) GDP growth. Essentially, tariffs in the short-term increases GDP growth (in the long term deadweight loss, and cost structure distortion comes in to play, but that doesn't matter yet), however , tariffs that are announced but not immediately implemented will result in a lower GDP growth, coupled with uncertainty surrounding the whole situation that translated into a cut in CapEx as companies scrambled to determine if tariffs would f*ck them over or not. This argument is further supported by the trends observed in the foreign exchange market. You may have heard in the news that we are experiencing a period of "Dollar Weakness", and while, yes, you can clearly see that the USD has fared rather poorly against other currencies in most major dollar pairs over the past few months. The agent behind this isn't just that the dollar happens to be weak, it is a combination of factors that generate noise and volatility in the forex market. The two main factors highlighted by the media are 1. The obvious political policy instability, pushing bond yields higher, plus a significant debt ceiling raise as per the BBB and 2. the expectations of interest rate cuts over the next year. The other, less recognized major factor to dollar weakness is exactly what we described above: Increased imports means more dollars flowing out of the economy. When these dollars land abroad, they are converted into the native currency, driving down the demand for the dollar. Notice how none of the reasons described above, actually have anything to do with what truly drives foreign exchange markets. Over time, the strength/weakness of a currency is directly correlated to the strength/weakness of the underlying economy. To say that we can expect dollar weakness due to the aforementioned reasons outright ignores the economic growth potential that exists in our economy at this current time, subsiding the out-of-proportion tariff fears as a proponent to an economic crisis. In an all-encompassing view, what I would describe to be occurring on the macro level is a sort of "slingshot" effect: Trade imbalances and private sector response to policy unclarity results in a pullback in economic growth, one that we are now experiencing as a short-term effect. From a medium-long term perspective, assuming that tariffs aren't persistent in the long term, we would see full fledge economic boom, driven by non other than the growth of our technology sector, which at it's core, lies the almighty semiconductor.
Growth of AI as a driver of Semiconductor demand: Stable trajectory or Bubble Territory?
Having laid the economic framework for picking the general direction our market is heading in, we can now begin to talk about the internal combustion occurring within the world of technology, and the two letter term associated with just about every cool thing in the business world, that is of course AI. Now just to clarify, AI is not new, its been around for at least 20 years and has a well established role in the world prior to the existence of ChatGPT. What changed so drastically in recent years is the breakthrough into a new form of artificial intelligence, known as "Artificial General Intelligence" or AGI. Long story short: AGI's primary difference in the business context is the colossal amount of electrical infrastructure and computing power that is demanded by the development of these mega language models. As a result of the high barrier for entry to this new industry, only 5 AGI companies have arisen to the global stage: OpenAI, Google DeepMind, Anthropic, Microsoft, and DeepSeek. Increasing competition in this space through more players entering the market is unlikely at this time as the cost to create a standalone AGI model is so astronomical. This is a particularly good thing because it tells us that AGI as an industry can result in natural monopolies. The ultra-intensive RnD costs and Data Center infrastructure demands make it more sensical to have a greater number of resources dedicated to producing 1 AGI model, instead of dividing resources to develop multiple less optimized models (similar to how a water company holds a natural monopoly as competition in that industry would result in no foreseeable benefit to it's customers). A further effect from this dynamic lies in how businesses in this industry scale to expand, and its pretty straightforward: the more megawatt computing power a model can access, the more parameters a model can account for, and the more vast the dataset that model can train on, with enhancing speed and efficiency (GPT 4o takes into account >500B parameters in a given query). We see the concept of natural monopoly playing out as the concentration of market capitalization is becoming more extreme where firms like Google, Microsoft, and NVIDIA are absorbing larger share of the market, while trading at ever increasing Price/Earnings multiples. To many, this reflects a trend we saw during the dot com bubble, however what makes the AGI industry different is the nature of the good or service provided. During the dot com boom, companies saw speculative value based on only the fact that their business existed on the .com domain. We know that each of these businesses are unique, providing a good or service across whatever industry they were part of, the only thing having in common was that dot com. The major oversight that took place during the turn of the dot com era was that the success of these businesses wasn't in truth due to them ending in .com, but whether the idea, and execution behind the underlying business is strong or not. Like how Amazon and Facebook saw unparalleled success not just because they were .coms, but because they were pioneering business models that would attract global demand to the services they were providing. The business of AGI has a sort of homogenous property. All AGI companies produce a service that is extremely similar in nature, the only ways they can compete with one another is through Capital Expenditure towards harnessing more computing power. This is the main reason capital is concentrating in a handful of companies trading at high multiples. To me, this is not an indication of a tech bubble but rather a product of how the AGI industry is poised to grow within our economy.
AGI as a Factor of Production
To get even more philosophical, we can think about how AGI itself enhances economic growth. We already see AGI tools applied in various ways, but the most widespread application pertains to the enhancement of human capital. While it is possible to make AGI models complete ongoing tasks completely on their own with zero human input, its far more common to see AGI tools be used, well, as tools. What I mean is that firms are not looking to replace human workers with AI ones (certain exceptions may include the manufacturing industry), instead they want to integrate AGI tools into their workforce as a means of optimizing regular processes, allowing them to access and process information with tremendous efficiency. The most observable economic outcome of this is firms being able to cut costs in human capital requirements, allowing them to achieve the same level of workflow with a smaller number of employees, or outsourcing solutions to business processes by way of automation utilizing AGI. The possibilities are endless and the economic impact of AGI appears to write itself new economic theory to explain how business growth is accelerating in unprecedented ways.
Semiconductor Physical Limitations: Blessing or Burden?
In 1965, Gordon Moore articulated his observation which would come to be known as Moore's Law. He observed that the number of transistors in an integrated circuit doubles approximately every 2 years. Based not so much on law of physics, Moore's law describes an empirical relationship between time and the number of transistors per chip, suggesting that the rate of production advancements would allow for such doubling to occur on a biannual basis. And to Gordon's own surprise, he was right. Transistor count for a given chip roughly doubled every 2 years for the following 50 years. However, Gordon also predicted that Moore's Law would come to an end in 2025, where transistor sizes would reach the physical limit of 2 nanometers (10-15 silicon atoms in width). While it may appear as a bottleneck to the semiconductor and AI industry, not being able to fit anymore transistors on one chip, but in reality, this limitation pressures companies to pursue innovations such as semiconductor packaging, which is NVIDIA's bread and butter. This technique allows for the stacking and integrating of many different chips to perform together as one. This technology has already proven wildly successful and is the backbone to virtually all of NVIDIA's GPU products. Google has invented their own method to getting around the physical limitation of silicon chips, producing AI-specialized integrated circuits known as Tensor Processing Units (TPUs). Catering these innovative solutions to expanding the frontier of AGI is almost a given.
How to play this market: A Technical Approach
If you have made it this far, I commend you. The following describes my approach to analyzing price activity in SOXL:
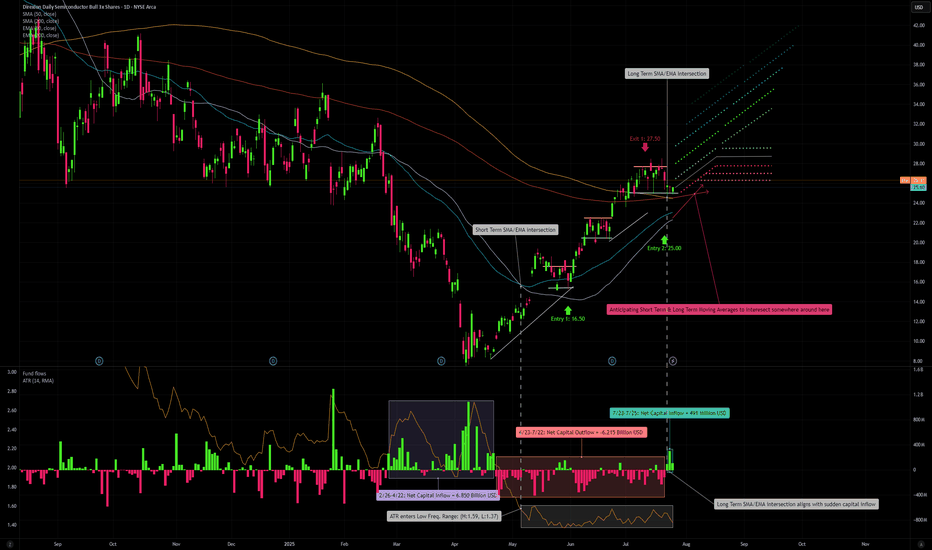
My First entry into SOXL took place on 5/30 with a unit cost of 16.50 USD. Two things can be noted prior to this entry. 1: Fund flows during late February, into March, and through April were extremely high, net inflow of 6.85 Billion USD, however price movement did not reflect the huge inflow until late April/early May where we began to see upward price direction. The beginning of June marked the start of the market bull rally which consolidated into our current price range of 25-28 USD, following contingent earnings releases of NASDAQ:ASML , NYSE:TSM , NASDAQ:NXPI and NASDAQ:INTC . The most recent pullback was a combination of a slightly concerning outlook from ASML, stating that tariffs on the EU would negatively affect projected sales growth for the 2026 fiscal year. As for TSM, there is not one concerning thing that could be said regarding the state of its business growth other than the New Taiwan Dollar gaining considerable strength over the USD amid trade relations between the US and Taiwan, affecting TSM's gross margin by an estimated 6%. NXPI released a sub par earnings and revenue growth outlook, but in my opinion this is not to be too heavily objectified as NXPI produces chips primarily for the Automotive sector, thus making it's sales heavily contingent on supply chain issues being faced by automotive manufacturers in leu of tariffs. NXPI carries a 3.5% market share in semiconductors whereas TSM carries a 68% market share. Lastly, INTC, earnings release I am almost embarrassed to talk about. If it were up to me I'd say they sell their plants in Ohio to TSM and look into opening a fruit stand instead. The most important earnings releases have yet to come though. NASDAQ:MSFT is just around the corner on 7/30, and NASDAQ:NVDA announces on 8/27. These two earnings reports will carry major weight in hinting the overall direction, momentum the market sees in AI demand growth, and the technology sector as a whole. Speculating, I have high expectations that both MSFT and NVDA will top all estimates, pushing the bar higher for 2025 into 2026.
If we look at our short-term 50-day SMA/EMA, you will notice a crossover occur on 5/6, a minor indication of a short term positive trend. Alone this is insignificant, but if we look at our 14-day Average True Range, we can see that this crossover aligns with a fall in ATR that would persist between the values of 1.37 and 1.59. This low ATR value signals that trailing volatility is actually quite low for semiconductors, considering the currently mixed market sentiment. Further along we see that price has crossed above both our long-term, 200-day SMA/EMA and a crossover occurred between the two on 7/23, serving as a small indication of a positive long term trend. Once again, not super significant on its own, but you will notice that the convergence aligns perfectly with a sharp increase in fund inflows, netting 491 Million USD in a matter of 3 trading days. If we see a continuation of net inflows over the several days, we can expect a near future extension of our bull rally, a semi-cyclical wave of inflows that concentrate during consolidation periods (which we have seen take place in the current price range between 25-28 USD following my first exit at 27.50 USD). If we extrapolate both our short-term and long-term SMA/EMA, we can anticipate a crossover to occur in the coming days to weeks. If this occurred, that would further reinforce our expectation for a positive long term trend. I have already locked in my entry 2 with a limit order executed at 25 USD. If all of the above conditions are met, I would confidently predict that we may see SOXL trade at around 42 USD in the coming months.
One more thing I would like to note, if we zoom out to our 5 year historical price progression, we can identify the previous high of 70.08 USD occurring on 7/11/2024. We know that the bull rally which took place in July of last year can be attributed to the first realization of AI as a driver for semiconductor demand, combined with renewed interest in GPU technology for applications in crypto. If we compare AI-related Capital Expenditure in fiscal year 2024 to AI-related Capital Expenditure of the first half of 2025 fiscal year: 246 Billion USD made up AI-related CapEx for all of 2024, vs first 6 months of 2025, adding up to 320 Billion USD. That is a 30% increase in capex, and we still have another 5-6 months to go. Just some food for thought.
Do you believe all of the above has been priced into SOXL, leave your thoughts in the comments!
Disclaimer
You must obviously keep in mind, SOXL is a 3x leveraged ETF, you can expect volatility with such type of investment. However, in capturing a bullish market, a 3x leveraged investment may produce greater than 3x the returns as the underlying (non leveraged) assets, due to the effect of compounding growth of returns over time. However, the same is true for sideways, or bearish markets, losses may be amplified to greater than 3x. If this is an uncertainty you do not wish to be exposed to, I would opt for the non-leveraged Semiconductor ETF ( NASDAQ:SOXX ), or divide your allocation across the top 5-10 equity holdings of SOXL. Please remember to employ your OWN due diligence before making any investment decision, as none of what I am saying shall serve as financial advise to you, the reader.
Economicindicators
Behind the Curtain: Bitcoin’s Surprising Macro Triggers1. Introduction
Bitcoin Futures (BTC), once viewed as a niche or speculative product, have now entered the macroeconomic spotlight. Traded on the CME and embraced by institutions through ETF exposure, BTC Futures reflect not only digital asset sentiment—but also evolving reactions to traditional economic forces.
While many traders still associate Bitcoin with crypto-native catalysts, machine learning reveals a different story. Today, BTC responds dynamically to macro indicators like Treasury yields, labor data, and liquidity trends.
In this article, we apply a Random Forest Regressor to historical data to uncover the top economic signals impacting Bitcoin Futures returns across daily, weekly, and monthly timeframes—some of which may surprise even seasoned macro traders.
2. Understanding Bitcoin Futures Contracts
Bitcoin Futures provide institutional-grade access to BTC price movements—with efficient clearing and capital flexibility.
o Standard BTC Futures (BTC):
Tick Size: $5 per tick = $25 per tick per contract
Initial Margin: ≈ $102,000 (subject to volatility)
o Micro Bitcoin Futures (MBT):
Contract Size: 1/50th the BTC size
Tick Size: $5 = $0.50 per tick per contract
Initial Margin: ≈ $2,000
BTC and MBT trade nearly 24 hours per day, five days a week, offering deep liquidity and expanding participation across hedge funds, asset managers, and active retail traders.
3. Daily Timeframe: Short-Term Macro Sensitivity
Bitcoin’s volatility makes it highly reactive to daily data surprises, especially those affecting liquidity and rates.
Velocity of Money (M2): This lesser-watched indicator captures how quickly money circulates. Rising velocity can signal renewed risk-taking, often leading to short-term BTC movements. A declining M2 velocity implies tightening conditions, potentially pressuring BTC as risk appetite contracts.
10-Year Treasury Yield: One of the most sensitive intraday indicators for BTC. Yield spikes make holding non-yielding assets like Bitcoin potentially less attractive. Declining yields could signal easing financial conditions, inviting capital back into crypto.
Labor Force Participation Rate: While not a headline number, sudden shifts in labor force data can affect consumer confidence and policy tone—especially if they suggest a weakening economy. Bitcoin could react positively when data implies future easing.
4. Weekly Timeframe: Labor-Driven Market Reactions
As BTC increasingly correlates with traditional markets, weekly economic data—especially related to labor—has become a mid-term directional driver.
Initial Jobless Claims: Spikes in this metric can indicate rising economic stress. BTC could react defensively to rising claims, but may rally on drops, especially when seen as signs of stability returning.
ISM Manufacturing Employment: This metric reflects hiring strength in the manufacturing sector. Slowing employment growth here could correlate with broader economic softening—something BTC traders can track as part of their risk sentiment gauge.
Continuing Jobless Claims: Tracks the persistence of unemployment. Sustained increases can shake risk markets and pull BTC lower, while ongoing declines suggest an improving outlook, which could help BTC resume upward movement.
5. Monthly Timeframe: Macro Structural Themes
Institutional positioning in Bitcoin increasingly aligns with high-impact monthly data. These indicators help shape longer-term views on liquidity, rate policy, and capital allocation:
Unemployment Rate: A rising unemployment rate could shift market expectations toward a more accommodative monetary policy. Bitcoin, often viewed as a hedge against fiat debasement and monetary easing, can benefit from this shift. In contrast, a low and steady unemployment rate may pressure BTC as it reinforces the case for higher interest rates.
10-Year Treasury Yield (again): On a monthly basis, this repeats and become a cornerstone macro theme.
Initial Jobless Claims (again): Rather than individual weekly prints, the broader trend reveals structural shifts in the labor market.
6. Style-Based Strategy Insights
Bitcoin traders often span a wide range of styles—from short-term volatility hunters to long-duration macro allocators. Aligning indicator focus by style is essential:
o Day Traders
Zero in on M2 velocity and 10-Year Yield to time intraday reversals or continuation setups.
Quick pivots in bond yields or liquidity metrics could coincide with BTC spikes.
o Swing Traders
Use Initial Jobless Claims and ISM Employment trends to track momentum for 3–10 day moves.
Weekly data may help catch directional shifts before they appear in price charts.
o Position Traders
Monitor macro structure via Unemployment Rate, 10Y Yield, and Initial Claims.
These traders align portfolios based on broader economic trends, often holding exposure through cycles.
7. Risk Management Commentary
Bitcoin Futures demand tactical risk management:
Use Micro BTC Contracts (MBT) to scale in or out of trades precisely.
Expect volatility around macro data releases—set wider stops with volatility-adjusted sizing.
Avoid over-positioning near major Fed meetings, CPI prints, or labor reports.
Unlike legacy markets, BTC can make multi-percent intraday moves. A robust risk plan isn’t optional—it’s survival.
8. Conclusion
Bitcoin has matured into a macro-responsive asset. What once moved on hype now responds to the pulse of the global economy. From M2 liquidity flows and interest rate expectations, to labor market stability, BTC Futures reflect institutional sentiment shaped by data.
BTC’s role in the modern portfolio is still evolving. But one thing is clear: macro matters. And those who understand which indicators truly move Bitcoin can trade with more confidence and precision.
Stay tuned for the next edition of the "Behind the Curtain" series as we decode the economic machinery behind another CME futures product.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Behind the Curtain: Macro Indicators That Move the Yen1. Introduction
Japanese Yen Futures (6J), traded on the CME, offer traders a window into one of the world’s most strategically important currencies. The yen is not just Japan’s currency—it’s also a barometer for global risk appetite, a funding vehicle for the carry trade, and a defensive asset when markets turn volatile.
But what truly moves Yen Futures?
While many traders fixate on central bank statements and geopolitical news, machine learning tells us that economic indicators quietly—but consistently—steer price action. In this article, we apply a Random Forest Regressor to reveal the top macroeconomic indicators driving 6J Futures across daily, weekly, and monthly timeframes, helping traders of all styles align their strategies with the deeper economic current.
2. Understanding Yen Futures Contracts
Whether you’re trading institutional size or operating with a retail account, CME Group offers flexible exposure to the Japanese yen through two contracts:
o Standard Japanese Yen Futures (6J):
Contract Size: ¥12,500,000
Tick Size: 0.0000005 = $6.25 per tick
Use Case: Institutional hedging, macro speculation, rate differential trading
o Micro JPY/USD Futures (MJY):
Contract Size: ¥1,250,000
Tick Size: 0.000001 = $1.25 per tick
Use Case: Retail-sized access, position scaling, strategy testing
o Margin Requirements:
6J: Approx. $3,300 per contract
MJY: Approx. $330 per contract
Both products offer deep liquidity and near 24-hour access. Traders use them to express views on interest rate divergence, U.S.-Japan trade dynamics, and global macro shifts—all while adjusting risk through contract size.
3. Daily Timeframe: Top Macro Catalysts
Short-term movements in Yen Futures are heavily influenced by U.S. economic data and its impact on yield spreads and capital flow. Machine learning analysis ranks the following three as the most influential for daily returns:
10-Year Treasury Yield: The most sensitive indicator for the yen. Rising U.S. yields widen the U.S.-Japan rate gap, strengthening the dollar and weakening the yen. Drops in yields could create sharp yen rallies.
U.S. Trade Balance: A narrowing trade deficit can support the USD via improved capital flow outlook, pressuring the yen. A wider deficit may signal weakening demand for USD, providing potential support for yen futures.
Durable Goods Orders: A proxy for economic confidence and future investment. Strong orders suggest economic resilience, which tends to benefit the dollar. Weak numbers may point to a slowdown, prompting defensive yen buying.
4. Weekly Timeframe: Intermediate-Term Indicators
Swing traders and macro tacticians often ride trends formed by mid-cycle economic shifts. On a weekly basis, these indicators matter most:
Fed Funds Rate: As the foundation of U.S. interest rates, this policy tool steers the entire FX complex. Hawkish surprises can pressure yen futures; dovish turns could strengthen the yen as yield differentials narrow.
10-Year Treasury Yield (again): While impactful daily, the weekly trend gives traders a clearer view of long-term investor positioning and bond market sentiment. Sustained moves signal deeper macro shifts.
ISM Manufacturing Employment: This labor-market-linked metric reflects production demand. A drop often precedes softening economic growth, which may boost the yen as traders reduce exposure to riskier assets.
5. Monthly Timeframe: Structural Macro Forces
For position traders and macro investors, longer-term flows into the Japanese yen are shaped by broader inflationary trends, liquidity shifts, and housing demand. Machine learning surfaced the following as top monthly influences on Yen Futures:
PPI: Processed Foods and Feeds: A unique upstream inflation gauge. Rising producer prices—especially in essentials like food—can increase expectations for tightening, influencing global yield differentials. For the yen, which thrives when inflation is low, surging PPI may drive USD demand and weaken the yen.
M2 Money Supply: Reflects monetary liquidity. A sharp increase in M2 may spark inflation fears, sending interest rates—and the dollar—higher, pressuring the yen. Conversely, slower M2 growth can support the yen as global liquidity tightens.
Housing Starts: Serves as a growth thermometer. Robust housing data suggests strong domestic demand in the U.S., favoring the dollar over the yen. Weakness in this sector may support yen strength as traders rotate defensively.
6. Trade Style Alignment with Macro Data
Each indicator resonates differently depending on the trading style and timeframe:
Day Traders: React to real-time changes in 10-Year Yields, Durable Goods Orders, and Trade Balance. These traders seek to capitalize on intraday volatility around economic releases that impact yield spreads and risk appetite.
Swing Traders: Position around Fed Funds Rate changes, weekly shifts in Treasury yields, or deteriorating labor signals such as ISM Employment. Weekly data can establish trends that last multiple sessions, making it ideal for this style.
Position Traders: Monitor PPI, M2, and Housing Starts for broader macro shifts. These traders align their exposure with long-term shifts in capital flow and inflation expectations, often holding positions for weeks or more.
Whatever the style, syncing your trading plan with the data release calendar and macro backdrop can improve timing and conviction.
7. Risk Management
The Japanese yen is a globally respected safe-haven currency, and its volatility often spikes during geopolitical stress or liquidity events. Risk must be managed proactively, especially in leveraged futures products.
8. Conclusion
Japanese Yen Futures are a favorite among global macro traders because they reflect interest rate divergence, risk sentiment, and global liquidity flows. While headlines grab attention, data tells the real story.
Stay tuned for the next installment of the "Behind the Curtain" series, where we continue uncovering what really moves the futures markets.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
US10Y: 10-Year Treasury Yield – Safe Bet or Yield Trap?(1/9)
Good morning, everyone! ☀️ US10Y: 10-Year Treasury Yield – Safe Bet or Yield Trap?
With the 10-year yield at 4.358%, is it time to lock in safety or wait for better rates? Let’s break it down! 🔍
(2/9) – YIELD PERFORMANCE 📊
• Current Yield: 4.358% as of Mar 25, 2025 💰
• Historical Context: Above pandemic lows (~1-2%), below early 2000s (5-6%), per data 📏
• Sector Trend: Inverted yield curve signals caution, per economic reports 🌟
It’s a mixed bag—let’s see what’s cooking! ⚙️
(3/9) – MARKET POSITION 📈
• Safe Haven: U.S. Treasuries are risk-free ⏰
• Income Appeal: 4.358% yield draws income seekers 🎯
• Potential Upside: If rates fall, bond prices rise 🚀
Firm in safety, with growth potential! 🏦
(4/9) – KEY DEVELOPMENTS 🔑
• Inverted Yield Curve: 2-year yield higher, hinting at slowdown, per data 🌍
• Fed Outlook: Expected rate cuts later in 2025, per posts on X 📋
• Market Reaction: Investors balancing income with economic risks 💡
Navigating through uncertainty! 💪
(5/9) – RISKS IN FOCUS ⚡
• Interest Rate Risk: If rates rise, bond prices drop 🔍
• Inflation Risk: Erodes real returns if inflation outpaces yield 📉
• Opportunity Cost: Missing higher returns from stocks ❄️
It’s a trade-off—risks are real! 🛑
(6/9) – SWOT: STRENGTHS 💪
• Risk-Free: No default risk, backed by U.S. government 🥇
• Liquidity: Active market for trading, per data 📊
• Tax Benefits: Interest exempt from state, local taxes 🔧
Got solid foundations! 🏦
(7/9) – SWOT: WEAKNESSES & OPPORTUNITIES ⚖️
• Weaknesses: Interest rate and inflation risks, per economic reports 📉
• Opportunities: Capital gains from falling rates, diversification benefits 📈
Can it deliver both income and growth? 🤔
(8/9) – POLL TIME! 📢
US10Y at 4.358%—your take? 🗳️
• Bullish: Buy now, rates will fall soon 🐂
• Neutral: Hold, wait for more clarity ⚖️
• Bearish: Wait for higher yields or better opportunities 🐻
Chime in below! 👇
(9/9) – FINAL TAKEAWAY 🎯
US10Y offers a steady yield with safety, but with an inverted curve, caution is advised. Gem or bust?
Behind the Curtain The Economic Pulse Behind Euro FX1. Introduction
Euro FX Futures (6E), traded on the CME, offer traders exposure to the euro-dollar exchange rate with precision, liquidity, and leverage. Whether hedging European currency risk or speculating on macro shifts, Euro FX contracts remain a vital component of global currency markets.
But what truly moves the euro? Beyond central bank meetings and headlines, the euro reacts sharply to macroeconomic data that signals growth, inflation, or risk appetite. Using a Random Forest Regressor, we explored how economic indicators correlate with Euro FX Futures returns across different timeframes.
In this article, we uncover which metrics drive the euro daily, weekly, and monthly, offering traders a structured, data-backed approach to navigating the Euro FX landscape.
2. Understanding Euro FX Futures Contracts
The CME offers two primary Euro FX Futures products:
o Standard Euro FX Futures (6E):
Contract Size: 125,000 €
Tick Size: 0.000050 per euro = $6.25 per tick per contract
Trading Hours: Nearly 24 hours, Sunday to Friday (US)
o Micro Euro FX Futures (M6E):
Contract Size: 12,500 € (1/10th the size of 6E)
Tick Size: 0.0001 per euro = $1.25 per tick per contract
Accessible to: Smaller accounts, strategy testers, and traders managing precise exposure
o Margins:
6E Initial Margin: ≈ $2,600 per contract (subject to volatility)
M6E Initial Margin: ≈ $260 per contract
Whether trading full-size or micro contracts, Euro FX Futures offer capital-efficient access to one of the most liquid currency pairs globally. Traders benefit from leverage, scalability, and transparent pricing, with the ability to hedge or speculate on Euro FX trends across timeframes.
3. Daily Timeframe: Key Economic Indicators
For day traders, short-term price action in the euro often hinges on rapidly released data that affects market sentiment and intraday flow. According to machine learning results, the top 3 daily drivers are:
Housing Starts: Surging housing starts in the U.S. can signal economic strength and pressure the euro via stronger USD flows. Conversely, weaker construction activity may weaken the dollar and support the euro.
Consumer Sentiment Index: A sentiment-driven metric that reflects household confidence. Optimistic consumers suggest robust consumption and a firm dollar, while pessimism may favor EUR strength on defensive rotation.
Housing Price Index (HPI): Rising home prices can stoke inflation fears and central bank hawkishness, affecting yield differentials between the euro and the dollar. HPI moves often spark short-term FX volatility.
4. Weekly Timeframe: Key Economic Indicators
Swing traders looking for trends spanning several sessions often lean on energy prices and labor data. Weekly insights from our Random Forest model show these three indicators as top drivers:
WTI Crude Oil Prices: Oil prices affect global inflation and trade dynamics. Rising WTI can fuel EUR strength if it leads to USD weakness via inflation concerns or reduced real yields.
Continuing Jobless Claims: An uptick in claims may suggest softening labor conditions in the U.S., potentially bullish for EUR as it implies slower Fed tightening or economic strain.
Brent Crude Oil Prices: As the global benchmark, Brent’s influence on inflation and trade flows is significant. Sustained Brent rallies could create euro tailwinds through weakening dollar momentum.
5. Monthly Timeframe: Key Economic Indicators
Position traders and institutional participants often focus on macroeconomic indicators with structural weight—those that influence monetary policy direction, capital flow, and long-term sentiment. The following three monthly indicators emerged as dominant forces shaping Euro FX Futures:
Industrial Production: A cornerstone of economic output, rising industrial production reflects strong manufacturing activity. Strong U.S. numbers can support the dollar, while a slowdown may benefit the euro. Likewise, weaker European output could undermine EUR demand.
Velocity of Money (M2): This metric reveals how quickly money is circulating in the economy. A rising M2 velocity suggests increased spending and inflationary pressures—potentially positive for the dollar and negative for the euro. Falling velocity signals stagnation and may shift flows into the euro as a lower-yield alternative.
Initial Jobless Claims: While often viewed weekly, the monthly average could reveal structural labor market resilience. A rising trend may weaken the dollar, reinforcing EUR gains as expectations for interest rate cuts grow.
6. Strategy Alignment by Trading Style
Each indicator offers unique insights depending on your approach to market participation:
Day Traders: Focus on the immediacy of daily indicators like Housing Starts, Consumer Sentiment, and Housing Price Index.
Swing Traders: Leverage weekly indicators like Crude Oil Prices and Continuing Claims to ride mid-term moves.
Position Traders: Watch longer-term data such as Industrial Production and M2 Velocity.
7. Risk Management
Currency futures provide access to high leverage and broad macro exposure. With that comes responsibility. Traders must actively manage position sizing, volatility exposure, and stop placement.
Economic indicators inform price movement probabilities—not certainties—making risk protocols just as essential as trade entries.
8. Conclusion
Euro FX Futures are shaped by a deep web of macroeconomic forces. From Consumer Sentiment and Oil Prices to Industrial Production and Money Velocity, each indicator tells part of the story behind Euro FX movement.
Thanks to machine learning, we’ve spotlighted the most impactful data across timeframes, offering traders a framework to align their approach with the heartbeat of the market.
As we continue the "Behind the Curtain" series, stay tuned for future editions uncovering the hidden economic forces behind other major futures markets.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Behind the Curtain: Unveiling Gold’s Economic Catalysts1. Introduction
Gold Futures (GC, MGC and 1OZ), traded on the CME market, are one of the most widely used financial instruments for hedging against inflation, currency fluctuations, and macroeconomic uncertainty. As a safe-haven asset, gold reacts to a wide range of economic indicators, making it crucial for traders to understand the underlying forces driving price movements.
By leveraging machine learning, specifically a Random Forest Regressor, we analyze the top economic indicators influencing Gold Futures on daily, weekly, and monthly timeframes. This data-driven approach reveals the key catalysts shaping GC Futures and provides traders with actionable insights to refine their strategies.
2. Understanding Gold Futures Contracts
Gold Futures (GC) are among the most actively traded futures contracts, offering traders and investors exposure to gold price movements with a range of contract sizes to suit different trading strategies. CME Group provides three types of Gold Futures contracts to accommodate traders of all levels:
o Standard Gold Futures (GC):
Contract Size: Represents 100 troy ounces of gold.
Tick Size: Each tick is 0.10 per ounce, equating to $10 per tick per contract.
Purpose: Ideal for institutional traders and large-scale hedgers.
Margin: Approximately $12,500 per contract.
o Micro Gold Futures (MGC):
Contract Size: Represents 10 troy ounces of gold, 1/10th the size of the standard GC contract.
Tick Size: Each tick is $1 per contract.
Purpose: Allows smaller-scale traders to participate in gold markets with lower capital requirements.
Margin: Approximately $1,250 per contract.
o 1-Ounce Gold Futures (1OZ):
Contract Size: Represents 1 troy ounce of gold.
Tick Size: Each tick is 0.25 per ounce, equating to $0.25 per tick per contract.
Purpose: Provides precision trading for retail participants who want exposure to gold at a smaller contract size.
Margin: Approximately $125 per contract.
Keep in mind that margin requirements vary through time as market volatility changes.
3. Daily Timeframe: Key Economic Indicators
Gold Futures respond quickly to short-term economic fluctuations, and three key indicators play a crucial role in daily price movements:
o Velocity of Money (M2):
Measures how quickly money circulates within the economy.
A higher velocity suggests increased spending and inflationary pressure, often boosting gold prices.
A lower velocity indicates stagnation, which may reduce inflation concerns and weigh on gold.
o Unemployment Rate:
Reflects the strength of the labor market.
Rising unemployment increases economic uncertainty, often driving demand for gold as a safe-haven asset.
Declining unemployment can strengthen risk assets, potentially reducing gold’s appeal.
o Oil Import Price Index:
Represents the cost of imported crude oil, influencing inflation trends.
Higher oil prices contribute to inflationary pressures, supporting gold as a hedge.
Lower oil prices may ease inflation concerns, weakening gold demand.
4. Weekly Timeframe: Key Economic Indicators
While daily fluctuations impact short-term traders, weekly economic data provides a broader perspective on gold price movements. The top weekly indicators include:
o Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP):
Measures the number of new jobs added in the U.S. economy each month.
Strong NFP numbers typically strengthen the U.S. dollar and increase interest rate hike expectations, pressuring gold prices.
Weak NFP figures can drive economic uncertainty, increasing gold’s safe-haven appeal.
o Nonfarm Productivity:
Represents labor efficiency and economic output per hour worked.
Rising productivity suggests economic growth, potentially reducing demand for gold.
Falling productivity can signal economic weakness, increasing gold’s appeal.
o Personal Spending:
Tracks consumer spending habits, influencing economic activity and inflation expectations.
Higher spending can lead to inflation, often pushing gold prices higher.
Lower spending suggests economic slowing, which may either weaken or support gold depending on inflationary outlooks.
5. Monthly Timeframe: Key Economic Indicators
Long-term trends in Gold Futures are shaped by macroeconomic forces that impact investor sentiment, inflation expectations, and interest rates. The most influential monthly indicators include:
o China GDP Growth Rate:
China is one of the largest consumers of gold, both for investment and jewelry.
Strong GDP growth signals robust demand for gold, pushing prices higher.
Slower growth may weaken gold demand, applying downward pressure on prices.
o Corporate Bond Spread (BAA - 10Y):
Measures the risk premium between corporate bonds and U.S. Treasury bonds.
A widening spread signals economic uncertainty, increasing demand for gold as a safe-haven asset.
A narrowing spread suggests confidence in risk assets, potentially reducing gold’s appeal.
o 10-Year Treasury Yield:
Gold has an inverse relationship with bond yields since it does not generate interest.
Rising yields increase the opportunity cost of holding gold, often leading to price declines.
Falling yields make gold more attractive, leading to price appreciation.
6. Risk Management Strategies
Given gold’s volatility and sensitivity to macroeconomic changes, risk management is essential for trading GC Futures. Key risk strategies may include:
Monitoring Global Liquidity Conditions:
Keep an eye on M2 Money Supply and inflation trends to anticipate major shifts in gold pricing.
Interest Rate Sensitivity:
Since gold competes with yield-bearing assets, traders should closely track interest rate movements.
Higher 10-Year Treasury Yields can weaken gold’s value as a non-yielding asset.
Diversification and Hedging:
Traders can hedge gold positions using interest rate-sensitive assets such as bonds or inflation-linked securities.
Gold often performs well in times of equity market distress, making it a commonly used portfolio diversifier.
7. Conclusion
Gold Futures remain one of the most influential instruments in the global financial markets.
By leveraging machine learning insights and macroeconomic data, traders can better position themselves for profitable trading opportunities. Whether trading daily, weekly, or monthly trends, understanding these indicators allows market participants to align their strategies with broader economic conditions.
Stay tuned for the next "Behind the Curtain" installment, where we explore economic forces shaping another key futures market.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Behind the Curtain: Economic Forces Fueling Crude Oil Futures1. Introduction
Crude Oil Futures (CL), traded on the CME, are a cornerstone of global energy markets. Representing a vital benchmark for the energy sector, these futures reflect shifts in supply, demand, and macroeconomic sentiment. As both a speculative and hedging instrument, CL Futures are closely tied to economic forces shaping the global economy.
In this article, we leverage machine learning insights from a Random Forest Regressor to uncover the top economic indicators influencing Crude Oil Futures across daily, weekly, and monthly timeframes. By identifying these drivers, traders can gain a data-driven perspective to navigate the dynamic crude oil market effectively.
2. Understanding Crude Oil Futures
o Contract Specifications:
Standard Contract: Represents 1,000 barrels of crude oil.
Tick Size: Each tick is 0.01 per barrel, equating to $10 per tick per contract.
Trading Hours: Nearly 24 hours, ensuring global access and liquidity.
o Micro Crude Oil Contracts (MCL):
Contract Size: Represents 100 barrels of crude oil, 1/10th the size of the standard CL contract.
Tick Size: Each tick is 0.01 per barrel, equating to $1 per tick per contract.
Purpose: Offers smaller-scale traders’ access to the crude oil market with lower capital requirements, making it ideal for those looking to hedge or test strategies.
o Margins:
Standard CL Contract Margin: Approximately $6,000 per contract (subject to market volatility).
Micro MCL Contract Margin: Approximately $600 per contract.
The combination of high liquidity, leverage, and the flexibility offered by Micro Crude Oil contracts makes CL Futures a versatile choice for a broad range of participants, from institutional investors to retail traders exploring smaller-scale strategies.
3. Daily Timeframe: Key Economic Indicators
Machine learning insights reveal that the following daily indicators play a crucial role in shaping Crude Oil Futures' movements:
U.S. Trade Balance: Measures the difference between exports and imports. A narrowing trade deficit signals improved economic health and potential upward pressure on oil demand, while a widening deficit may indicate weakened economic sentiment, weighing on crude prices.
Unemployment Rate: Reflects labor market conditions and overall economic health. A declining unemployment rate often correlates with increased energy consumption due to stronger economic activity, boosting crude oil prices.
Building Permits: Tracks new residential construction permits issued. Rising permits reflect economic confidence and can signal increased energy demand for construction activity, providing upward momentum for crude prices.
4. Weekly Timeframe: Key Economic Indicators
Weekly indicators provide medium-term insights into crude oil market dynamics. The top drivers include:
Corporate Bond Spread (BAA - 10Y): Reflects the difference between corporate bond yields and Treasury yields. Widening spreads signal economic uncertainty, potentially reducing crude oil demand. Narrowing spreads suggest stability, supporting higher crude prices.
U.S. Trade Balance (again): At the weekly level, trade balance trends highlight the interplay between global trade and crude oil demand, influencing market sentiment over several days.
Housing Price Index: Indicates trends in real estate values, reflecting consumer confidence and economic stability. Rising housing prices often signal strong economic conditions, indirectly bolstering crude oil demand.
5. Monthly Timeframe: Key Economic Indicators
Monthly indicators provide a long-term perspective on Crude Oil Futures trends, highlighting macroeconomic forces at play. The top monthly drivers are:
Natural Gas Prices: As a competing energy source, fluctuations in natural gas prices can impact crude oil demand. Rising natural gas prices often lead to increased crude consumption, while declining prices may pressure oil demand downward.
U.S. Trade Balance (again): Over a monthly timeframe, the trade balance reflects sustained shifts in international trade dynamics. Persistent trade deficits may signal weaker global economic activity, affecting crude oil prices negatively, whereas trade surpluses may support demand.
Net Exports: A critical measure of a country’s export-import balance, net exports reveal global demand for domestic products, including crude oil. Surpluses suggest robust international demand, often leading to upward pressure on oil prices, while deficits indicate weaker sentiment.
6. Applications for Different Trading Styles
Economic indicators provide actionable insights tailored to specific trading styles:
Day Traders: Focus on daily indicators such as U.S. Trade Balance, Unemployment Rate, and Building Permits to anticipate intraday volatility. For example, an unexpected improvement in building permits might signal stronger economic activity, potentially boosting crude oil prices intraday.
Swing Traders: Weekly indicators like Corporate Bond Spread (BAA - 10Y) and Housing Price Index offer insights into intermediate trends. For instance, narrowing bond spreads often reflect economic stability, aligning with medium-term bullish positions in Crude Oil Futures.
Position Traders: Monthly indicators such as Natural Gas Prices and Net Exports are essential for capturing long-term macroeconomic shifts. Sustained increases in natural gas prices, for example, might support prolonged bullish sentiment in crude oil markets.
7. Risk Management Strategies
Risk management is crucial when trading Crude Oil Futures due to the inherent volatility of energy markets. Key strategies include:
Hedging Volatility: Utilize correlated assets, such as natural gas or refined product futures, to hedge against price swings.
Monitoring Leverage: Adjust position sizes based on volatility and margin requirements to minimize risk exposure during periods of heightened uncertainty.
Timeframe Diversification: Incorporate insights from daily, weekly, and monthly indicators to create a balanced trading approach. For example, while daily indicators may signal short-term volatility, monthly metrics provide stability for longer-term trades.
8. Conclusion
Crude Oil Futures are deeply influenced by economic indicators across varying timeframes. From the U.S. Trade Balance and Building Permits driving daily fluctuations to Natural Gas Prices and Net Exports shaping long-term trends, understanding these relationships is critical for navigating the energy market.
By leveraging data-driven insights from machine learning models, traders can align their strategies with market dynamics and improve decision-making. Whether you're a day trader, swing trader, or position trader, these economic forces offer a framework for more informed and strategic trading.
Stay tuned for the next installment in the "Behind the Curtain" series, where we unveil the economic forces shaping another critical futures market.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Is Gold the Ultimate Safe Haven in 2025?In the labyrinthine world of finance, gold has once again captured the spotlight, breaking records as speculative buying and geopolitical tensions weave a complex narrative around its valuation. The precious metal's price surge is not merely a reaction to market trends but a profound statement on the global economic landscape. Investors are increasingly viewing gold as a beacon of stability amidst an ocean of uncertainty, driven by the Middle East's ongoing unrest and the strategic maneuvers of central banks. This phenomenon challenges us to reconsider the traditional roles of investment assets in safeguarding wealth against international volatility.
The inauguration of Donald Trump as President has injected further intrigue into the gold market. His administration's initial steps, notably the delay in imposing aggressive tariffs, have led to a nuanced dance between inflation expectations and U.S. dollar strength. Analysts from major financial institutions like Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley are now dissecting how Trump's policies might steer inflation, influence Federal Reserve actions, and ultimately, dictate gold's trajectory. This intersection of policy and market dynamics invites investors to think critically about how political decisions can reshape economic landscapes.
China's burgeoning appetite for gold, exemplified by the frenzied trading of gold-related ETFs, underscores a broader shift towards commodities as traditional investment avenues like real estate falter. The Chinese central bank's consistent gold acquisitions reflect a strategic move towards diversifying reserves away from the U.S. dollar, particularly in light of global economic sanctions. This strategic pivot in one of the world's largest economies poses a compelling question: are we witnessing a fundamental realignment in global financial power structures, with gold at its core?
As we navigate through 2025, gold's role transcends simple investment; it becomes a narrative of economic resilience and geopolitical foresight. The interplay between inflation, monetary policy, and international relations not only affects gold's price but also challenges investors to adapt their strategies in an ever-evolving market. Can gold maintain its luster as the ultimate Safe Haven, or will new economic paradigms shift its golden allure? This enigma invites us to delve deeper into the metal's historical significance and its future in a world where certainty is a luxury few can afford.
Behind the Curtain: Top Economic Influencers on ZN Futures1. Introduction
The 10-Year Treasury Note Futures (ZN), traded on the CME, are a cornerstone of the fixed-income market. As a vital benchmark for interest rate trends and macroeconomic sentiment, ZN Futures attract institutional and retail traders alike. Their liquidity, versatility, and sensitivity to economic shifts make them a go-to instrument for both speculation and hedging.
In this article, we delve into the economic forces shaping ZN Futures’ performance across daily, weekly, and monthly timeframes. By leveraging machine learning, specifically a Random Forest Regressor, we identify the most impactful indicators influencing Treasury futures returns. These insights can help traders fine-tune their strategies and navigate the complexities of this market.
2. Product Specifications
Contract Size:
The standard ZN Futures contract represents $100,000 face value of 10-Year Treasury Notes.
Tick Size:
Each tick corresponds to 1/64 of 1% of par value. This equals $15.625 per tick, ensuring precise pricing and manageable risk for traders.
Margins:
Approximately $2,000 per contract (changes through time).
Micro Contract Availability:
While the standard contract suits institutional traders, the micro-sized Yield Futures provide a smaller-scale option for retail participants. These contracts offer reduced tick values and margin requirements, enabling broader market participation.
3. Daily Economic Drivers
Machine learning models reveal that daily fluctuations in ZN Futures are significantly influenced by the following indicators:
Building Permits: A leading indicator of housing market activity, an increase in permits signals economic confidence and growth. This optimism often puts upward pressure on yields, while a decline may reflect economic caution, boosting demand for Treasuries.
U.S. Trade Balance: This metric measures the difference between exports and imports. A narrowing trade deficit typically signals improved economic health, leading to higher yields. Conversely, a widening deficit can weaken economic sentiment, increasing Treasury demand as a safe-haven asset.
China GDP Growth Rate: As a global economic powerhouse, China’s GDP growth influences global trade and financial flows. Strong growth suggests robust international demand, pressuring Treasury prices downward as yields rise. Slower growth has the opposite effect, enhancing Treasury appeal.
4. Weekly Economic Drivers
When analyzing weekly timeframes, the following indicators emerge as significant drivers of ZN Futures:
Velocity of Money (M2): This indicator reflects the speed at which money circulates in the economy. High velocity signals robust economic activity, often putting upward pressure on yields. Slowing velocity, on the other hand, may indicate stagnation, increasing demand for Treasury securities.
Consumer Sentiment Index: This metric gauges the confidence level of consumers regarding the economy. Rising sentiment suggests stronger consumer spending and economic growth, often pressuring bond prices downward as yields rise. Conversely, a decline signals economic caution, favoring safe-haven assets like ZN Futures.
Nonfarm Productivity: This measures output per hour worked in the nonfarm sector and serves as an indicator of economic efficiency. Rising productivity typically reflects economic strength and may lead to higher yields, while stagnation or declines can shift sentiment toward Treasuries.
5. Monthly Economic Drivers
On a broader monthly scale, the following indicators play a pivotal role in shaping ZN Futures:
Net Exports: This metric captures the difference between a country’s exports and imports. A surplus indicates strong global demand for domestic goods, signaling economic strength and driving yields higher. Persistent deficits, however, may weaken economic sentiment and increase demand for Treasuries as a safe haven.
10-Year Treasury Yield: As a benchmark for longer-term borrowing costs, movements in the 10-Year Treasury Yield reflect investor expectations for economic growth and inflation. Rising yields suggest optimism about future economic conditions, potentially reducing demand for Treasury futures. Declining yields indicate caution, bolstering Treasury appeal.
Durable Goods Orders: This indicator measures new orders placed with manufacturers for goods expected to last three years or more. Rising orders signal business confidence and economic growth, often leading to higher yields. Conversely, a decline in durable goods orders can indicate slowing economic momentum, increasing Treasury demand.
6. Applications for Different Trading Styles
Economic indicators provide distinct insights depending on the trading style and timeframe:
Day Traders: Focusing on daily indicators like Building Permits, U.S. Trade Balance, and China GDP Growth Rate to anticipate short-term market movements. For example, an improvement in China’s GDP Growth Rate may signal stronger global economic conditions, potentially driving yields higher and pressuring ZN Futures lower.
Swing Traders: Weekly indicators such as Velocity of Money (M2), Consumer Sentiment Index, and Nonfarm Productivity could help identify intermediate trends. For instance, rising consumer sentiment can reflect increased spending expectations, potentially prompting bearish positions in ZN Futures.
Position Traders: Monthly metrics like Net Exports, 10-Year Treasury Yield, and Durable Goods Orders may offer a macro perspective for long-term strategies. A sustained increase in durable goods orders, for instance, may indicate economic expansion, influencing traders to potentially adopt bearish sentiment on ZN Futures.
7. Conclusion
The analysis highlights how daily, weekly, and monthly economic indicators collectively influence ZN Futures. From more immediate fluctuations driven by Building Permits and China GDP Growth Rate, to longer-term trends shaped by Durable Goods Orders and the 10-Year Treasury Yield, each timeframe provides actionable insights for traders.
By understanding these indicators and incorporating machine learning models to uncover patterns, traders can refine strategies tailored to specific time horizons. Whether intraday, swing, or long-term, leveraging these insights empowers traders to navigate ZN Futures with greater precision.
Stay tuned for the next installment in the "Behind the Curtain" series, where we examine economic drivers behind another key futures market.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Behind the Curtain: Key Influencers of S&P 500 Futures Returns1. Introduction
The S&P 500 Futures (ES) represents one of the most actively traded futures contracts globally, serving as a benchmark for U.S. equity markets. Its liquidity and versatility make it a prime choice for traders seeking exposure to market movements. However, the factors driving these movements are far from random. Economic indicators often play a pivotal role in influencing the direction and volatility of S&P 500 Futures.
In this article, we dive into how various economic indicators shape the performance of S&P 500 Futures on daily, weekly, and monthly timeframes. Leveraging machine learning, specifically a Random Forest Regressor, we’ve identified the top drivers of these futures’ returns. The findings offer traders actionable insights to fine-tune their strategies and understand the broader market dynamics.
2. Understanding S&P 500 Futures
Product Specifications:
Tick Size: Each tick represents 0.25 index points, equivalent to $12.50 per tick.
Trading Hours: Nearly 24-hour trading cycle, ensuring liquidity across time zones.
Micro Contracts:
Micro E-mini S&P 500 Futures (MES): Designed for smaller-scale traders with a contract size 1/10th of the standard E-mini contract.
Advantages: Lower initial margin requirements and smaller tick values allow traders to manage positions more flexibly.
Margin Requirements:
Initial and maintenance margins vary based on volatility and market conditions. Currently around $15,500 per contract.
Micro contracts offer significantly lower margin requirements, making them ideal for retail traders or those testing strategies. Currently around $1,550 per contract.
3. Key Economic Indicators Influencing S&P 500 Futures
Daily Impacts:
1. Labor Force Participation Rate:
Reflects the percentage of the working-age population that is employed or actively seeking employment.
A rise in this rate often signals economic optimism, driving equities higher.
2. Building Permits:
Tracks the number of new residential construction permits issued.
A strong rise in permits indicates confidence in the housing market, which can positively
influence broader economic sentiment and equities.
3. Initial Jobless Claims:
A leading indicator of labor market health, providing real-time insights into layoffs.
Weekly fluctuations can significantly impact intraday futures trading.
Weekly Impacts:
1. Corporate Bond Spread (BAA - 10Y):
A measure of credit risk in the economy, reflecting the difference between corporate bond yields and Treasury yields.
Widening spreads often signal economic uncertainty, weighing on equity markets.
2. Velocity of Money (M2):
Represents the rate at which money circulates in the economy.
High velocity can indicate economic expansion, while slowing velocity may suggest stagnation, affecting equity futures trends.
3. Net Exports:
Tracks the balance of a country’s exports and imports.
Positive trends often boost market optimism, whereas persistent deficits can trigger concerns about economic health.
Monthly Impacts:
1. Oil Import Price Index:
Reflects the cost of imported crude oil, which has ripple effects on production costs across industries.
Rising oil import prices may pressure corporate earnings, impacting the broader S&P 500 index.
2. PPI: Processed Foods and Feeds:
Tracks price changes in processed agricultural products, offering insights into supply chain pressures.
Sharp increases can hint at inflationary risks, influencing long-term equity market sentiment.
3. Consumer Sentiment Index:
o Measures consumer confidence, a leading indicator of economic health.
o High sentiment often signals robust consumer spending, which supports equities.
4. Applications for Different Trading Styles
Day Traders:
Focus on daily indicators like Initial Jobless Claims and Labor Force Participation Rate.
Example: A sudden drop in jobless claims could signal short-term economic strength, providing day traders with bullish opportunities.
Swing Traders (Weekly):
Leverage weekly trends like Corporate Bond Spread or Velocity of Money (M2).
Example: A narrowing bond spread might indicate improving business confidence, aligning with medium-term bullish positions.
Position Traders (Monthly):
Use monthly indicators such as Oil Import Price Index and Consumer Sentiment Index to identify macroeconomic trends.
Example: Rising consumer sentiment could indicate a stronger economy, supporting long-term bullish strategies in S&P 500 Futures.
5. Risk Management Through Indicator Analysis
Refining Entry and Exit Points: Use indicator data to align trades with anticipated market shifts. For instance, an uptick in the Oil Import Price Index might signal upcoming headwinds for equities.
Managing Leverage: Understanding the volatility drivers like Treasury Yields can help traders adjust position sizes to manage risk effectively.
Diversification Across Timeframes: Incorporate insights from multiple timeframes to hedge risks. For example, while short-term indicators may suggest volatility, long-term metrics can provide stability signals.
Hedging Strategies: Use correlated assets or options to mitigate downside risks. Combining economic indicator analysis with market seasonality can enhance portfolio resilience.
6. Conclusion
Economic indicators provide invaluable insights into the drivers of S&P 500 Futures, helping traders align their strategies with market trends. Whether focusing on daily volatility from indicators like Initial Jobless Claims or broader monthly trends such as the Consumer Sentiment Index, understanding these relationships can enhance trading decisions.
By leveraging machine learning and data-driven analysis, this article highlights how indicators shape market movements across various timeframes. The insights empower traders to adopt tailored approaches—whether intraday, swing, or long-term—while improving risk management practices.
This framework not only applies to S&P 500 Futures but can also be extended to other markets. Stay tuned for the next article in the "Behind the Curtain" series, where we explore another futures market and its relationship with key economic indicators.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Behind the Curtain: Economic Indicators Shaping Corn Futures1: Introduction
Corn Futures (ZC), traded on the CME, play a vital role in global markets, particularly in the agriculture and food industries. As a commodity with widespread applications, Corn Futures are influenced by a multitude of factors, ranging from seasonal weather patterns to broader economic trends. Understanding these influences is critical for traders seeking to navigate the market effectively.
In this article, we leverage machine learning, specifically a Random Forest Regressor, to identify key economic indicators that have historically correlated with Corn Futures' price changes. By analyzing daily, weekly, and monthly timeframes, we aim to provide a clearer picture of how these indicators potentially shape market behavior and offer actionable insights for traders.
The findings are presented through visual graphs highlighting the top economic indicators across different timeframes. These insights can help traders fine-tune their strategies, whether for short-term speculation or long-term investment.
2: Understanding the Key Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide a glimpse into various facets of the economy, influencing commodity markets such as Corn Futures. Using the Random Forest model, the following indicators emerged as significant for Corn Futures on different timeframes:
Daily Timeframe:
Oil Import Price Index: Reflects the cost of importing crude oil, impacting energy costs in agriculture, such as fuel for equipment and transportation.
Durable Goods Orders: Tracks demand for goods expected to last three years or more, often signaling broader economic activity that can influence commodity demand.
Natural Gas Prices: Critical for the production of fertilizers, which directly impacts corn farming costs.
Weekly Timeframe:
China GDP Growth Rate: Indicates global demand trends, as China is a major consumer of agricultural products.
Housing Starts: Reflects construction activity, indirectly influencing economic stability and consumer behavior.
Corporate Bond Spread (BAA - 10Y): A measure of credit risk that can signal changes in business investment and economic uncertainty.
Monthly Timeframe:
Retail Sales (YoY): Gauges consumer spending trends, a crucial driver of demand for corn-based products.
Initial Jobless Claims: Acts as a measure of labor market health, influencing disposable income and consumption patterns.
Nonfarm Productivity: Indicates economic efficiency and growth, impacting broader market trends.
By understanding these indicators, traders can interpret their implications on Corn Futures more effectively.
3: How to Use This Information
The timeframes for these indicators provide unique perspectives for different trading styles:
Daily Traders: Indicators like the Oil Import Price Index and Natural Gas Prices, which are highly sensitive to short-term changes, are valuable for high-frequency trading strategies. Daily traders can monitor these to anticipate intraday price movements in Corn Futures.
Swing Traders (Weekly): Weekly indicators, such as the China GDP Growth Rate or Housing Starts, help identify intermediate-term trends. Swing traders can align their positions with these macroeconomic signals for trades lasting several days or weeks.
Long-Term Traders (Monthly): Monthly indicators, such as Retail Sales and Nonfarm Productivity, provide insights into overarching economic trends. Long-term traders can use these to assess demand-side factors impacting Corn Futures over extended periods.
Additionally, traders can enhance their strategies by overlaying these indicators with seasonal patterns in Corn Futures, as weather-related supply shifts often coincide with economic factors.
4: Applications for Risk Management
Understanding the relationship between economic indicators and Corn Futures also plays a critical role in risk management. Here are several ways to apply these insights:
Refining Entry and Exit Points: By correlating Corn Futures with specific indicators, traders can potentially time their entries and exits more effectively. For example, a sharp rise in the Oil Import Price Index might signal increased production costs, potentially pressuring corn prices downward.
Diversifying Trading Strategies: Leveraging daily, weekly, and monthly indicators allows traders to adapt their strategies across timeframes. Short-term volatility from energy prices can complement long-term stability signals from broader economic metrics like GDP Growth.
Mitigating Uncertainty: Tracking indicators such as Corporate Bond Spreads can provide early warnings of economic instability, helping traders hedge their Corn Futures positions with other assets or options.
Seasonal Hedging: Combining indicator-based insights with seasonal trends in Corn Futures can enhance risk-adjusted returns. For instance, aligning hedging strategies with both economic and weather-related factors could reduce downside exposure.
5: Conclusion
The analysis highlights how diverse economic indicators shape Corn Futures prices across multiple timeframes. From daily volatility influenced by energy costs to long-term trends driven by consumer spending and productivity, each indicator provides unique insights into market dynamics.
Traders can use this framework not only for Corn Futures but also for other commodities, enabling a more data-driven approach to trading. The combination of machine learning and economic analysis presents opportunities to refine strategies and improve outcomes in the competitive world of futures trading.
Stay tuned for the next article in this series, where we delve into another futures market and its relationship with key economic indicators.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com - This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
Why is the Swiss Franc Defying the Odds?In a global economy where central banks are leaning towards softer monetary policies, the Swiss Franc is charting its own course—strengthening against the odds. But what forces are truly at play here? Is it merely the cautious whispers of the Swiss National Bank, or is there a deeper undercurrent, tied to inflation expectations and global safe-haven flows? As we peel back the layers, we uncover a narrative that challenges conventional wisdom. Discover the intricate dynamics that could redefine how we perceive currency resilience in today's volatile market landscape.
The franc's unexpected strength has sparked a flurry of theories. Some point to the SNB's potential reluctance to cut interest rates as aggressively as its peers. Others suggest that the widening gap between Swiss and global inflation expectations could be fueling the franc's appreciation. Yet, the franc's safe-haven status and its role in carry trades add another layer of complexity to this puzzle.
The EUR/CHF currency pair, a barometer of the Eurozone and Switzerland's economic health, is particularly sensitive to the franc's strength. As the franc appreciates, it can impact trade balances, inflation, and overall economic competitiveness.
As the global economic landscape continues to evolve, the enigma of the Swiss franc's resilience persists. Is this a temporary anomaly, or a harbinger of a new era in international finance? Only time will tell.
Overall Sentiment for US Economy from January to May 2024The period from January to May 2024 has been marked by significant bearish sentiment due to multiple geopolitical events. The escalation of conflicts in Ukraine, increased US-China trade tensions, disruptions in the Red Sea, and heightened hostilities in the Middle East have collectively contributed to market instability. These events led to increased energy prices, supply chain disruptions, and heightened global volatility, which pressured the US Dollar Index.
The overall bearish impact on the dollar was driven primarily by inflationary pressures from higher oil prices and increased geopolitical risks, reducing demand for the dollar as a safe haven. Large institutions had to adjust their portfolios and manage risks strategically to navigate the volatile environment.
Macro Monday 8 - S&P500/M2 Money SupplyMACRO MONDAY 8
S&P500 / M2 Money Supply ( SP:SPX / $WMN2S)
M2 is a broad measure of the US money supply that includes cash, checking deposits, and other types of deposits that are readily convertible to cash such as CDs.
M2 is seen as a reliable metric for forecasting/predicting inflation and for this reason it can be used as leading economic indicator. For example, when there is more cash made available or too much, more cash typically gets spent. A little more can be good, too much or too sudden an increase can increase the risk of inflation. That's why the Federal Reserve constricts the money supply when inflation rears its ugly head. At present the Federal Reserve is decreasing the M2 Money supply in an effort to slow down spending in order to control and reduce the rate of inflation. Since April 2022 the M2 Money Supply has reduced from $22 Trillion down to $20.82 Trillion.
The money supply and its impact on Inflation combined with current interest rates has major ramifications for the general economy, as they heavily influence job availability, consumer spending, business investment, currency strength, and trade balance.
The M2 Money Supply also has a major impact on the stock market and can act as catalyst for increased purchases of stocks (when the money supply is increasing as more money is available) and can also cause the selling of stock when money supply is tight or tightening as it is at present (as less money is available in the wider economy).
The Chart – Accounting for Money Supply
As noted above the M2 Money Supply is reducing and it is expected that this may result in the S&P500 making lower lows as the supply of money continues to contract.
The S&P500 performance looks very different when it is adjusted to account for the increases and decreases of the money supply. We can achieve this by dividing the S&P500 by the M2 Money Supply (Chart 1).
Chart 1 – S&P / M2 Money Supply
- Since 1996 the Major Resistance Zone has stopped every progression higher.
- In 2007 a rejection from the resistance zone resulted in the Great Financial Crisis
- Major recessions are labelled with red arrows & market corrections with blue arrows.
- Since GFC there have been a number of rejections from the resistance zone which have
coincided with notable corrections for the S&P500 (see blue arrows).
- The most notable of these rejections was the COVID Crash in March 2020.
- We are at the resistance zone now and it appears we are struggling to breach above it and
may be rejected again. Given we have been rejected by this level 5 times since the 2007
Great Financial Crisis, it seems wise to remain cautious and expect a rejection from this
level again.
Chart 2 – S&P500 & M2 Money supply (Segregated)
- This chart shows you the S&P price action in isolation and underneath the M2 Money
Supply for reference.
- The declining M2 Money supply is like a weight or float pushing and pulling the S&P500
price action in its direction.
- The M2 Money supply may gravitate down towards its long term trend line over the coming
year(s) and one would expect the S&P500 to follow its lead and also gravitate lower.
- Interestingly, on Chart 2 you can see that the level that the M2 Money Supply and the
S&P500 were at prior to the pandemic would present an S&P500 price tag of $3,350.
Summary
Its seems unlikely that the S&P500 is about to break higher due to the overhead long term resistance zone on Chart 1 which helped predict the last two recessions (red arrows) and a handful of corrections (blue arrows).
There is a strong likelihood of continued M2 Money Supply normalization towards its long term trend line on Chart 2, especially considering Federal Reserves continued efforts to constrict the money supply through quantitative tightening to help quell inflation. These efforts will likely subdue any attempt of positive price action on the S&P500.
It is important to recognise that the Dot Com Bubble in 2000 pressed through the resistance zone on Chart 1 demonstrating just how big a bubble it was. It was initially rejected from the resistance zone in March 1997, however the M2 Money Supply was increasing at this time so whilst this outcome is always possible, it does not presently seem probable with M2 Money supply decreasing and likely continuing to decrease going forward.
Another potential outcome is a false break out above the resistance zone on Chart 1. We have had an unprecedented increase in to the money supply since the March 2020 COVID Crash and this could have a lagging effect which eventually pushes us over the resistance zone. Fiscal Stimulus which is harder to predict could also help us arrive at this scenario. Regardless, if these circumstances are met with continued decreasing M2 Money Supply, I believe that it would be a short lived breach of the resistance zone resulting in maybe a $4,980 S&P500 price tag (a higher high) followed by a severe correction. That is IF M2 Money supply is still decreasing as the S&P500 makes those higher highs.
And finally we have to consider what most people would consider to be the most unrealistic scenario, a Dot Com Style bubble towards the top red line on Chart 1. As improbable as this is, a combination of factors could lead us into this scenario;
- The aforementioned lagging effects of the unprecedented never before seen increase in
the M2 Money Supply since the pandemic.
- Continued or new Fiscal Stimulus from the US government.
- The bullish AI narrative (which appears to be dissipating at present)
This final bullish scenario is worthy of consideration especially factoring in the comparisons of the 2023 AI hype to the 2000 internet boom. As we enter a new technological epoch with the likes of Augmented Reality, Cryptocurrencies and AI, are we getting ahead of ourselves again? Do these technologies need a little more time to mature much like the internet? Are we overextended like we were in 2000? It’s hard to answer no to any of these questions but against the backdrop of record levels of Quantitative Easing and Fiscal Stimulus we have to keep an open mind as the Fed tries to simmer us down from these record levels of liquidity
It will be very interesting to watch these charts over coming weeks and months to see if we get our anticipated rejection from the resistance zone on Chart 1.
A special mention to Ben Cowen from "Intothecryptoverse" who originally brought this style chart to my attention. My chart could be considered a snapshot of his view however I hope I have added to it in some way with the above commentary and some correlations I have noticed.
Thank you for reading to the end. I hope these charts help frame todays market for you going forward.
I’ll keep you posted on any major changes.
PUKA
Countries with the Highest Debt-to-GDP Ratio 🌍💰📈
The world's financial landscape is a tapestry of economic prowess and fiscal challenges. A critical indicator of a nation's economic health is its debt-to-GDP ratio, a measure that reveals the extent to which a country's debt burdens its economy. In this insightful exploration, we'll delve into the figures that highlight countries grappling with the highest debt-to-GDP ratios. With real-world examples, we'll shed light on the complexities of global debt dynamics and their potential impact on the world economy.
Understanding Debt-to-GDP Ratio
The debt-to-GDP ratio is a crucial metric that reflects a country's ability to manage its debt relative to the size of its economy. A higher ratio indicates a greater level of indebtedness. Let's examine why this metric is so significant and its implications:
1. Greece: A Tale of Economic Turmoil
Greece serves as a prominent example of a country with a high debt-to-GDP ratio. In the early 2010s, Greece faced a sovereign debt crisis that shook the European Union. Its debt-to-GDP ratio exceeded 180%, signaling unsustainable levels of debt. The crisis forced Greece to implement severe austerity measures and seek international bailouts.
2. Japan: A Unique Fiscal Challenge
Japan represents a distinctive case where a high debt-to-GDP ratio coexists with economic stability. Japan's debt-to-GDP ratio is among the highest globally, surpassing 200%. However, it has maintained economic stability due to unique factors such as a high domestic savings rate and central bank policies.
3. United States: Juggling Debt and Economic Growth
The United States, with a debt-to-GDP ratio exceeding 100%, showcases the balance between debt and economic growth. While a high ratio can raise concerns, the U.S. has managed its debt effectively, leveraging its economic strength to service its obligations.
The debt-to-GDP ratio is a critical barometer of a nation's fiscal health and economic stability. Understanding the complexities and nuances of this metric is essential for evaluating a country's financial resilience and potential risks. As we explore countries with the highest debt-to-GDP ratios, it becomes evident that each nation's economic circumstances are unique. While a high ratio can signal challenges, factors such as economic policies, domestic savings, and global financial dynamics play pivotal roles in shaping a country's fiscal destiny. Ultimately, the global economy is an intricate web of financial interdependencies, and monitoring these debt ratios is a vital component of navigating this complex landscape. 🌍💰📈
Do you like this post? Do you want more articles like that?
Navigating Forex Success: Mastering the Most Vital Fundamentals
Forex trading, the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, offers endless opportunities for profit. Yet, success in this dynamic arena hinges on a solid understanding of fundamental analysis. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the most crucial forex fundamentals that every trader should grasp. We will provide real-world examples to illustrate their impact and share how they can influence your trading decisions.
The Cornerstones of Forex Fundamentals
1. Interest Rates: Central banks set interest rates, which have a significant influence on currency values. Higher interest rates in a country can attract foreign capital, boosting the value of its currency.
2. Economic Indicators: Economic data releases, such as GDP, employment figures, and inflation rates, provide insights into a country's economic health. Positive data can lead to a stronger currency, while negative data may weaken it.
3. Political Stability and Economic Performance: Political stability and the overall health of an economy play a crucial role in currency valuation. Countries with stable governments and strong economic performance tend to have stronger currencies.
Real-World Examples
Example 1: EUR/USD and Interest Rates:
Example 2: GBP/USD and Economic Indicators:
Mastering the most vital forex fundamentals is essential for navigating the complex world of forex trading successfully. By staying informed about interest rates, economic indicators, political stability, and economic performance, you can make informed trading decisions and better understand the forces driving currency markets. With these fundamentals as your foundation, you'll be better equipped to seize opportunities and manage risks in the ever-evolving world of forex. 🌍📈💰
What do you want to learn in the next post?
How to use ECONOMIC INDICATORS for informed trading decisionsHello everyone! Here you have some information that I consider useful on how to interpret and use economic indicators and data to make informed trading decisions in the foreign exchange market:
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) - GDP is a measure of a country's economic output and is considered to be one of the most important indicators of economic growth. A higher GDP indicates a stronger economy, which can lead to an increase in demand for the country's currency.
Unemployment Rates - Unemployment rates measure the percentage of the workforce that is currently without a job. A low unemployment rate indicates a strong economy, which can lead to an increase in demand for the country's currency.
Inflation - Inflation measures the rate at which the average price level of a basket of goods and services in an economy is increasing. High inflation can lead to a decrease in demand for the country's currency, while low inflation can lead to an increase in demand.
Interest Rates - Interest rates are the cost of borrowing money and are set by central banks. High interest rates can attract foreign investment, leading to an increase in demand for the country's currency.
Trade Balance - The trade balance measures the difference between a country's exports and imports. A positive trade balance indicates that a country is exporting more than it is importing, which can lead to an increase in demand for the country's currency.
Political Stability - Political stability is an important factor to consider when trading in the foreign exchange market. A stable political environment can lead to an increase in demand for a country's currency, while political instability can lead to a decrease in demand.
In summary, GDP, unemployment rates, inflation, interest rates, trade balance and political stability are important economic indicators to keep an eye on when making trading decisions in the foreign exchange market. By considering these indicators, along with other market conditions, traders can make more informed decisions about when to buy or sell a particular currency.
Please note that the above information is not a financial advice and only for educational purpose, Economic indicators are important but not the only factor to consider while making trading decisions and It's always important to do your own research and consider your own risk tolerance before making any trades.
What are new-home sales and why do they matter to the economy?Upcoming week we have two important major events happening for the U.S , one of them is the new-home sales. But what exactly are new-home sales, and why do they matter? In this post, we'll break down what new-home sales are and explain why they're so important to the overall health of the economy. You also be more prepared and informed why the market moved in a certain way. Lets move on...
What are new-home sales and why do they matter to the economy?
New-home sales are a measure of trading activity in the market for newly built homes. The new-home sales data are important leading indicators of economic activity, providing timely information on changes in the demand for new homes, which directly affects decisions regarding investment, production, and employment. The data on new-home sales also provide valuable information on the market fundamentals that are shaping trading conditions in the market for newly built homes. The data can be used to inform decision-making about pricing, product mix, and other strategic considerations. In addition, the data can be used to assess market conditions and identify emerging trends. As such, new-home sales data are an important tool for monitoring and understanding the health of the economy.
See historical graph here:
fred.stlouisfed.org
Impact of new-home sales
When new-home sales activity levels rise, it has a positive impact on the economy as a whole. For consumers, this increased activity level leads to currency being put back into circulation. When builders see an increase in new-home sales, they are able to reinvest that currency into building more homes, which in turn provides more jobs for other industry players. The increased activity also has a positive impact on the stock market and it's currency, as builders and other companies who stocks are traded publicly see their stock prices increase. This provides more stability in the markets and can lead to more investors feeling confident about putting their money into the markets. Ultimately, when new-home sales activity levels increase, it provides a boost to the economy as a whole.
New-home sales are an important economic indicator because they signal overall consumer confidence and spending. Increased new-home sales activity levels have a ripple effect throughout the economy, benefiting consumers, builders, and other industry players. We shall see what impact the new-home sales will have this week on EURUSD.
We can currently see we are stuck in a range between support and resistance - let's see what the week will bring.
Trade safe around these hours! Cheers.