Elliott wave : corrective wave How to use fibonacci retracement and extension
this entire trend was started at 1857 and ends at 1900 with wxy zigzag corrective wave.
wave x is subdivide into abc flat correction which retraced upto 0.382 of wave X at 1870
wave y made 1.382 projection of wave w at 1900.
the entire wxy trend made 50% retracement at 1878.
(retracement after wave y overlap wave x high which made clear that these are corrective wave not the impulsive wave )
how to trade ?
buy at 0.383 retracement of wave X and exit at 1.382 projection
sell at 1.382 projection at 1900 and exit at 0.50 retracement
Educational
How do I Calculate Reward/Risk? $IIPR as an ExampleIn my recent "Trade Plotting" educational posts I have shared, I referenced scaling out of my position at 2.5x my risk and then closing my position at 4.5x my risk.
I had couple followers asking for clarification as to how do I determine my risk on trades and how does that translate into scaling out and/or closing out the entire position.
Its really straightforward. Before I put on any position, I know exactly where I am going to enter and exactly where my stop loss is, which means, I know exactly how much i am going to lose per share if the stock turns south on me. Knowing how much per share I am going to lose drives the size of my position and therefore, defining my exact risk in dollars.
Knowing that, I use Fib Retracement tool to project upwards (in case of a long position) my reward multiples. For clarification, I labeled these as R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 (R = Return) on the chart.
Remember that the tighter the distance is between your entry and your stop loss (AKA having a tight stop loss), the faster the stock is going to hit your R targets and the wider the distance between your entry and your stop loss, the more distance the stock has to move up to hit your Rs.
I normally take half my position anywhere between R2 and R3. If I enter with a very tight stop (distance between Entry and Stop very small) because I am expecting the stock to start its run very soon after I enter, I normally hold on to the entire position well beyond R3 (as the distance to get there is relatively short).
Hope this helps, if you have any questions, firing them off in the comments below. Thanks!
The Powerful Strategic to accumulate XRP: Welcome:
In this special analysis, I want to take these themes to discuss with you an introduction :
1. How to accumulate XRP using a modered leverage
2. How to determine the XRP price when you buy, the price that you bought XRP when you use any crytpocurrency Bitcoin, Ethereum or any crytpocurrency as funds knowing the price that you bought XRP when you buy XRP and what price do you want to sell all your XRP, and what broker I use
3. How to recognize all your XRP profits in your cryptocurrency that you have in fund it, whether it's Bitcoin, Ethereum or whatever.
4. How you will need patience to earn in long term between 9 months to half one year.
5. The model and exercise
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
I. How to accumulate XRP using a modered leverage:
For accumulate XRP, you will need first to know all risk that you see in the leveraged in the trading, but we can't to overleveraged and you will need be wise and judicious. So, I reccomedn to have a good capital maybe $500-$1,000 in your trading account. So, this it's a first step : Bought a XRP contract of 500 to 1,000 XRP and keep this position toward the long term. Later that you bought XRP contract of 500 to 1,000 XRP contract you will need to be patience of it.
Summary: Bought 500-1,000 XRP contract, be secure to have a good capital minimum $500 and maximum $1,000 in your trading account and keep this position for long term in long position.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
II. How to determine the XRP price when you buy, the price that you bought XRP when you use any crytpocurrency Bitcoin, Ethereum or any crytpocurrency as funds knowing the price that you bought XRP when you buy XRP and what price do you want to sell all your XRP, and what broker I use:/b]
Once that you have a plan to bought between 500 to 1,000 XRP contract you will need to know the price what you bought XRP. Example: You bought 755 XRP at $0.32 cents. So, the $0.32 cents you will need to be aware of it that was the price that you bougth these XRP contracts. Another hand, later that you know these 2 thing: quantity of XRP in your contract and the price what you bought XRP, you will need to know what it's your depsoit funds whether it's Bitcoin, Ethereum or any cryptocurrency to know this basic details in what crypto you fund in your trading account to know in what price you bought XRP and what price on Bitcoin or Ethereum you buy XRP. And also in the end you will need to know finally the exact price that you want to closed up your long posiiton in XRP knowing the price to sell all XRP contracts.
Summaries and Examples:
1. You bought 755 XRP at $0.32 cents , and you buy these XRP contract when Bitcoin was $24,500 USD . Now, look and noticed that you use Bitcoin funds to make trading and noticed that it's a form to earn satothis. Now, once that you have this details my own reccomendation it's be aware take notes in your notebok and point that as reminder.
2. Your price to end will be $35 dollars to sell all XRP contract when XRP reach up $35 USD in the future. Now, knowing that you will be aware on it.
3. Now, the brokers that I use it's Quantfury, Prime XBT and recentrly Bybit, both to trade cryptocurrency.
a) In exception in Quantfury you can to use Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin and Dash to deposit like deposit method. And in Bybit you can to
deposit Bitcoin to trade BTC/USD, Ethereum to trade ETH/USD, Litecoin de trade LTC/USD, EOS to trade EOS/USD and XRP to trade
XRP/USD, but in Bybit I'm enfocous more in XRP, but more later we will going to discuss this part.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
III. How to recognize all your XRP profits in your cryptocurrency that you have in fund it, whether it's Bitcoin, Ethereum or whatever:
Once that you know the part I and II you can to have a knoledge so practice and theory on it. The quantity of XRP that you have in your XRP contract to long position, the price that you bought XRP and the price on Bitcoin, Ethereum or any crytpocurrency that you bought XRP that you will need noticed on it. And the closed up of XRP contract knowing our target possible.
Now, talking about to recognize all your XRP profits in yuor cryptocurrency that we can to use to count how much Bitcoin, Ethereum or any cryptocurrency we earnings.
So, I talking that you bought 755 XRP contracts at $0.32 cents, obviously the value it's $241.60 USD. Now, if you're target will be $35 USD so you will need to multiply 755 XRP and $35 USD or 755 XRP * $35 USD = $26,425 USD. But, now, this it's not your earnings, the second step it's deduct $241.60 USD (That was the value of your XRP contracts). So, your potential earnings will be $26,183.40 USD . Now, if you see this it's not all. For that, we would need to check how it's $26,183.40 USD in your Bitcoin value when you bought XRP contract knowsing the Bitcoin price when you bought XRP. So, let's say that the Bitcoin price was $24,500 USD using the same example.
So, for that you divided your profit that are $26,183.40 USD with the Bitcoin price when you bought XRP that was $24,500 USD that it's $24,500 USD. The formula will be $26,183.40 USD/$24,500 USD = 1.06 BTC. So, you get 1.06 BTC, and that will be your first Bitcoin simple and magic.
Sugerence: First count in US Dollar, later deduct the value of XRP with the final profit, and later that you get your real profit, you will need to know the Bitcoin price or Ethereum price or any cryptocurrency to know the conversion just divided your final profit and the Bitcoin, Ethereum or any cryptocurrency price when you bought XRP. That I explain how can you to get you first Bitcoin or imagine to accumulate Ethereums using this secret strategy that nobody talk you.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IV. How you will need patience to earn in long term between 9 months to half one year:
The part 4 it's so important, you will need to be patience, take a lot discipline between 9 months to hld one year approximately. This it's my possible calculation. This part it's so simple.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
V. The model and exercise:
And finally, this it's my favorite par, the models and exercise. You can get understand how it's work. if you don't understand too, I reccomend to continue read for above to below with cautions to get an understanding.
So, for that reason I create this part 5 to show you a nice strategic to accumulate a lot Ethereum in Quantfury and a lot XRP in Bybit. So, I will enfocous more in it.
Ethereum Strategic:
Yesterday, I bought 1,054 XRP at 0.3213 cents. This have a value of $338.65 USD and I use Ethereum assets in Quantfury app trading to accumulate more Ethereum. I bought 1,000 XRP when Ethereum was around of $621 USD approximately.
In these screenshoot I show you for your convenience my possibles targets for XRP in monthly chart and also my possibls 3 targets profit.
Now, my supposed that my target for XRP will be $100 USD.
Now, to know this. So, first I multiply my 1,054 XRP bought yesterday and supposed that I want to sell my XRP at $100 USD. That it's equal at $100,000 USD in profit. So, the second step it's deduct the value of your original XRP contract taht it's $338.65 USD with $100,000 USD that was my profits. The formula will be $100,000 USD - $338.65 USD = $99,661.35 USD. My final profit will be $99,661.35 USD.
Now, I want to know how much Ethereum I earn if I bought 1,054 XRP when Ethereum was $621 USD. In that case, we divided $621 WITH $99,61.35 USD or the formula $621/$99,661.35 = 160.48 ETH. So, I could have a potential huge earnings of 160.48 ETH. And 160.48 ETH it's so crazy to get this quantity. But imagine that Ethereum it's have a cot of $4,500 USD for each ETH. So, you will multiply 160.48 ETH with $4,500 USD that it' s $722,160 USD. So, that it's so huge earnings and also, to say you that it's a good way to become rich or millonaire if nobody talk this strategy with Ethereum just buying 1,000 XRP contract with leveraged modered. This it's my exercise for you that you can to apply and know how the trading benefit you can to receive it in your wallet. So, I use Ethereum in my Quantfury App to accumulate ETH making trading and also, apply this secret strategy that your broker don't wan't you to know it.
And you can to apply this strategic using Dash, Litecoin or Bitcoin in Quantfury app. Now, in exeption, Bybit offer for us a XRP deposit method to just trade XRP/USD and I can to apply the same strategic that I show you in the Bitcoin example and my Ethereum strategic to accumulate more ETH to long term between 9 month to half one year just buying 1,000 XRP contract and having a good capital of $854 USD that I have in Ethereum or equal approximately at 1.30 ETH.
🎓 EDUCATION 2: STOP Trading (Only) with Technicals ❌Happy Thursday traders! It’s time to continue with our Educational Series on how to become a successful trader with a professional trading approach. It's holiday season, and closed markets mean more time to sharpen our trading skills! Let's go...
In the last post, we touched on the main ingredients of a successful trader (check the link to "related idea"). Let’s reinforce those again:
1. Market Analysis – Your “Analyst” side. Here, you are going to combine Fundamentals, Intermarket analysis, Sentiment analysis, and (the correct) Technical analysis (FIST approach).
2. Trading – Your “Trader” side. Once the analyst in you spots a promising trade idea, the trader in you is responsible to execute the trade with proper entry and exit levels.
3. Management – Your “Manager” side. Every trader is a risk manager. Your manager side is responsible to manage your trade and risk levels, scale in and out of positions, open the correct position sizes, evaluate the reward-to-risk of your trades, etc.
Alright, so far we are still covering your “Analyst” side. Your analyst side determines whether you will buy EURUSD, sell GBPJPY, buy gold, and sell silver. It’s the part of your trading that constantly scans for profitable trade ideas and setups in the markets, and passes them on to your “Trader” side.
Why You Shouldn’t Rely on Technical Analysis?
The majority of new traders I see in the retail space place too much attention on technical analysis. They search the internet for TA articles, look for the “holy grail” indicator, read dozens of technical analysis books, but still don’t manage to improve their trading performance.
The truth is, they don’t understand the markets. I don’t care how many TA books you’ve read in your entire life, if you don’t understand how markets work and what moves prices up and down, you won’t succeed as a trader.
Unfortunately, almost every retail trading website promotes and publishes those articles, because they are attracting clicks of inexperienced traders.
Here is a hint: When I worked in the trading department of a large European bank, I didn’t even look at charts. There are almost no charts and no indicators on the trading floors of big banks and hedge funds!
Do you really think that banks will move hundreds of millions into a trade because the 50-day MA crossed the 100-day MA, or because the price formed a Head & Shoulders pattern? The first time you do this in a bank will likely be your last day as a professional trader.
So why do retail traders trade like that? Because they don’t know of better ways to trade. No one has taught them that trading based purely on technical analysis will never work. It’s in nobody’s interest to teach you this because large market participants need the “dumb money”. Yes, they make a profit when you trade badly and lose money.
So, what’s moving the market if it’s not technicals?
The Forex market is the marketplace for the world’s currencies, and currencies are influenced by supply and demand. To be more precise, interest rates influence currencies, with higher interest rates increasing demand for a currency (therefore leading to higher prices) and lower interest rates decreasing demand for a currency (therefore leading to lower prices.)
We as Forex traders are interest rate traders. We trade currencies based on (short-term) views about their future interest rates. For example, let’s say the market expects higher inflation rates (inflation represents the change in the price of goods and services during a year) in Australia, which could lead to a response from the Reserve Bank of Australia by hiking interest rates. This will create demand for the AUD (remember, global capital is always chasing yield), which in turn would lead to a higher exchange rate of the AUD.
If you only followed technicals and identified a bearish divergence on the RSI in AUD/USD - and you entered short - it’s your fault. The pair would likely move higher on higher interest rate expectations in Australia.
So, when do technical levels work? When the market trades in fair value (in fundamental equilibrium), you’ll find that simple technical rules work. If large market participants agree that the current exchange rate of a currency pair is “fair” given the current fundamentals, smaller players may move the market when the price reaches a support or resistance level, or when the price breaks above or below a triangle. Unfortunately, markets are always in a state of flux and rarely in equilibrium, so following other analytical disciplines (besides technical analysis) will improve your trading performance dramatically.
This chart shows the Band of Agnosticism. This band represents a span of exchange rates where fundamental-based traders are unlikely to join the market because the market is already in a fundamental fair-value zone. As the exchange rate starts to approach the upper or lower band, fundamental-based traders (which happen to be large banks and hedge funds) start considering opening new positions. The volume of their orders pushes the price back inside what is considered fair value.
Professional traders first look at a variety of other factors before they decide what currency pair they want to trade. Once we identify a good trading candidate (our “Analyst” side does that), then it’s time to open the chart and find areas where we could enter with a long position (and those are not trendline breakouts!)
We will cover all of this, step by step, in the coming Educational posts.
Don't forget to FOLLOW to receive all future trade ideas and educational posts!
Happy holidays everyone. 🎆
KAVAUSDT Fib Retracement 1H - Need your advice!Hello,
I found this Fib retracement fitting this pair that I have been tracking for a while now. I first studied the 1W, then I started noticing that the price trend on 1H was hitting the Fib Retracement zones very clearly. You can see how the price is bouncing off the 0.786 level and struggling to enter into the higher zone.
I am a total noob at this, and I am posting this chart to get some guidance from the community on what this means, and where it could be headed. I posted this to show people that this trend was in play, and for us to educate each other. I would love to learn from your experience and knowledge, so please share and comment what you think.
I wish you guys all the success in this business,
Rizwan.
⭐ STAGES OF TRADER's FORMING ⭐Hello! Traders professional growth involves going through several stages.
Let's talk more about them.
🔥1. Unconscious incompetence
💡 randomly opens and completes transactions without a specific trading system;
💡 doesn't care about risk management;
💡 often changes the direction of trade on the spot, following the price;
💡 keeps afloat only for small successful deals and doesn't care about losses at all;
💡 but as soon as loses, motivation immediately runs out.
🔥 2. Conscious incompetence
💡 Do you change your trading system several times in half a year without ever exploring a single one?
💡 You are actively looking at your trading history trying to figure out what you are doing wrong.
💡 Are you still making impulsive mistakes that cost a lot of money?
💡 Do you repeat the same trading mistakes again and again?
🔥3. The moment of "EURECA"
💡 No longer changes the system, but focuses on main and works with it.
💡 Begins to maintain a trading plan and a trading journal.
💡 The understanding comes, that trade is a daily routine.
💡 Understands, that in order to earn money, he needs to work on all the components of his system.
🔥 4. Conscious competence
💡 Understood the rules of the game and stopped losing money.
💡 Begins to make a steady profit.
🔥5. Unconscious competence
That's a stage of mastery👊🏻. You follow your trading plan on autopilot.✈
Just one question will help you to verify have you reached the highest level or not: ❗do you feel stress, when you're trading ? If so, then you have not reached this stage.❗
Thank you for staying with me💋
Always sincere with You🧡
Your Rocket Bomb🚀💣
USDJPY BUY USDJPY sitting at solid support.. also at bottom of channel that it's been forming
The green circle is the buy zones and the arrows give you a sense of how I expect it to move...
simple break above trend, goes up and hits resistance, then falls down to the trend line to test and then go higher...
The price labels show where I plan to take partial profits as well as my final take profits.
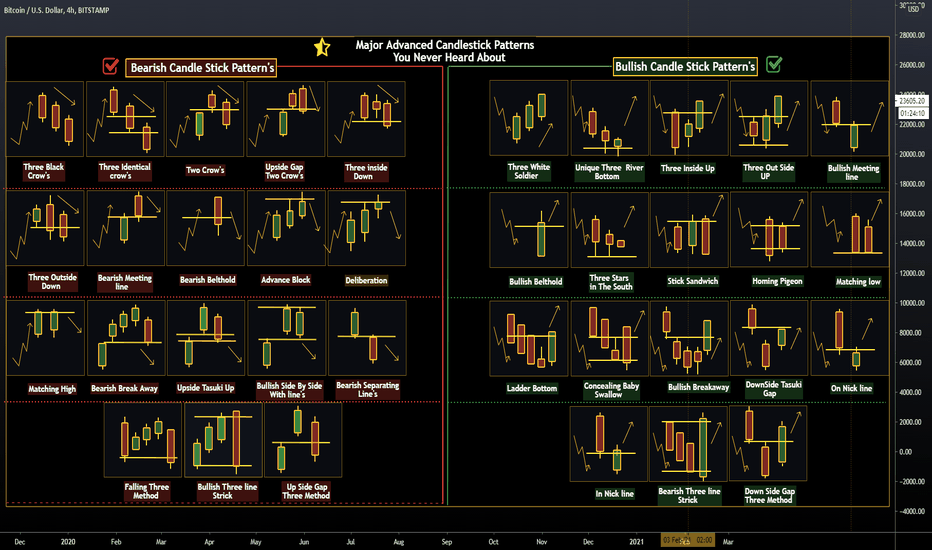
Major Advanced Candlestick Patterns You Never HeardCandlestick Definition
-----
What Is A Candlestick?
A candlestick is a type of price chart used in technical analysis that displays the high, low, open, and closing prices of a security for a specific period. It originated from Japanese rice merchants and traders to track market prices and daily momentum hundreds of years before becoming popularized in the United States. The wide part of the candlestick is called the "real body" and tells investors whether the closing price was higher or lower than the opening price (black/red if the stock closed lower, white/green if the stock closed higher).
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Candlestick charts display the high, low, open, and closing prices of a security for a specific period.
Candlesticks originated from Japanese rice merchants and traders to track market prices and daily momentum hundreds of years before becoming popularized in the United States.
Candlesticks can be used by traders looking for chart patterns.
The candlestick's shadows show the day's high and low and how they compare to the open and close. A candlestick's shape varies based on the relationship between the day's high, low, opening and closing prices.
Candlesticks reflect the impact of investor sentiment on security prices and are used by technical analysts to determine when to enter and exit trades. Candlestick charting is based on a technique developed in Japan in the 1700s for tracking the price of rice. Candlesticks are a suitable technique for trading any liquid financial asset such as stocks, foreign exchange and futures.
Long white/green candlesticks indicate there is strong buying pressure; this typically indicates price is bullish. However, they should be looked at in the context of the market structure as opposed to individually. For example, a long white candle is likely to have more significance if it forms at a major price support level. Long black/red candlesticks indicate there is significant selling pressure. This suggests the price is bearish. A common bullish candlestick reversal pattern, referred to as a hammer, forms when price moves substantially lower after the open, then rallies to close near the high. The equivalent bearish candlestick is known as a hanging man. These candlesticks have a similar appearance to a square lollipop, and are often used by traders attempting to pick a top or bottom in a market.
Traders can use candlestick signals to analyze any and all periods of trading including daily or hourly cycles—even for minute-long cycles of the trading day.
Two-Day Candlestick Trading Patterns
There are many short-term trading strategies based upon candlestick patterns. The engulfing pattern suggests a potential trend reversal; the first candlestick has a small body that is completely engulfed by the second candlestick. It is referred to as a bullish engulfing pattern when it appears at the end of a downtrend, and a bearish engulfing pattern at the conclusion of an uptrend. The harami is a reversal pattern where the second candlestick is entirely contained within the first candlestick and is opposite in color. A related pattern, the harami cross has a second candlestick that is a doji; when the open and close are effectively equal.
Three-Day Candlestick Trading Patterns
An evening star is a bearish reversal pattern where the first candlestick continues the uptrend. The second candlestick gaps up and has a narrow body. The third candlestick closes below the midpoint of the first candlestick. A morning star is a bullish reversal pattern where the first candlestick is long and black/red-bodied, followed by short candlestick that has gapped lower; it is completed by a long-bodied white/green candlestick that closes above the midpoint of the first candlestick.
15 Types of Financial Market Participants ExplainedIn this post, I’ll be going over the 15 types of financial market participants as listed above.
You want to keep your friend close, and your enemies closer. As an investor or a trader, jumping into the market without knowing what these entities are doing is like jumping into a battlefield with just a stick in your hand.
So understanding the roles of each of these entities can help you significantly later as you mature as an investor, especially if you’re a beginner.
Investment Banks
- Investment banks buy, sell, and issue stocks and bonds, lead mergers and acquisitions, conducts market research, and provide asset management services.
- They act as a bridge between people who want to invest their capital, and people who need investments.
- Investment banks can be more specifically divided into two types: bulge brackets and boutiques.
- Bulge brackets are general investment banks like Goldman Sachs, JP Morgan, Morgan Stanley, and Deutsche Bank.
- Boutiques are more specialized investment banks such as Lazard, Evercore, and Guggenheim.
Structure of an Investment Bank
- A general investment bank can be divided into three offices: the front, middle, and back office.
- The front office consists of four divisions: the investment banking division, sales and trading, asset management division, and research division.
- The front office refers to the divisions that directly interact with clients, and are in full charge of generating profits for the company.
- The image of investment bankers portrayed in movies generally all refer to the front office. These are the people who make six figure monthly salaries.
- The middle office is in charge of supporting the front office.
- They are responsible for risk management or capital management.
- The back office is in charge of the operations of the investment bank as a company, so it includes IT, HR, and other administrative teams.
Front Office Divisions Explained
1) Investment Banking Division (IBD)
- The investment banking division is in charge of everything that happens in the primary market.
- The primary market is where securities are created, and the secondary market is where those securities are traded.
- Normally when retail investors invest, it all happens in the secondary market.
- In the primary market, investment banks offer a variety of services including the issuance of stocks and bonds, leading an IPO, or leading an M&A.
- Teams are normally divided by sectors, but they can also be divided into specific teams depending on the deal they’re doing.
- Their day to day work involves company valuation, industry analysis, analyzing a company’s financials, preparing for presentations, and financial modelling. (When I say financial modelling, I mean that they use excel. They don’t really use extremely sophisticated statistical models in this division.)
2) Sales and Trading
- When you think of Ivy League alumni who work in finance, it usually refers to people in the investment banking division, or in sales and trading.
- But recently, this division has been dying, and is on a downtrend.
- Trading can be divided into two types: prop trading or proprietary trading, and flow trading.
- Prop trading refers to the type of trading that we know, where traders buy low, and sell high.
- Flow trading refers to order flows, where if a client makes an order the trading desk fills that order on the client’s behalf.
- In that process, they leave a small profit margin and take a certain amount of fees.
- In the past, both types of trading were extremely active.
- But with the global financial crisis in 2008, prop trading within investment banks got banned, according to the Volcker rule.
- As a result, most major banks spun off their prop trading desks, and the people who used to be prop traders in investment banks left to create their own hedge fund.
- What’s left now is flow trading, but since flow trading refers to simply filling orders on the customer’s behalf, this process has recently been automated to a huge extent, especially with the emergence of high frequency trading
- Along with this, their profit margins and commission started to decline, and the sales and trading industry as a whole is shrinking over time.
- As such, the teams left in this division are teams such as high frequency trading teams, quant teams, and OTC market traders. (OTC refers to over-the-counter, which is where customized products are bought and sold, as opposed to standardized products that we see in secondary markets.)
3) Research
- The research division is in charge of market research.
- They make analyst reports that we’re familiar with.
- But this is another division that’s dying.
- Research conducted by these institutions were actually provided to their clients as a token of gratitude for using their services, and paying commission.
- But, with brokers like WeBull and Robinhood offering zero commission, their business model deteriorated.
- Especially in Europe, laws have been set to distinguish payments for commissions and payments for research material, and people don’t really want to pay money for services like these.
- Lastly, with the development of data science, the way research is conducted has completely changed.
- It has become more technical, using machine learning techniques of pattern recognition, and it’s becoming more common on the buy side.
Mutual Funds, Hedge Funds, Proprietary Trading Firms
- In the case of mutual funds, the capital of the fund comes from people, or the general public.
- The capital for hedge funds come from accredited investors who qualify the capital requirement.
- Normally, these investors need to invest a minimum of $500,000 to $1 million.
- In the case of prop trading firms, they trade with their own money. Hence the term ‘proprietary’.
- In terms of their investments, mutual funds are mostly limited to investments in stocks and bonds.
- Hedge funds and prop trading firms don’t have any limitations or regulations in terms of the asset they want to invest in.
- Even in terms of the trading/investment strategies that are used, mutual funds strategies are quite limited and regulated heavily, as opposed to hedge funds or prop trading firms that have no restrictions in their strategies.
- The logic behind restricting strategies that mutual funds use is that mutual funds manage capital of the general public, and thus have to be more careful with how they manage their funds.
- The regulations that the government poses on mutual funds are essentially ways to protect the general public from potential losses that might incur.
- As such, even when it comes to revealing information, mutual funds need to be transparent about everything.
- In the case of hedge funds, the government acknowledges that accredited investors with $3-4 million to invest are probably aware of the potential risks, and thus is relatively less limited in having to reveal their information.
- Lastly, in the case of prop trading firms, because they’re trading with their own money, they have no obligation to reveal any of their information.
- This is why prop trading firms use exclusive trading techniques and strategies that cannot be exposed to the general public.
- Mutual funds take a 1-2% management fee, and don’t take any other incentive fees.
- Thus, they focus on gathering as many people as possible in order to capitalize on a huge management fee.
- They are also legally allowed to advertise and do sales.
- Hedge funds take 1-2% as management fees, and 15-20% in incentives. This is also known as the Two and Twenty.
- Hedge funds are also limited from advertising.
- Lastly, prop trading companies take all of the profits they generate, and thus do not need any advertising at all.
- Examples of mutual funds include Vanguard, Fidelity, and State Street.
- Famous hedge fund examples include Bridgewater Associates, Renaissance Technologies, and Elliott.
- Lastly, prop trading companies are companies like D. E. Shaw, Hudson River Trading, and DRW.
Private Equity
- Private equities are very similar to hedge funds in terms of their nature, the way they receive management fees and incentives.
- But as opposed to hedge funds that normally invest and trade in the secondary market, private equities directly invest in a company. Hence the name ‘private’ equity.
- A prime example is a leveraged buyout fund. This is when private equities acquire a huge stake within a company, increase its profitability, and sell their stake for a higher price.
- In movies, these people are portrayed as bloodless and merciless people who lay off tens of thousands of workers to cut costs of a company.
- Similarly, there are venture Capital funds that invest in early startups, and Growth Equity Funds that invest in startups at later stages.
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs), Index Funds
- Before I explain index funds, it’s important that you understand exchange traded funds, or ETFs.
- An ETF is essentially a basket of securities that trades on an exchange like a stock.
- In mutual funds, when they have a fund that tracks an underlying index, it’s called an index fund.
- Similarly, an ETF that tracks an underlying index is an Index ETF.
- An Index ETF is essentially the same thing, but a security listed on an exchange, into smaller bits, so that individuals can buy and sell the ETF like a stock.
- For instance, for an individual to invest in all 500 companies on the S&P 500 index is extremely difficult.
- What institutions do is, they buy the shares of all 500 companies on the client’s behalf, creating a basket with all companies.
- From there, they sell the ownership of the basket to clients, which is the ETF.
- Because these companies actually own the underlying asset, they are not exposed to the risk of bankruptcy.
- This is a passive fund, in which a fund manager does not really intervene actively.
- Thus, the fund manager of an Index ETF just needs to mechanically buy and sell shares according to the index, so that the ETF can perform in correlation to the index.
- Ever since the global financial crisis in 2008, quantitative easing has pushed market indices to move upwards over time, making passive Index ETFs a very attractive option for investment.
Sovereign Wealth Funds, Pension Funds, Endowment Funds
- A sovereign wealth fund is a state-owned investment fund that invests in financial assets, and is run by the state.
- A pension fund is a fund that is set up by contributions from employers, unions, or other organizations to provide retirement benefits to its employees or members.
- Pension funds are one of the largest players in the market by size.
- They invest in stocks and bonds, but also increasingly stated exposing themselves to other asset classes.
- There are also endowment funds, which is a fund that invests with the money that was gifted to them.
- These funds are often run by universities, nonprofit organizations, and sometimes even churches.
- The funds operated by Harvard and Yale are known as Super Endowment Funds due to their fund size and impressive returns.
- A general portfolio that consists of 60% stocks and 40% bonds would give an annual return of 5.4%.
- Super Endowment Funds have managed to reach an annual return rate of 11.5% over the past 20 years.
- These funds have great network value, easy access to premium information, and expertise in alternative asset class investments.
- This means that they don’t invest in just stocks and bonds, but also real estate, private equities, emerging equities, global bonds, and natural resources.
Brokers, Dealers, Exchanges
- Brokers play the role of middlemen who connect buyers and sellers within a market, and profit from commissions.
- Exchanges play the same role within the cryptocurrency market.
- Dealers play the role of market makers for customized financial products that are traded in the OTC markets.
- Essentially, they take the opposite position of the person trying to trade.
- Dealers mostly do business with institutional investors, because individual investors normally don’t trade customized financial products.
- As a rule of thumb, when someone says dealers, think of investment bankers who trade interest rate swaps, bonds, or CBS over the counter.
Insurance Companies
- Moving onto insurance companies; they receive premiums from their clients, and while their role is to pay their clients back in case of an accident, during day to day operations, they also participate in the financial markets with the capital they have.
- However, compared to the size of their fund, they play a relatively less significant role in the market.
Federal Reserve Board
- The Federal Reserve Board, or Fed, consists of 12 regional federal banks.
- They control the national monetary policy, supervise and regulate banks, and maintain financial stability.
- There’s a colloquial term that ‘the Fed prints money’, but this is not to be taken literally.
- One of the ways in which they control money supply is by buying or selling bonds in the open market, also called the open market operations.
- One of the reasons that all asset markets have been so bullish ever since the market drop in March is because the Fed has increased money supply at an unprecedented rate, thereby inflating asset prices.
Limited Liability Companies
- Limited liability companies are also players within the financial markets.
- They initiate share buybacks, give out dividends to shareholders, and insider transactions take place as well, which is actually highly illegal.
- Insider transaction refers to an insider of the company trading the company’s shares based on information asymmetry.
- For instance, if an executive at Pfizer bought the company’s shares before the vaccine announcement, knowing that the vaccine was ready, that would be considered insider trading, and he’d do jail time for it.
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
- The Securities and Exchange Commission is in charge of imposing federal securities laws and regulating the stock and options exchange.
- In the example suggested previously of an executive from Pfizer, the SEC would be the entity to investigate the case.
Retail Investors, Accredited Investors
- Retail investors refer to the general public that take part in the financial market.
- These are the people who work 9-5 jobs, and invest in stocks over the long run, or sometimes they’re full time traders and investors.
- Accredited investors are similar to retail investors in that they are an individual, but they’re different from other retail investors in the sense that they’re acknowledged by the SEC.
- Essentially, the government understands that an accredited investor has more knowledge and capital, and is capable of bearing more risk compared to the average retail investor.
- Thus, they get more opportunities to participate in the financial market that normal retail investors don’t.
- For instance, they can buy private companies that aren’t listed on the secondary markets, and they can invest their capital in hedge funds.
- To become an accredited investor in the US, your net worth must exceed $1 million, not including primary residence, or your annual income must exceed $200,000 for the past 2 years, or $300,000 in annual income with your spouse for the past 2 years.
If you like this educational post, please make sure to like, and follow for more quality content!
If you have any questions or comments, feel free to comment below! :)
$ATVI Plotting a Trendline Breakout TradeA trade setup that I shared here that ended up a text book setup. For education purpose, I've annotated on the chart my thoughts as to why the stock was on my watchlist, and when I entered and exited the trade. I'm hoping these trade examples provide some type of coaching for newer traders.
PRICE ACTION WINNING TRADE – BULLISH RE-ENTRY STRATEGY Hi traders,
This is a 45-minute chart of the BTCUSD.
A bullish Pin Bar seen we took the trade.
after a bullish move price fell and hit stop-loss orders placed around the low of the Pin Bar (a common pattern stop level).
The market recovered quickly and offered a re-entry chance with a second bullish Pin Bar. We bought as price broke above its high.
After our entry, the market rose with a strong thrust.
I strongly recommend that you adopt this re-entry trading approach. It offers a trading technique that lowers trade frequency and increases probability of success.
Thank you.
CANDLSTICK or BARS. What common?There are public rules for graphing price movements on the charts of various market assets.
There are two main types of designation:
Candles
They were invented by the Japanese rice merchant Homma Munehisa, which is why they got the name - Japanese candles.
The candlestick gives information about deals within the selected period:
- Opening - the initial price of the period, the price of the first deal.
- High - the maximum price of the period
- Low - reasonable price of the period
- Close - the closing price of the period, the price of the last deal.
- The bod y of the candle is the distance between the open and close.
- Candle shadow - deviations from the opening and closing prices, maximum and minimum values of prices.
Depending on which direction the price went: rose or fell - the candlestick can be bearish or bullish.
Bars
This type of image is not much different from candles. They consist of exactly the same parts and display all the same information.
The bar is rather a more compact candlestick image. Instead of a full-fledged "body", only a vertical stroke is displayed.
What kind of depiction of price movements do you prefer?
Traders, if you liked this idea or if you have your own opinion about it, write in the comments. I will be glad 👩💻
Fibonacci Levels - Rocket Bomb's EDU post 🔥Hi guys, as I promised, this post is about Fibonacci Levels for YOU!🧡
Leonardo Fibonacci is a great mathematician who lived in the XI century. The scientist deduced a number of natural numbers, which later began to bear his name.
Each number in the series was the sum of the two previous numbers: 1 + 1 = 2; 1 + 2 = 3; 2 + 3 = 5 etc.
The result is a series of numbers: 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, etc.
Fibonacci numbers have some properties:
📌Division of any number of the series into the subsequent tends to 0.618 (the golden ratio in ancient Greek and ancient Egyptian cultures);
📌dividing any number of the series by the next + 1 tends to 0.382;
📌dividing the subsequent number of the series by the previous one tends to 1.618;
📌division of the number of the series by the second number preceding it tends to 2.618.
Fibonacci numbers are often used not only in technical analysis , but also in physics, astronomy and other disciplines.💪🏻
Fibonacci levels are a tool that sets horizontal support and resistance levels on the price chart based on price movement.
It's important to understand, that Fibo levels work well when there is a trend in the market.
How to determine Fibonacci levels?
To determine Fibonacci levels, you need to find the recent significant high and low of the last price movement. When plotting levels for a downtrend, the first point should be at the maximum and the second at the minimum. For an uptrend, you need to do the opposite. Click on the low of the price swing and drag the cursor to the high. In this case, the construction of levels always occurs from left to right.
How to trade by Fibonacci levels?
The basic variant with an upward movement: we determined the minimum and maximum, set the levels, waited for a rollback, entered the market. The price continues to move - we drag the levels to a new maximum, wait for our rollback level, and enter the market.
In a downward movement, we do the same, entering a movement on a pullback.
The technical analysis usually uses the number 0.618 or 61.8%, 0.382 or 38.2%, as well as the psychological half (middle) of 50%.
✔ Very often, based on these coefficients in the technical analysis of the market, Fibonacci lines, Fibonacci levels and Fibonacci periods are built.
Fibonacci lines are built relative to significant highs / lows and represent support or resistance lines, from which they make a purchase or sale.
Fibonacci numbers - the magic of numbers that works in trading and in everyday life .
💥You can simply draw arbitrary horizontal lines on the chart, and ... oh that's mystic... they will also be worked out both in the past and in the future.💥
We can make some conclusions:
🔵Fibonacci tool draws support and resistance lines on the chart based on price movement;
🔵the Fibonacci tool is always applied on the price chart from left to right, both in the case of long positions in an uptrend, and in the case of short positions in a downtrend;
🔵the levels marked between the beginning and the end of the price movement are correction levels, they show which levels the price is likely to return to;
🔵the most common Fibonacci retracement levels are 38.2%, 50% and 61.8%, they are often used to enter the market;
🔵there are two ways to use correction levels to enter the market: aggressive (entry at each of the levels) and passive (waiting for the price to correct in the originally observed direction);
🔵It's important to note that Fibonacci levels are not a trading system, they are an additional tool that only suggests possible correction levels; it should be used only in combination with a trading system or as part of a trading system.
I hope everything was clear for You, and You found this post as helpful🙏🏻
I really wanna be useful to you, guys!
I make every post with love and it brings me extraordinary pleasure!🙏🏻
Thank you for staying with me💋
Always sincere with You🧡
Your Rocket Bomb🚀💣
audcad educational hello everyone
audcad is the pair that I wanna analysis about its LONG market
I wrote everything in the chart
but notice that there are all for bullish market
if market changed and we saw bearish market I will send a confirmation on this post As : price reached SL
and then we would think about short positions
Right now We have many reason if price goes up to go long
I Imaging its better to Wait until break that resistance line then go long
and the point is Targets would be cut lines From weekly time frame which are confirmed with at least 3 impacts
but Make your confirmations for your targets
good luck and have fun
Everything You Need to Know About SPACsIn this analysis, I'll be covering everything you need to know about Special Purpose Acquisition Companies, or SPACs, and my own strategy that I use to choose for risk minimization, and profit maximization.
SPAK, the chart above, is an ETF that was specifically designed to invest in SPAC companies.
This is not investment advice. This is for educational and entertainment purposes only. I am not responsible for the profits or loss generated from your investments. Trade and invest at your own risk.
1. What is a SPAC?
- SPAC stands for Special Purpose Acquisition Company.
- They’re also called Blank Check Companies or Shell Companies. But what is this special purpose that they’re talking about?
- Their purpose is to acquire an existing company, so that it’s available for trades and investments in the stock market.
- They need to acquire a company within a given time frame between 18 to 24 months, sometimes 36 months depending on the conditions.
2. SPAC vs. IPO
- Normally, companies go public through a process called an Initial Public Offering, or an IPO.
- There’s another method called Direct Listing, which is the method that Spotify and Slack used to go public, but for the sake of simplicity, we’ll just look at a comparison of IPOs and SPACs.
- In terms of time period, SPACs can help companies go public much faster than if they were to go public through an IPO.
- The process is also much simpler, and has less requirements, and it also costs less to go public through a SPAC.
- But, the company’s valuation is discounted, when they get listed through a SPAC.
- So for instance, if a company that has an enterprise value of 100 billion were to do an IPO, they’d be valued as a 100 billion dollar company, whereas if they get listed through a SPAC, they’d be discounted as an 80 billion dollar company.
3. Who Makes SPACs?
- Normally, people with a reputation in the market make these SPACs.
- For instance, Bill Ackman, who’s the CEO of Pershing Square Capital, is extremely well known as one of the best investors, and a lot of people want to bet their money on him.
- So people like Bill Ackman are the ones who gather investors up, and create a SPAC.
4. Constituents
- When a SPAC is created, and goes through an IPO, the shares are owned by three entities: the founder, individuals, and PIPE, which stands for Private Investment in Public Equity.
- Private stake refers to the shares that the founders, or the creators of the SPAC get.
- Public stke refers to the shares that individuals buy when the SPAC gets listed.
- PIPE refers to the investors who lend money to the SPAC so that they can acquire a company.
- So for instance, Let’s say that SPAC is trying to acquire a $10 Billion dollar company, but they only have $5 billion in their trust.
- A PIPE can hop in, and lend the remaining $5 billion to the SPAC, and in return, they get shares of the acquiring company for a cheap price.
5. One SPAC Unit
- One SPAC unit consists of 1 share and the warrant that comes with the share.
- The Warrant is essentially the right to purchase the SPAC share at a designated price later in the future.
- It essentially acts as an incentive for the SPAC investors who take on risk.
- But you can use the warrant only within a designated time period, which is usually divided into two conditions:
1) either 30 days after the new company’s IPO
2) Or 365 days after the SPAC IPO
6. SPAC Trust Account
The money for the SPAC is deposited in a trust, and the funds cannot be used for any other purposes than acquiring a company or refunding the investment seeds back to the investors, in case an acquisition does not happen.
7. Negotiation and Acquisition
- When the SPAC gets listed, it’s time for people to search for companies to acquire, and negotiate.
- Once everything is prepared, they now move onto searching innovative firms, normally between a timeframe of 18 to 24 months, sometimes a little longer depending on the conditions.
- The business that they acquire needs to be at least 80% of the value of the trust account.
- So for instance, if the trust account has $10 billion, the company that the SPAC acquires needs to be at least around $ 8 billion in fair market value.
- Once the negotiation is done, and the acquisition is announced, they go through a process of getting permission from the SPAC shareholders.
- If the SPAC shareholders agree to the acquisition, they get shares of the new company equivalent to the shares of the SPAC they hold, at a 1:1 ratio.
- If they were to disagree, they can simply cash out their stake.
8. Example
Here's an example to help your understanding:
- A SPAC sponsored by BIll Ackman’s Pershing Square Capital made its debut to the New York Stock Exchange, with the largest blank-check IPO (PSTH).
- The offering includes 200 million units at $20 each, railing $4 billion in proceeds. Each unit consists of one common share and one-ninth of a warrant, exercisable at $23.
- So the ticker of this SPAC is PSTH, and the company they’re acquiring hasn’t been announced yet, so let’s just say that they’re buying a company called Mike’s Burgers, which’ll be listed under the ticker MIKE.
1. As an investor, you buy 9 shares of PSTH at $20 as soon as it gets listed.
2. You now have 9 shares, and a warrant that you can use, since 1 unit of the stock includes 1 ninth of a warrant.
3. So you have 9 shares, and a right to purchase 1 more share at $23.
4. Let’s say Mike’s Burgers got listed on the New York Stock Exchange, and the stock goes wild because the burgers taste great.
5. After the IPO, the stock trades at $50 a share.
6. You, as an investor, think that the stock prices could go higher for whatever reason.
7. So, you decide to wait 3 more weeks, so you can use your warrant.
8. 3 weeks later, the stock soars a bit more, and trades at $60 a share.
9. You now have 9 shares that you bought at $20, and you use the right to purchase 1 more share at $23.
10. You then sell all 10 shares at market value. So, when you sell all your shares for $600, and you’re left with an initial investment of $203, and $397 in profits.
11. So in a trade like this, you could double your investment easily.
9. Risks
- First of all, there are risks involved with PIPEs selling their stake.
- It’s not like these entities have a lockup period, they can sell their shares as long as they have permission granted from the SEC, so there’s risk involved in that.
- For instance, Nikola’s stock prices (NKLA) plummeted after its PIPE sold all their stake.
- Secondly, you’re investing in a paper company and you don’t know which company they’ll acquire.
- Normally, SPACs are run by veteran investors who know what they’re doing, but there’s absolutely no guarantee that the company it acquires will be a good one.
- For instance, there were rumors about how Bill Ackman’s SPAC would be acquiring Airbnb (ABNB) , but as you guys know, it turned out to be false.
- So as an investor, who’s not an insider, it’s hard to invest in a paper company without knowing what’ll happen to the SPAC company.
10. How to Choose the Right SPACs
- So, we obviously want to minimize risk, and maximize our returns, and to do that, it’s important to choose the right SPACs to get into.
- I’ll be providing my own strategy on finding the right SPACs. I’ll call this the 2N strategy.
- The key of this strategy is the combination of narrative and numbers .
- This is how I select stocks to invest as well, but the approach to SPACs are slightly different.
- What do I mean by narrative? I mean that the SPAC or the company that they’re acquiring, needs to have a good story.
- They need to have a good leader for the SPAC, they need to acquire a company in a prominent field, and a management team with expertise in the field.
- So here are some things I’d look for:
- First of all, I would want to see a figure who’s already acknowledged and successful.
- Of course it’d be better if they have a successful SPAC deal experience. (Bill Ackman is a good example of someone I’d have my money on.)
- I’d also look at the backgrounds of members of the management team.
- Look into what their expertise is, their work experience, professional backgrounds, and any noteworthy achievements.
- This type of information is normally all available on the SPAC’s website, but you can also look them up on linkedin.
- Also look into the institutions that are involved.
- If big names like BlackRock and CVC are taking part, and they hold SPAC shares, that’s good news.
- You want to make sure that acknowledged institutions are behind the project.
- Last but not least, it’s important to look at the industry that the SPAC has eyes on.
- You want to take part in a prominent industry, and obviously the trend is tech.
- Electric vehicle SPACs have also shown some crazy gains recently, but make sure you invest in a SPAC that operates in a field that you’re familiar with, and has high growth potential.
- Now, let’s take a look at what I mean by numbers.
- Before we can talk about numbers, we first need to understand how we can capitalize on SPAC opportunities .
- The best thing about SPACs is that you can minimize your losses, or even trade risk free if you’re lucky enough.
- The offering price of a SPAC stock varies, depending on the company, but normally it’s around $10.
- And the best thing about investing SPACs is that there is a price floor.
- It’s not that prices are legally prevented from trading below the initial IPO price, but there’s no reason for it to be traded anything below than its offering price, because in the unlikely case that an acquisition does not take place, everyone gets a refund anyways.
- So basically, given that you enter at the offered price, there’s nothing to lose, and everything to gain. This is what makes SPACs special.
You might ask, how much is there to gain?
- The answer is at least as much as its net asset value.
- In case you don’t know, the net asset value is calculated by subtracting all liabilities from the assets a company has, and dividing it up by the total number of common shares.
- If you actually do your due diligence, and calculate the net asset value of the SPAC you’re investing in, you’ll realize that the net asset value normally ranges around $10.10 to $10.25 right off the bat.
- This means that you have a 1-2.5% default return before even taking into account the warrant value, which is substantial, and the upside opportunity.
- So, going back to what I mean by numbers, you want to either find a SPAC that is traded at around its offered price or below its offered price.
- A SPAC that is already trading at 3 times its offered price probably won’t get you the best returns.
- You want to find a SPAC that’s cheap.
- Also, make sure you check the trust value, the SPAC’s market cap, and their net asset value.
- You want to make sure you get into companies with a high trust value, and a net asset value that is not too far from its market price.
Conclusion
As long as investors conduct their own research, there is huge opportunity they can capitalize on, with very little to no downside. Thus, I highly encourage that people start exploring the world of SPACs, and maybe even consider adding prominent companies to their portfolios early on.
If you like this analysis, please make sure to like the post, and follow for more quality content!
I would also appreciate it if you could leave a comment below with some original insight :)
📚 Learn More 💰 Earn More with us: FLAG = Impulse + Correction📚 LEARN MORE
💰 EARN MORE
With ForecastCity
FLAG pattern Definition:
A FLAG pattern is a continuation chart pattern, named due to its similarity to a flag on a flagpole.
A flag is a relatively rapid chart formation that appears as a small channel after a steep trend, which develops in the opposite direction.
After an uptrend, it has a downward slope. After a downtrend, it has an upward slope.
IMPULSE Definition:
A “flag” is composed of an explosive strong price move forming a nearly vertical line.
This is known as the "IMPULSE" or ”flagpole”.
The sharper the spike on the flagpole, the more powerful the bull flag can be.
Corrective Wave Definition:
After an uptrend, it has a downward slope. After a downtrend, it has an upward slope.
This downward or upward slop known as "Corrective Wave".
Flag patterns can be bullish or bearish:
A bullish flag is known as a Bull Flag.
A bearish flag is known as a Bear Flag.
How to Trade FLAG Patterns:
When the trend line resistance on the flag breaks, it triggers the next leg of the trend move, and the price proceeds ahead.
Breakouts happen in both directions but almost all flags are continuation patterns.
This means that Flags in an uptrend are expected to break out upward and Flags in a downtrend, are expected to break out downward.
❤️ If you find this helpful and want more FREE forecasts in TradingView
. . . . . Please show your support back,
. . . . . . . . Hit the 👍 LIKE button,
. . . . . . . . . . Drop some feedback below in the comment!
❤️ Your Support is very much 🙏 appreciated! ❤️
💎 Want us to help you become a better Forex trader ?
Now, It's your turn !
Be sure to leave a comment let us know how you see this opportunity and forecast.
Trade well, ❤️
ForecastCity English Support Team ❤️