Pending Orders Are Not Set in Stone – Context Still MattersIn a previous educational article, I explained why I almost never trade breakouts on Gold.
Too many fakeouts. Too many emotional traps.
Instead, I stick to what works:
• ✅ Buying dips
• ✅ Selling rallies
But even these entries — placed with pending orders — are not automatic.
Because in real trading, price is not just a number — it’s a narrative.
And if the story changes, so should the trade.
________________________________________
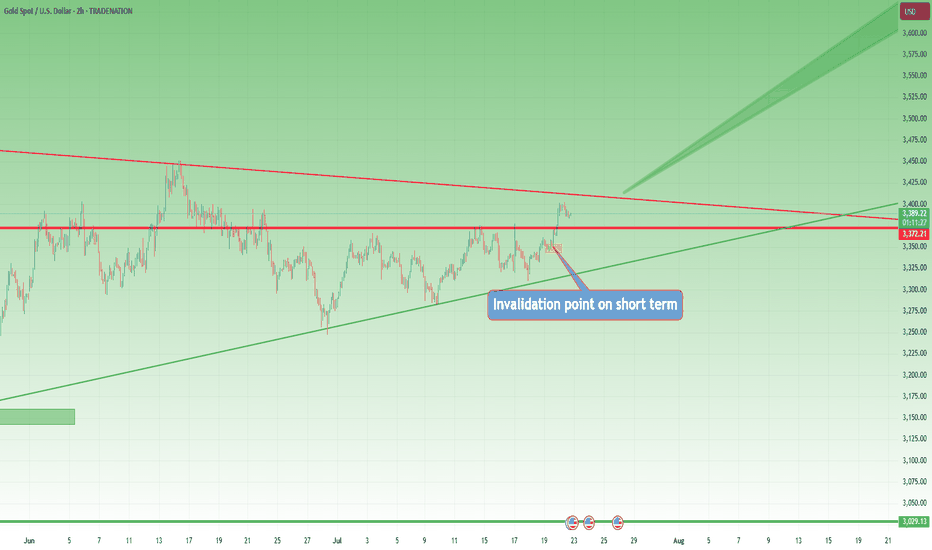
🎯 The Setup – Buy the Dip Around 3400
Let’s take a real example from yesterday.
In my analysis, I mentioned I would look to buy dips near 3400, a former resistance now acting as support.
Price dropped to 3405, just a few points above my pending buy at 3402.
We saw a clean initial bounce — confirming that short-term support was real.
But I missed the entry by 30 pips.
So far, so good.
But here’s the important part — what happened next changed everything.
________________________________________
🧠 The Rejection Shifted the Entire Story
The bounce from 3405 was immediately sold into at 3420, a newly formed short-term resistance (clearly visible on the 15-minute posted chart).
After that, price started falling again — heading back toward my pending order.
📌 At that point, I cancelled the order. Why?
Because the context had changed:
• Bulls had tried once — and failed at 3420
• Sellers were clearly active and waiting above
• A second drop into my level wouldn’t be a clean dip — it would be retest under pressure.
The market was no longer giving me a “buy the dip” setup.
It was showing me a failed recovery. That’s a very different trade.
________________________________________
💡 What If It Had Triggered?
Let’s imagine that price had hit 3402 first, triggering my order.
Then rebounded, failed at 3420, and started dropping again.
Even then, I wouldn’t hold blindly.
Once I saw the rejection at 3420, I would have understood:
The structure had shifted.
The bullish case is weakening.
Exit early — breakeven or small controlled loss.
________________________________________
🔁 Sequence > Level
This is the most important principle:
• ✅ First down, then up = healthy dip → shows buyers are still in control
• ❌ First up, then down = failed breakout → shows selling pressure is stronger
Two scenarios. Same price. Opposite meaning.
That’s why you should look for:
Not just where price goes — but how it gets there.
________________________________________
🔒 Pending Orders Are Conditional
Many traders treat pending orders like traps:
“Just let price come to my level, and I’m in.”, but you should refine a little
✅ Pending orders should be based on a conditional expectation
❌ Not a fixed belief that the zone must hold
If the market tells a different story, remove the order.
No ego. No drama. Just process.
________________________________________
📌 Final Thought
Trading isn’t just about catching a price.
It’s about understanding price behavior.
First down, then up = strength.
First up, then down = weakness.
Let the market show its hand — then decide if you want to play.
Disclosure: I am part of TradeNation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analyses and educational articles.
Educationalidea
Feed Your Ego or Feed Your Account- Your Choise🧭 From Rookie to Realization
I’ve been trading since 2002. That’s nearly a quarter of a century in the markets.
I’ve lived through it all:
• The early days, when the internet was slow and information was scarce
• The forums, the books, the overanalyzing
• The obsession with finding “the perfect system”
• And later… the dangerous phase: needing to be right, because I have a few years of experience and I KNOW
At one point, I thought that being a good trader meant calling the market in advance — proving I was smarter than the rest.
But the truth is: the market doesn't pay for being right. It pays for managing risk, always adapting and executing cleanly.
________________________________________
😤 The Psychological Trap Most Traders Fall Into
There’s one thing I’ve seen consistently over the last 25 years:
Most traders don’t trade to make money.
They trade to feel right.
And this need — this psychological craving to validate an opinion — is exactly what keeps them from growing.
You’ve seen it too:
• The guy who’s been screaming “altcoin season” for 2 years
• Who first called it when EGLD was at 80, TIA, and others that kept dropping
• But now that something finally moves, he says:
“See? I was right all along, altcoin season is here”
He’s not trading.
He’s rehearsing an ego story, ignoring every failed call, every drawdown, every frozen position.
He doesn’t remember the trades that didn’t work — only the one that eventually did.
This is not strategy.
It’s delusion dressed up as conviction.
________________________________________
📉 The Market Doesn’t Care What You Think
Here’s the reality:
You can be right in your analysis — and still lose money.
You can be wrong — and still come out profitable.
Because the market doesn’t reward your opinion.
It rewards how well you manage risk, entries, exits, expectations, and flexibility
I’ve seen traders who were “right” on direction but blew their accounts by overleveraging.
And I’ve seen others who were wrong on their first two trades — but adjusted quickly, cut losses, and ended green overall in the end.
This is what separates pros from opinionated amateurs.
________________________________________
📍 A Real Example: Today’s Gold Analysis
Let’s take a real, current example — my own Gold analysis from this morning.
I said:
• Short-term, Gold could go to 3450
• Long-term, the breakout from the weekly triangle could take us to 3800
Sounds “right,” right? But let’s dissect it:
Short-term:
✅ I identified 3370 as support
If I buy there, I also have a clear invalidation level (below 3350)
If it breaks that and hits my stop?
👉 I reassess — because being “right” means nothing if the trade setup is invalidated
And no, it doesn’t help my PnL if Gold eventually reaches 3450 after taking me out.
Long-term:
✅ The weekly chart shows a symmetrical triangle
Yes — if we break above, the measured move targets 3800
But…
If Gold goes below 3300, that long-term scenario is invalidated too.
And even worse — if Gold trades sideways between 3000 and 3500 for the next 5 years and finally hits 3800 in 2030, that “correct call” is worth nothing.
You can't build a career on "eventually I was right."
You need precision, timing, risk management, and the ability to say:
“This setup is no longer valid. I’m out.”
________________________________________
💡 The Shift That Changed Everything
It took me years to realize this.
The day I stopped needing to be right was the day I started making consistent money.
I stopped arguing with the market.
I stopped holding losers out of pride.
I stopped needing to "prove" anything to anyone — especially not myself.
Now, my job is simple:
• Protect capital
• Execute with discipline
• Let the edge do its job
• And never fall in love with my opinion
________________________________________
✅ Final Thought – Let Go of Being Right
If you’re still stuck in the “I knew it” mindset — let it go.
It’s not helping you. It’s costing you.
The best traders lose small, admit mistakes fast, and stay emotionally neutral.
The worst traders hold on to “being right” while their account burns.
The market doesn’t owe you respect.
It doesn’t care if you called the top, bottom, or middle.
It pays the ones who trade objectively, flexibly, and without ego.
After almost 25 years, this is the one thing I wish I had learned sooner:
Don’t try to win an argument with the market.
Just get paid.
Disclosure: I am part of TradeNation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analyses and educational articles.
Stop Watching Your Trades All Day!How to Break Free from Screen Addiction and Become a More Focused, Profitable Trader
Have you ever found yourself glued to your screens, watching every tick of the market, feeling your stress levels spike with every price fluctuation?
If so, you’re not alone.
Most traders, at some point, fall into this trap.
It feels productive, even necessary, to monitor your trades constantly.
But the reality is that it’s one of the most damaging habits you can develop.
In this article, I’ll show you why this behavior is hurting your trading results and how to break free from it, so you can trade smarter, stress less, and live more.
________________________________________
⚠️ The Cortisol Trap – Why Watching Every Tick is a Psychological Minefield
Every time you check the market and see a fluctuation in your trades, your body releases cortisol, the primary stress hormone.
While cortisol is useful in fight-or-flight situations (like dodging a car on the street), it’s terrible for trading.
Here’s why:
• Cortisol reduces rational thinking – It pushes your brain into reactive mode, not analytical mode.
• It triggers impulsivity – You become more likely to close winning trades too early or move your stop loss in desperation.
• It burns your mental energy – Leaving you drained, unfocused, and emotionally volatile.
Simply put: Too much screen time = too much cortisol = bad trading decisions.
If you want to win consistently, you need to break this cycle.
________________________________________
🎯 Distraction from Higher Priorities – Why Trading Should Be a Part of Life, Not All of It
Trading is meant to give you freedom — not steal it.
Yet, too many traders become slaves to the screen, obsessing over every tick.
But here’s the truth:
You don’t need to be in front of your screen all day to be a great trader.
In fact, doing so can rob you of the mental clarity and emotional balance needed for high-quality trading.
When you step away from the charts:
• You give your strategic mind time to work,
• You focus on other important aspects of life — family, health, personal growth,
• You develop a longer-term perspective on the market, which is crucial for real success.
Balance is the key to sustainable success, both in trading and in life.
________________________________________
✅ 3 Benefits of Breaking Free from Screen Addiction
✅ Benefit #1: Better Decision-Making
When you stop reacting to every tick:
• You make calmer, more rational trading decisions,
• You avoid low-probability setups and revenge trading,
• You focus on quality over quantity.
Instead of jumping on every tiny move, you become a strategic sniper in the market, waiting for high-probability setups.
________________________________________
🧘 Benefit #2: Improved Quality of Life
Life is not just about trading.
Reducing screen time frees you up for other meaningful activities:
• Exercise,
• Hobbies,
• Time with family and friends.
A well-rounded life supports better mental health, which, in turn, improves your trading performance.
Remember, a clear mind is a profitable mind.
________________________________________
⏱️ Benefit #3: Increased Productivity
Believe it or not, less screen time = more productivity.
Why?
Because you’ll:
• Spend less time reacting and more time preparing,
• Conserve your mental energy for important decisions,
• Create time for deep market analysis instead of random impulse trades.
This disciplined approach leads to better trading outcomes over time.
________________________________________
🔔 How to Trade with Less Screen Time – 3 Practical Step s
🔔 Action #1: Use Alerts Wisely
Instead of staring at charts all day, let technology work for you:
• Set alerts at key price levels,
• Use trading apps to get notifications when your levels are hit,
• Let the market come to you — not the other way around.
Example: If you want to buy Gold at 3200 support, set an alert and go for a walk.
You’ll be notified when price approaches, so you can act, not react.
________________________________________
📅 Action #2: Create a Balanced Schedule
Build a daily routine that includes more than just trading:
• Morning exercise,
• Reading or journaling,
• Spending time with loved ones,
• Working on long-term goals.
When you’re mentally balanced, you’ll trade better and more profitably.
________________________________________
📊 Action #3: Review Your Trading Plan Regularly
Spend time reviewing your trades instead of watching them:
• Look at your journal,
• Analyze your stats,
• Identify mistakes and strengths.
This should only take once a week — and it’s far more valuable than hours of pointless screen time.
________________________________________
🧠 Final Words
As the saying goes:
“Sometimes, less is more.”
Stop watching your trades all day.
Lower your stress, regain your focus, and remember why you started trading in the first place — to build wealth and live freely, not to become a slave to the screen.
Trade well.
Build wealth.
Live fully. 🚀
Disclosure: I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analyses and educational articles.
Serios Traders Trade Scenarios, Not Certaintes...If you only post on TradingView, you're lucky — moderation keeps discussions professional.
But on other platforms, especially when you say the crypto market will fall, hate often knows no limits.
Why?
Because most people still confuse trading with cheering for their favorite coins.
The truth is simple:
👉 Serious traders don't operate based on certainties. They work with living, flexible scenarios.
In today's educational post, I'll show you exactly how that mindset works — using a real trade I opened on Solana (SOL).
________________________________________
The Trading Setup:
Here’s the basic setup I’m working with:
• First sell: Solana @ 150
SL (stop-loss): 175
TP (take-profit): 100
• Second sell: Solana @ 160
SL: 175
TP: 100
I won’t detail here why I believe the crypto market hasn’t reversed yet — that was already explained in a previous analysis.
Today, the focus is how I prepare my mind for different outcomes, not sticking to a fixed idea.
________________________________________
The Main Scenarios:
Scenario 1 – The Pessimistic One
The first thing I assume when opening any position is that it could fail.
In the worst case: Solana fills the second sell at 160 and goes straight to my stop-loss at 175.
✅ This is planned for. No drama, no surprise. ( Explained in detail in yesterday's educational post )
________________________________________
Scenario 2 – Pessimistic but Manageable
Solana fills the second sell at 160, then fluctuates between my entries and around 165.
If I judge that it’s accumulation, not distribution, I will close the trade early, taking a small loss or at breakeven.
________________________________________
Scenario 3 – Mini-Optimistic
Solana doesn’t even trigger the second sell.
It starts to drop, but stalls around 120-125, an important support zone as we all saw lately.
✅ In this case, I secure the profit without waiting stubbornly for the 100 target.
Important tactical adjustment:
If Solana drops below 145 (a support level I monitor), I plan to remove the second sell and adjust the stop-loss on the initial position.
________________________________________
Scenario 4 – Moderately Optimistic
Solana doesn’t fill the second order and drops cleanly to the 100 target.
✅ Full win, perfect scenario for the first trade
________________________________________
Scenario 5 – Optimistic but Flexible
Solana fills the second sell at 160, then drops but gets stuck at 120-125(support that we spoken about) instead of reaching 100.
✅ Again, the plan is to close manually at support, taking solid profit instead of being greedy.
________________________________________
Scenario 6 – The Best Scenario
Solana fills both sell orders and cleanly hits the 100 target.
✅ Maximum reward.
________________________________________
Why This Matters:
Scenarios Keep You Rational. Certainties Make You Fragile.
In trading, it's never about being "right" or "wrong."
It's about having a clear plan for multiple outcomes.
By thinking in terms of scenarios:
• You're not emotionally attached to a single result.
• You're prepared for losses and quick to secure wins.
• You're flexible enough to adapt when new information appears.
Meanwhile, traders who operate on certainties?
They get blindsided, frustrated, and emotional every time the market doesn’t do exactly what they expected.
👉 Trading scenarios = trading professionally.
👉 Trading certainties = gambling with emotions.
Plan your scenarios, manage your risk, and stay calm. That's the trader's way. 🚀
No Setup, No Trade: Staying Sane in Gold’s MadnessToday, Gold hit $3500.
And while that may not sound like a shock on its own, what is unprecedented is the fact that in the past 10 days, Gold has climbed 5,000 pips.
That's not a normal rally.
That’s a vertical explosion.
And yes — it is looking “overextended”, but so it dit at 3300...
But then it went up another 2000 pips.
Will it drop? Probably — and hard.
When? No one knows.
Will it rise another 2000 pips before that?
Again, no one knows.
This is where most traders lose themselves — not because they don’t have tools, but because they pretend to know what’s unknowable.
________________________________________
🎯 The Strongest Skill: Admit When You Don’t Know
Every trader wants clarity.
But real professionals know when they’ve entered the fog.
The market is not obligated to give you structure just because you want to trade.
And the worst trades often happen when:
• You think it's overbought (but it keeps going)
• You think it’s due for a correction (but it doesn't care)
• You think it can't go higher (but it does)
This isn’t analysis — it’s wishful thinking.
________________________________________
🧠 Do You Actually Have Edge? Ask Yourself:
1. Do I see a structured setup, or just a reaction to “how far it’s gone”?
2. Can I define my entry, stop, and exit in advance?
3. Am I trading because I have a plan — or because it feels like a top (or simply have nothing better to do)?
If you can’t answer these — you don’t have edge.
You’re just guessing with conviction.
________________________________________
✅ The Only Thing That Matters: A Valid Trade
If you’re going to trade this madness, make sure your trade is:
• Planned (with defined risk)
• Repeatable (not emotional)
• Based on structure or volatility patterns
Otherwise, it’s just ego vs. market.
And the market always wins that fight.
________________________________________
🧘♂️ Final Thought: When Things Get Wild, Stay Sane
There’s no shame in stepping aside when things make no sense.
In fact, that’s where the real skill begins.
“Knowing when you don’t know isn’t weakness — it’s your strongest edge.”
So take a breath.
Zoom out.
And wait for the moment when you actually know what you're doing — not just think you do.
________________________________________
And remember:
No setup, no trade. No clarity, no risk. No ego, no drama.
Disclosure: I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analyses and educational articles.
Possible vs. Probable in Trading — Most Traders Ignore ThisOne of the biggest mistakes traders make — especially beginners — is confusing what is possible with what is probable.
This confusion leads to poor decisions, unnecessary risks, and eventually, losses that could have been easily avoided.
Possible and Probable Are NOT the Same Thing
Let's make this very clear:
• Possible means it can happen.
• Probable means it is likely to happen, based on evidence and context.
In life, many things are possible — but that doesn’t mean we should live our lives preparing for each possible (and often extreme) event.
To give you a real-life example: it’s possible that something falls from the roof top of a builing and hits you while shopping and die. Sadly, this actually happened in Romania about a month ago.
But as rare and tragic as it is, it’s not probable. And it definitely doesn’t mean that we should stop going outside, right?
Trading Is a Game of Probabilities, Not Possibilities
When trading, we are not betting on what is possible.
If we did, we would enter trades every time we imagine a price could go higher or lower — and that would be a disaster.
Instead, we are betting on what is probable — based on:
• Technical analysis
• Price action
• Market context
• Volume
• Sentiment
⚠️ Yes, it is always possible for price to go in either direction.
But our edge comes from identifying what is more likely to happen based on the data we have.
Why This Difference Is Crucial for Your Trading Success
✅ Focusing on probabilities means:
• You enter only high-probability setups.
• You manage risk properly because you accept that nothing is 100% sure.
• You avoid chasing trades just because "it’s possible" something happens.
❌ Focusing on possibilities leads to:
• Overtrading
• Emotional decisions
• Hoping instead of following a plan
• Blowing up accounts
Conclusion: Trade Like a Professional — Trade Probabilities
Remember:
"Anything is possible, but not everything is probable."
If you want to survive and thrive in the markets, focus on probabilities — not on fantasies of what could happen.
You are not trading "maybe this happens", you are trading "this is likely to happen, and I’m managing my risk if it doesn’t".
Make this shift in mindset, and you’ll already be ahead of most traders out there.
Googles next Move where to Long next + Wickless Candles Hi in this video I highlight what to look for in the chart to take shorts and where to fill Longs next . In addition to that I provide a small educational idea of looking out for Wickless candles and how they can add value to your analysis . Please like follow share and ask any questions that you have and thankyou for your support
The Right Questions to Ask Before Entering a TradeEvery day, traders—especially beginners—ask the same recurring question:
❓ What do you think Gold will do today? Will it go up or down?
While this seems like a logical question, it’s actually completely wrong and one that no professional trader would ever ask in this way.
Trading is not about predicting the market like a fortune teller. Instead, it's about analyzing price action, managing risk, and executing trades strategically.
So, instead of asking, "Will Gold go up or down?" , a professional trader asks three critical questions before taking any trade.
Let's break them down.
________________________________________
Step 1: Identifying the Right Entry Point
Let’s say you’ve done your analysis, and you believe Gold will drop. That’s great—but that’s just an opinion. What really matters is execution.
🔹 Where do I enter the trade?
Professional traders don’t jump into the market impulsively. They use pending orders instead of market orders to wait for the right price.
If you believe Gold will fall, you shouldn’t just sell at any price. You need to identify a key resistance level where a reversal is likely to happen.
For example:
• If Gold is trading at $2900, and strong resistance is at $2920, a professional trader will set a sell limit order at that resistance level rather than shorting randomly.
This approach ensures that you enter at a strategic point where the probability of success is higher.
________________________________________
Step 2: Setting the Stop Loss
🔹 Where do I place my stop loss?
A trade without a stop loss is just gambling. Managing risk is far more important than being right about market direction.
The key is to determine:
✅ How much risk am I willing to take?
✅ Where is the invalidation level for my trade idea?
For example:
• If you are shorting Gold at $2920, you might place your stop loss at $2935—above a recent high or key technical level.
• This way, if the price moves against you, you have a predefined maximum loss, avoiding emotional decision-making.
Professional traders never risk more than a small percentage of their account on a single trade. Risk management is everything.
________________________________________
Step 3: Setting the Take Profit Target
🔹 Where do I set my take profit, and does the trade make sense in terms of risk/reward?
Before taking any trade, you must ensure that your reward outweighs your risk.
For example:
• If you risk $15 per ounce (short at $2920, stop loss at $2935), your take profit should be at least $30 away (for a 1:2 risk/reward).
• A good target in this case could be $2890 or lower.
This means that for every dollar you risk, you aim to make two dollars—ensuring long-term profitability even if only 40-50% of your trades succeed.
If the trade doesn’t offer a good risk/reward, it’s simply not worth taking.
________________________________________
Conclusion: The “Set and Forget” Mentality
Once you’ve answered these three key questions and placed your trade, the best approach is to let the market do its thing.
✅ Set your entry, stop loss, and take profit.
✅ Follow your trading plan.
✅ Avoid emotional reactions.
Many traders lose money because they constantly interfere with their trades—moving stop losses, closing positions too early, or hesitating to take profits.
Instead, adopt a professional approach: set your trade and let it run.
📌 Final Thought:
The next time you find yourself asking, “Will Gold go up or down today?” , stop and ask yourself:
📊 Where is my entry?
📉 Where is my stop loss?
💰 Where is my take profit, and does the risk/reward make sense?
This is how professional traders think, plan, and execute—and it’s what separates them from amateurs.
👉 What’s your biggest struggle when it comes to executing trades? Let’s discuss in the comments! 🚀
Disclosure: I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analyses and educational articles.
Stepwise Distribution: How "Big Boys" Unload an Asset (Gold Ex.)In financial markets, price movements are not always the result of simple supply and demand dynamics. Large investors—hedge funds, market makers, and institutional traders—use advanced techniques to enter and exit positions without causing drastic market reactions. One such strategy is stepwise distribution, a method through which they gradually sell off assets while the price still appears to be rising.
What Is Stepwise Distribution?
Stepwise distribution is a process where large players liquidate their positions gradually, preventing panic or a sudden price drop. The goal is to attract retail buyers, maintaining the illusion of a bullish trend until all institutional positions are offloaded.
S tages of Stepwise Distribution
1. Markup Phase
- Institutions accumulate the asset at low prices.
- Retail traders are drawn in by the uptrend and start buying.
- The bullish trend is strong, supported by increasing volume.
2. Hidden Distribution
- The price continues rising, but large players begin selling in increments.
- Volume increases, yet price movements become smaller.
- Fake breakouts appear—price breaches a resistance level but quickly reverses.
3. The Final Trap (Bull Trap)
- One last price surge attracts even more retail buyers.
- Smart money finalizes unloading their positions.
- Retail traders get trapped in long positions, expecting the trend to continue.
4. Final Breakdown
- After institutions have fully exited, the price begins to fall.
- Liquidity dries up, leaving retail traders stuck in losing positions.
- The pattern confirms itself as lower highs and lower lows start forming.
________________________________________
Stepwise Distribution in Gold: A Recent Example
In recent days, Gold prices have shown an interesting example of stepwise distribution. While it does not meet every characteristic of a textbook distribution pattern, market dynamics suggest that large players are offloading their positions in a controlled manner.
1. Technical Structure and Market Perception Manipulation
During the last upward leg, support levels were strictly respected, creating the illusion of strong demand. At first glance, this seems like a bullish signal for retail traders. However, in reality:
• Big players temporarily halted selling to avoid triggering panic.
• They maintained the illusion of strong support to attract more buyers.
• Retail traders believed that “smart money” was buying, when in fact institutions were merely waiting for the right moment to finalize distribution.
2. Investor Psychology and How It’s Exploited
Human psychology plays a critical role in stepwise distribution. Here’s how different types of traders react:
• Retail FOMO traders (Fear of Missing Out) – Seeing Gold approach all-time highs, they aggressively enter long positions, ignoring subtle distribution signals.
• Pattern-based traders – Many traders use support levels as buying zones, unaware that these levels are being artificially maintained by institutional traders.
• “Buy the Dip” mentality – Each minor pullback is quickly bought up by retail traders, providing liquidity for large investors to sell more.
3. The Critical Moment: Support Break and Market Panic; Friday's drop
Eventually, after the distribution is complete, the “strong” support level suddenly breaks. What happens next?
• Retail traders’ stop-losses are triggered, accelerating the decline.
• A lack of real demand – All buyers have already been absorbed, leaving no liquidity to sustain the price.
• Widespread panic – Retail traders who bought during the final surge now start selling at a loss, reinforcing the downward move.
Conclusion:
Stepwise distribution is not just a technical pattern—it’s a psychological and strategic market operation. In the case of Gold, we observed a controlled distribution where smart money avoided causing panic until they had fully offloaded their positions.
If you learn to recognize these signals, you can avoid market traps and gain a better understanding of how large investors maximize their profits while retail traders are left with losing positions.
Disclosure: I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analyses and educational articles.
Gold- To trade or not to trade? High risk environment!!!!!Gold has been on an incredible run, with seven consecutive green weeks and the last three marking all-time highs.
While this might seem like a strong bullish signal, traders must exercise caution. Markets that extend too far in one direction can become unstable, leading to sharp corrections. Whether you're trading TRADENATION:XAUUSD or any other asset, it's crucial to evaluate whether it's the right time to enter a trade—or if it's wiser to stay on the sidelines.
The Dilemma: To Trade or Not to Trade?
One of the biggest mistakes traders make is feeling compelled to be in the market at all times. Trading is not about always having a position but about making high-probability trades at the right time. As the saying goes, "Cash is also a position."
Before entering a trade, ask yourself:
✅ Is the market offering a clear setup?
✅ Are you trading with the trend or trying to catch tops and bottoms?
✅ Does the risk-reward ratio justify the trade?
✅ Are you trading based on logic or emotion?
If you cannot confidently answer these questions, it might be best to wait for a better opportunity.
Why Trading Gold Requires Extra Caution These Days
1️⃣ Extended Rallies Increase Risk
Gold's extended rally means that the market has already moved significantly higher. While it can still go higher, the risk of a pullback increases with every new high. Jumping in late can result in getting caught in a correction.
2️⃣ Market Sentiment is Overheated
When everyone is overly bullish, smart money (institutions and large traders) often starts taking profits. This can lead to sharp sell-offs that wipe out late buyers.
3️⃣ Volatility Can Be Brutal
Gold is known for its large price swings on highs.
If you’re not careful with position sizing and stop losses, you could see your account take a serious hit.
When Should You Consider Trading?
- Look for pullbacks instead of chasing highs – Buying Gold after a reasonable correction is a better approach than buying at extreme levels.
- Wait for price action confirmation – Pin bars, inside bars, or breakouts from consolidation areas can offer better risk-reward opportunities.
- Ensure a favorable risk-reward ratio – A trade should offer at least a 1:2 risk-reward ratio to be worth the risk.
- Align with strong technical levels – Key support zones (e.g., 50-day moving average, Fibonacci retracements, horizontal levels) can provide safer entry points.
Conclusion: Patience Pays in Trading
There’s no need to rush into trades just because a market is moving. Many traders lose money by trying to force trades when conditions are not favorable . Sometimes, the best trade is no trade at all.
Gold’s extended rally calls for extra caution. If you're looking to trade it, wait for a healthy pullback, strong price action confirmation, and proper risk management before entering. Otherwise, staying on the sidelines and waiting for a better setup might be the smartest move.
Disclosure: I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analyses and educational articles.
Stockholm Syndrome in Crypto Trading: Why We Stay LoyalLet’s be honest: altcoins haven’t been performing as well as many would like.
As I’ve started pointing this out through posts and videos, I’ve received a fair share of criticism. Whenever I mention the possibility of a market decline, I’m met with hate, while others who claim the market is heading to the moon are celebrated.
What’s baffling is that no one seems to ask, “Hey, you’ve been saying ‘altcoin season’ is coming for a year, yet we’re still stuck around the same prices. What’s going on?”
This got me thinking: Could this be a form of Stockholm Syndrome in trading?
________________________________________
What is Stockholm Syndrome in Trading?
Stockholm Syndrome is a psychological phenomenon where hostages develop positive feelings towards their captors. In trading, it’s a bit like this: traders grow emotionally attached to a losing market, even when all signs point to the fact that things aren’t going well.
Instead of cutting losses and accepting reality, they keep holding on, hoping things will change – just like a hostage hoping for their captor's kindness.
In trading, this manifests as traders continuing to support a market (like coins or certain stocks) that isn’t performing, even when the evidence suggests it’s time to move on.
They become attached to the idea that a specific asset will turn around and deliver massive profits – even when the price action doesn’t back that up.
________________________________________
The Comfort of Familiarity
Many traders are caught in the cycle of constant hope and “what ifs.” It’s much easier to stay attached to the narrative that specific coins will eventually “take off” than to admit that their portfolios might be stuck sideways or even bear market.
It's also easy to get drawn into the excitement of “moonshots” and grand promises of big returns. The altcoin season, the bull run, the new innovations – these ideas are comforting, even when the market isn’t cooperating.
But here’s the catch: sticking with a market that’s not performing well out of loyalty is dangerous. It stops you from adapting, from making the necessary moves to protect your capital, and from taking advantage of more promising opportunities elsewhere.
________________________________________
The Reality of the Market
Altcoins have been on a rollercoaster. The hope for altcoin season has been building up for over a year now, yet many traders are still facing stagnant or even declining prices. When faced with this reality, we often see two types of responses:
1. The Blind Optimist:
Some traders will continue to hold and buy into altcoins, even when it’s clear the market isn’t moving in their favor. They believe that the next big move is just around the corner, and they refuse to let go of the dream.
2. The Critic:
Others, like me, will point out the slow or negative price action, urging caution and suggesting that a pullback or continued consolidation is more likely. But when we do, we’re met with anger, disbelief, or even accusations of “fear-mongering.”
It’s frustrating to see those who remain hopeful get so emotionally attached to a failing asset, while others who try to see things more clearly get met with hostility.
________________________________________
The Dangers of Stockholm Syndrome in Trading
When traders fall into this “Stockholm Syndrome,” they stop questioning their strategies and beliefs. They become too emotionally involved with a market that isn’t giving them the results they want.
This prevents them from making the tough decisions they need to make to protect their portfolios – whether that’s cutting losses or re-allocating capital to more promising assets.
It’s also a trap that keeps you stuck in an echo chamber of hope and denial, rather than facing the market with logic and clear-headed analysis.
The longer you stay loyal to an asset that’s underperforming, the more you risk watching your portfolio sink further.
________________________________________
Breaking Free: A Rational Approach to Trading
The key to successful trading is learning to let go of emotional attachment. Don’t hold onto an asset simply because you’ve been told it will perform or because you’ve invested a lot of time and money into it.
Here are a few ways to break free from the Stockholm Syndrome in trading:
1. Focus on the facts:
Look at the actual price action and market conditions, not the narrative you’ve built around it. If the market isn’t moving, don’t force a belief that it will soon.
2. Admit when it’s time to move on:
It’s not about being right or wrong – it’s about protecting your capital. If an asset isn’t performing, consider cutting your losses and finding new opportunities that align with your trading strategy.
3. Stay flexible:
The market is dynamic, and you need to be able to adjust your strategy based on current conditions. Don’t get stuck in a “one-size-fits-all” approach.
4. Let go of the need to be loyal:
Trading isn’t about loyalty; it’s about profits and risk management. Sometimes, moving on is the best decision for your financial health.
________________________________________
Conclusion
If you’ve been stuck in the cycle of hoping that altcoins will suddenly surge, or waiting for the long-awaited altcoin season, it might be time to reconsider your approach. It’s important to recognize when you’re emotionally attached to a market that isn’t performing, and break free from that attachment.
By focusing on logical analysis, cutting losses when necessary, and staying flexible in your approach, you can avoid the dangers of Stockholm Syndrome in trading and move towards more profitable opportunities.
Remember: Trading isn’t about loyalty to a coin or a narrative – it’s about making smart, objective decisions that will help you grow your capital.
Mastering 2025 in Trading: Dive into Psychological PreparationThe year 2025 has well begun, and while many traders may have set goals and plans, the true challenge lies in executing them with consistency and mental clarity.
The markets are already moving, and it’s crucial to recalibrate and solidify your psychological foundation to thrive this year.
Let’s explore seven advanced strategies to mentally prime yourself for trading success, with actionable insights to implement immediately.
________________________________________
1. Conduct a Comprehensive Annual Review
Although the calendar has turned, reviewing your 2024 performance is still invaluable for shaping your 2025 approach.
• Steps to Take:
o Evaluate Performance: Analyze trades from 2024 to identify patterns, strengths, and areas needing improvement. Reflect on both technical execution and emotional responses.
o Analyze Metrics: Beyond win rates, consider risk-reward ratios, maximum drawdowns, and adherence to your trading plan. Did you manage risk effectively? Were you disciplined in execution?
o Adjust Accordingly: Use these insights to adapt your strategy. For instance, if you performed better in trending markets, focus on those setups this year.
• Advanced Tip: Take note of how you handled different market conditions—such as high volatility versus range-bound markets—and create specific strategies for handling similar scenarios in 2025.
________________________________________
2. Develop Mental Toughness
The start of a new year often brings heightened emotions—excitement, pressure, or even lingering frustration from the previous year. Mental toughness is essential for maintaining discipline and objectivity.
• Strategies for Resilience:
o Daily Visualization: Spend five minutes each morning visualizing how you’ll respond to various scenarios (e.g., unexpected losses or sudden market spikes).
o Emotion Tracking: Alongside your trading journal, log your emotions before, during, and after trades. This will reveal emotional triggers that may affect decision-making.
• Advanced Tip: Practice reframing setbacks. Instead of viewing a loss as failure, see it as feedback. Develop a personal mantra, such as "Every trade is a lesson," to maintain a growth mindset.
________________________________________
3. Establish a Pre-Trading Routine
Consistency is key, and a structured pre-trading routine can help you start each session with focus and clarity.
• Key Elements of an Advanced Routine:
o Market Context Review: Assess broader market narratives, such as macroeconomic events, sector performance, or sentiment shifts, to understand the trading landscape.
o Refinement of Strategy: Define specific setups you’re looking for and remind yourself of your risk parameters.
o Mindfulness Practice: Spend five minutes meditating or practicing controlled breathing to center yourself before the trading session.
• Advanced Tip: Include a quick "mental rehearsal" of your trading plan. Imagine executing trades calmly and sticking to your rules, even in volatile conditions.
________________________________________
4. Set Specific, Measurable Goals
With the year already started, it’s important to focus on actionable goals that emphasize process over outcomes.
• Process-Oriented Goals:
o Instead of vague profit targets (e.g., "earn 20% this year"), focus on measurable habits, such as "review every trade for compliance with my plan."
o Break annual goals into quarterly, monthly, or weekly objectives to maintain momentum.
• Advanced Tip: Use a habit tracker or performance dashboard to monitor your adherence to rules, emotional discipline, and progress toward milestones. Adjust goals based on your evolving performance.
________________________________________
5. Create a Structured Trading Plan
Your trading plan isn’t static—it should evolve as you gain insights and adapt to market conditions. Starting the year with a clear, structured plan is vital.
• Enhancements for 2025:
o Adapt to Volatility: Assess the first 20 days of trading this year to gauge volatility and adjust your risk parameters if needed.
o Scenario Planning: Incorporate contingency plans for unexpected events, such as black swan market moves.
• Advanced Tip: Review and tweak your trading plan bi-weekly during the first quarter to ensure it aligns with both market realities and your performance.
________________________________________
6. Balance Information Intake
In today’s information-rich world, traders must strike a balance between staying informed and avoiding information overload.
• Steps to Filter Information:
o Set Boundaries: Allocate specific times to consume news and stick to them. Avoid constant updates, which can lead to emotional decision-making.
o Focus on Sources: Select a handful of reliable news outlets that align with your trading focus, and ignore sensationalist or irrelevant content.
• Advanced Tip: Use AI tools or curated platforms to filter market-relevant data. For example, set alerts for key economic releases instead of scrolling through endless feeds.
________________________________________
7. Embrace Continuous Learning
The beginning of the year is the perfect time to commit to self-improvement, not just in strategy but also in trading psychology.
• Actionable Learning Framework:
o Daily Microlearning: Dedicate 10–15 minutes daily to reading, watching videos, or studying advanced topics such as behavioral finance or quantitative analysis.
o Weekly Reflection: Use weekends to review your trading journal, analyze mistakes, and refine your approach.
o Community Engagement: Participate in forums, webinars, or mentorship programs for shared insights and accountability.
• Advanced Tip: Focus on specific weaknesses identified in your annual review. For example, if exiting trades too early was an issue in 2024, study advanced exit strategies and backtest them.
________________________________________
Conclusion
The markets have already started testing traders in 2025, but it’s never too late to fortify your psychological and strategic foundation. By implementing these seven advanced techniques, you can navigate the challenges and seize the opportunities that the year presents.
Remember, trading success is a marathon, not a sprint. Begin the year with a disciplined and resilient approach, and you’ll be well-positioned for sustainable growth. Here’s to a prosperous and fulfilling trading journey in 2025!
The Four Horsemen of Trading: Overcoming the Emotional Pitfalls
Investing and trading are often viewed as purely logical activities. Many assume that success in the markets depends solely on mastering data, charts, and economic theories. However, the reality is that emotions frequently play an outsized role in influencing decisions, often to the detriment of traders. In his 1994 classic I nvest Like the Best, James O'Shaughnessy described the four common psychological pitfalls that derail investors: fear, greed, hope, and ignorance. These "Four Horsemen of the Investment Apocalypse" are as relevant today as ever, especially in the new market conditions and uncertanty.
Let’s explore each of these emotional pitfalls in detail, understand their impact, and discuss strategies to overcome them.
________________________________________
1. Fear: The Paralyzing Grip of Uncertainty
Fear is perhaps the most immediate and visceral emotion traders experience. It manifests in two primary ways: the fear of losing money and the fear of missing out.
Fear of Losing Money
This fear often causes traders to exit positions prematurely, robbing them of potential profits. For instance, a trader may close a trade the moment it moves slightly against them, even if their analysis indicates a high likelihood of eventual success. This behavior stems from a deep-seated aversion to loss, amplified by the memory of past trading failures.
Fear of Missing Out
FOMO drives traders to enter markets impulsively, often at inopportune times. Seeing a rapid price increase can tempt traders to jump in without proper analysis, only to be caught in a reversal.
How to Overcome Fear
• Develop a Plan: A solid trading plan with predefined entry, exit, and stop-loss levels helps remove the uncertainty that fuels fear.
• Focus on the Process: Shift your attention from individual trade outcomes to the consistency of following your strategy.
• Accept Losses as Part of Trading: View losses as a natural and manageable aspect of trading rather than personal failures.
________________________________________
2. Greed: The Endless Pursuit of More
Greed is the counterbalance to fear. It drives traders to seek excessive gains, often at the expense of sound decision-making. Greed clouds judgment, leading to overleveraging, chasing unrealistic profits, and deviating from planned strategies.
Examples of Greed in Trading
• Moving profit targets further as a trade approaches them, hoping for larger gains.
• Ignoring exit signals in anticipation of an extended rally, only to watch profits evaporate.
• Taking on larger positions than risk management rules would typically allow, driven by overconfidence.
How to Overcome Greed
• Set Realistic Goals: Establish achievable profit targets based on market conditions and your trading strategy.
• Stick to Risk Management Rules: Never risk more than a predetermined percentage of your trading account on a single trade.
• Practice Gratitude: Recognize and appreciate the profits you’ve made instead of constantly chasing more.
________________________________________
3. Hope: Holding Onto Losing Trades
Hope is a double-edged sword in trading. While optimism can keep traders motivated, unchecked hope often leads to poor decisions. Traders driven by hope may hold onto losing positions far longer than they should, convinced that the market will eventually "come back." This refusal to cut losses can result in significant drawdowns.
The Danger of Hope
Hope clouds rational judgment. Instead of objectively assessing the market’s signals, hopeful traders anchor their decisions on a desired outcome. This emotional attachment to trades often leads to ignoring stop-loss levels or adding to losing positions, compounding the damage.
How to Overcome Hope
• Use Stop-Loss Orders: Always set stop-loss levels when entering a trade and stick to them without exception.
• Detach Emotionally from Trades: View trades as probabilities, not certainties. Focus on long-term outcomes rather than individual results.
• Review Performance Regularly: Regularly assess your trading performance to identify patterns of hopeful decision-making and correct them.
________________________________________
4. Ignorance: Trading Without Knowledge
Ignorance is the foundational pitfall that enables fear, greed, and hope to thrive. A lack of knowledge or preparation often leads traders to make uninformed decisions, increasing the likelihood of costly mistakes.
Manifestations of Ignorance
• Entering trades based on rumors or tips without independent analysis.
• Failing to understand market dynamics, such as how economic events impact prices.
• Overestimating the predictive power of a single indicator or strategy without considering the broader context.
How to Overcome Ignorance
• Invest in Education: Learn about trading strategies, technical analysis, risk management, and market fundamentals.
• Stay Informed: Keep up with economic news, market trends, and industry developments.
• Practice in Simulated Environments: Use demo accounts to refine your strategies and gain experience before risking real capital.
________________________________________
Combating the Four Horsemen: A Holistic Approach
To succeed in trading, you must address all four horsemen simultaneously. Here’s a comprehensive strategy to help you stay disciplined:
1. Create a Detailed Trading Plan: A well-thought-out plan acts as a roadmap, reducing the influence of emotional decisions.
2. Implement Strict Risk Management: Set clear rules for position sizing, stop-loss levels, and profit targets to minimize the impact of fear and greed.
3. Keep a Trading Journal: Record every trade, including the rationale behind it, the emotions you felt, and the outcome. Reviewing this journal helps you identify and correct emotional patterns.
4. Develop Emotional Awareness: Practice mindfulness to recognize when emotions are influencing your decisions, and take a step back when necessary.
5. Seek Continuous Improvement: Trading is a skill that requires ongoing refinement. Stay curious, learn from your mistakes, and adapt to changing market conditions.
________________________________________
Final Thoughts
The Four Horsemen—fear, greed, hope, and ignorance—are ever-present challenges for traders. By recognizing these emotional pitfalls and implementing strategies to mitigate their impact, you can make more disciplined and objective decisions. Success in trading is not just about mastering the markets; it’s about mastering yourself. Approach each trade with preparation, detachment, and a commitment to continuous learning, and you’ll be well on your way to conquering these formidable adversaries.
The TrumpCoin Craze: What’s Really Going On?Yesterday, something truly bizarre happened in the world of crypto. Donald Trump—yes, that Donald Trump—launched his very own cryptocurrency, TrumpCoin ($TRUMP).
At first, like everyone else, I thought his account had been hacked.
I mean, launching a meme coin just days before his presidential inauguration? Come on...
But nope, it’s 100% real. Verified.
Like many others, I got curious and, let’s face it, greedy. So, I bought in. The result? I cashed out at a nice 3x profit, enough for a fun night out. But before we dive into the crazy market activity, let me clarify a couple of things:
- I’m not a Trump fan. This isn’t about politics.
- I don’t think this is a rug pull, at least not intentionally .
It seems more like someone who doesn’t fully understand how crypto works decided to jump in.
A Brief Timeline of Chaos
TrumpCoin was announced on his social platforms, including Truth Social and X (formerly Twitter). Initially, everyone thought it was fake news. I mean, a meme coin with his name on it? Right before inauguration day? It screams “scam.” But soon after, major crypto news outlets confirmed its legitimacy.
And then the madness began. Within hours:
- Market cap: Over $14 billion at the time of writing(and climbing).
- Trading volume: A jaw-dropping $11 billion in just one day.
- Price swings: The coin hit a high of $3.30 before dipping below $1.50 and now is above $4.
Trump’s company, CIC Digital LLC, reportedly holds 80% of the coin supply, making this a financial windfall for him—even if the project crashes.
The Crypto Community Splits
This move has divided the crypto space. On one hand, you have people who are treating $TRUMP like any other speculative asset. ( Hi, that’s me! )
On the other, there are folks who see it as a statement of loyalty to Trump. Then there’s a third group—the skeptics—who warn that this could end in disaster.
The real problem? Newbies are piling in without understanding what they’re doing. The hype is pulling in people who don’t know a rug pull from a blockchain. They’re buying and buying, hoping to ride the wave, and are likely to get burned when the bubble bursts.
Is This a Rug Pull?
Let’s address the elephant in the room. With 80% of the supply in Trump’s control, the setup raises eyebrows. But is this an intentional scam? Probably not. If anything, this feels more like a PR stunt gone wild—a way to cash in on his fame and make a splash before returning to the White House.
That said, the outcome could still be the same. At some point, the hype will die, the price will tank, and many will lose money. The bigger it gets, the harder it’ll fall.
My Take: Enjoy the Ride, but Be Careful
TrumpCoin is the epitome of crypto’s wild side: volatile, unpredictable, and more about hype than substance. If you’re diving in, know what you’re getting into. For me, it was a quick trade—buy low, sell high, and get out. But I worry about the inexperienced investors who are holding on, hoping for it to hit $10, $20, or even higher.
So, here’s my advice:
Don’t invest more than you can afford to lose.
Take profits while you can.
Remember, just because something is popular doesn’t mean it’s sustainable.
Whether $TRUMP reaches a $25 billion, $50 billion market cap or crashes spectacularly, one thing’s for sure—it’s going to be one heck of a ride.
Stay safe out there, and happy trading!
Lucky vs. Repeatability: A Key Insight for Smarter TradingTrading is a journey, one filled with highs, lows, and a constant drive to improve.
Recently, I came across an idea on Podcast that truly resonated with me: the concept of luck versus repeatability.
This distinction is critical—it’s the difference between chasing short-term gains that may never happen again and developing a strategy that can deliver consistent results over time. Let me explain.
The Role of Luck: Lessons from the 2017 ICO Boom
Think back to 2017, the golden age of initial coin offerings (ICOs). When a new crypto token launched, there was a rush to buy it, often driving the price up by 10x, 50x, or even 100x in a matter of days.
For many, this was a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity to turn small investments into life-changing wealth.
But what happened next?
That strategy no longer works today. The sheer number of tokens being created—thousands daily—means money is now spread too thin for any single token to experience those explosive gains. What worked in 2017 relied on luck, not on a repeatable edge in the market.
Luck is a fascinating aspect of trading. It can make you rich once, but without the skills to preserve and grow that wealth, it often fades away as quickly as it appeared.
Repeatability: Why Market Cycles Matter
Now let’s contrast this with something far more enduring: market cycles.
Markets have always oscillated between fear and greed.
During times of greed, prices often surge beyond their intrinsic value.
Conversely, fear can drive prices below their true value. These cycles aren’t random—they’re rooted in human psychology and have been evident for decades.
For example, during bull markets, optimism often pushes valuations to unsustainable levels. Then, a sudden shock—be it economic, political, or otherwise—triggers a wave of fear, and the cycle reverses.
This ebb and flow have happened in the past, and will likely continue into the future.
This is what makes market cycles repeatable. Unlike luck, which depends on being in the right place at the right time, repeatability allows you to build a foundation for sustainable success.
Compounding: The Key to Long-Term Growth
Once you adopt a repeatable trading strategy, you unlock the power of compounding. Even with a modest starting capital, consistent returns can lead to significant growth over time. The beauty of compounding lies in its exponential nature—small gains, when reinvested, can snowball into substantial wealth.
This doesn’t happen overnight, but that’s the point. Repeatable strategies thrive on patience and discipline, allowing you to grow your account steadily and responsibly.
A Common Mistake in Pullback Trading
Let’s take a practical example: pullback trading.
Many traders focus on waiting for the price to re-test a key level, like previous resistance that could turn into support. While this approach makes sense in theory, the market doesn’t always play by the rules. Prices often fail to re-test those levels, continuing their move without offering the ideal entry point.
The solution? Plan for multiple scenarios. Understand that pullbacks can vary in depth and structure, and be prepared to adapt. Flexibility is key when applying any repeatable strategy.
A Thought to Keep in Mind
One of the most liberating truths about trading is this: the market doesn’t care about you. It doesn’t know your goals, your dreams, or your trades. Losses aren’t personal—they’re just part of the game.
The real question is how you respond to them. Each loss is an opportunity to reflect, learn, and refine your approach. Over time, this process turns a good strategy into a great one.
Final Thoughts
As traders, we’re constantly faced with choices. Should we chase the next big thing, hoping for a stroke of luck? Or should we focus on developing strategies grounded in repeatable principles?
For me, the answer is clear. While luck may occasionally play a role, it’s the repeatable strategies—those built on solid foundations—that lead to lasting success.
The next time you evaluate a trading approach, ask yourself: Is this lucky, or is it repeatable? The answer might just reshape the way you trade.
The Hardest Part About Trading Isn't The Charts-Its Your MindWhen I first started trading, I thought the key to success was all about the strategy. If I could just figure out the right indicators or master technical analysis, I’d be unstoppable.
But the truth hit me hard. I wasn’t losing because I didn’t understand the charts—I was losing because I didn’t understand myself.
Here’s how I learned that the biggest battle in trading isn’t with the market—it’s with your own mind.
Lesson 1: Stop Obsessing Over Results
I used to get way too caught up in the outcome of every single trade. A win would make me feel on top of the world, but a loss? That would send me into a spiral. I’d overanalyze, doubt myself, and sometimes even swear I was done trading altogether.
One day, I realized I was focusing on the wrong thing. Instead of asking, “Did I win or lose?” I started asking, “Did I follow my plan?”
That simple shift changed everything for me. I started measuring success by how consistent I was, not by whether every trade was a winner. The funny thing? Once I started doing that, the wins came more naturally.
Lesson 2: Losses Aren’t Failures
I’ll never forget the trade that wiped out 30% of my account. It was gut-wrenching. I felt like I’d failed—not just as a trader, but as a person.
It took me a long time to understand that losses are part of trading. Even the best traders take hits. What separates the pros from the rest is how they handle those losses.
Now, instead of beating myself up, I treat losses as a chance to learn. Did I miss something in my analysis? Did I break my rules? Sometimes, the market just didn’t cooperate, and that’s okay.
Lesson 3: Don’t Let Emotions Run the Show
I can’t tell you how many times I’ve let emotions wreck me. Chasing losses, revenge trading, doubling down on bad positions—I’ve done it all. And every single time, it made things worse.
The biggest game-changer for me was journaling my trades. Not just the technical stuff, but how I felt during the trade.
-Was I calm or anxious?
-Was I trading because it was a good setup or because I felt like I had to?
It was eye-opening to see how much my emotions were driving my decisions. Now, if I feel frustrated or off, I don’t even touch the charts. I’d rather miss a trade than make a bad one.
My Biggest Takeaway I Learned
Trading isn’t just about the market—it’s about you. The strategies, the charts, the setups—they’re important, but they’re not enough. You need to master your mind if you want to master the market.
I’m not perfect, and I still have tough days. But every step I’ve taken to manage my emotions, stay consistent, and focus on the process has brought me closer to where I want to be.
If you’re struggling with the mental side of trading, I get it. I’ve been there. Send me a DM or check my profile—I’m happy to share what worked for me and help however I can. You don’t have to do this alone.
Kris/Mindbloome Trading
Trade What You See
How Often Do Professional Traders Actually Trade?One of the biggest misconceptions in trading is the belief that successful traders are constantly active in the market. Many imagine professionals glued to their screens, executing trade after trade, chasing every price movement. The reality is much different. Professional traders focus more on quality than quantity. They understand that in the world of trading, less is often more.
The Pitfalls of Over-Trading
Over-trading is one of the most common reasons traders struggle, particularly beginners. There’s a certain allure to being “in the action,” and it’s easy to confuse frequent trading with productivity. However, every time you take a position, you are exposing your account to risk. Without a solid reason for entering, backed by a clear trading edge, trading becomes nothing more than gambling.
Amateur traders often fall into this trap. They believe that the more they trade, the faster they will achieve their goals. But what they fail to realize is that over-trading often leads to poor decision-making, over-leveraging, and emotional trading—all of which can quickly deplete a trading account.
Professional traders take the opposite approach. They know that the market will always present opportunities, and there’s no need to chase every move. Instead, they focus on patiently waiting for setups that align with their proven strategies, where they have a clear edge. This disciplined approach minimizes unnecessary risk and maximizes profitability over the long term.
The Foundation of Success: Mastering One Strategy
Professional traders don’t rely on luck or randomness to succeed. Their consistency comes from mastering a specific trading strategy. Instead of dabbling in multiple approaches, they dedicate time and effort to understanding and refining one methodology. This gives them the ability to quickly identify high-quality setups that fit their criteria.
For example, some traders specialize in price action trading, focusing on candlestick patterns and market structure to guide their decisions. Others might rely on Elliott Waves or fundamental analysis. The key is that they don’t deviate from their chosen method, and they don’t let market noise distract them.
By sticking to one strategy, professional traders also develop a deep understanding of how it performs under different market conditions. This reduces uncertainty and helps them avoid impulsive trades, which often stem from frustration or fear of missing out (FOMO).
Patience and Discipline: The Cornerstones of Professional Trading
Patience is arguably the most underrated skill in trading. While it’s easy to talk about, it’s much harder to practice, especially for beginners who feel pressured to “do something” whenever the market moves. Professionals, however, are comfortable sitting on the sidelines for extended periods if necessary.
They understand that waiting for the right opportunity is far more valuable than being constantly active. This patience stems from experience and the knowledge that not every market movement is worth trading. Many professionals only trade a few times a week, or even less, because they’re selective about the setups they act on.
Discipline complements patience. It’s one thing to recognize a good trading opportunity, but it’s another to follow through with proper execution. Professional traders have strict plans in place, outlining their entry, stop loss, and target levels. They don’t deviate from these plans, even when emotions or market conditions tempt them to.
This disciplined approach ensures that their trading decisions are consistent and not influenced by short-term emotions or irrational impulses.
Trading Frequency: How Often Do Professionals Trade?
The frequency of trades among professionals varies, but those who achieve consistent success often lean towards less frequent trading. Swing traders, who operate on daily or 4-hour charts, might place only a handful of trades each week or even month. Positional traders take this approach even further, sometimes executing just a few well-considered trades per year.
The common denominator among these traders is their selectivity. They don’t trade for the sake of trading. Instead, every position they take is deliberate, guided by a well-defined setup that aligns with their strategy. For them, trading less frequently doesn’t mean missing out—it means focusing on high-probability opportunities while avoiding unnecessary risks.
One reason professionals favor fewer trades is their preference for higher timeframes. Daily and 4-hour charts provide a clearer, more reliable perspective on the market, filtering out the noise and unpredictability of smaller timeframes. This approach allows them to make informed, calculated decisions and avoid the stress and over-analysis that come with constant market monitoring.
The Power of Quality Over Quantity
One of the most important lessons in trading is that quality matters far more than quantity. Professional traders know this, which is why they prioritize high-probability setups over constant activity.
They view trading as a long-term game, where consistency is the goal. Every trade they take has a clear reason behind it, supported by their strategy and risk management rules. They don’t trade for excitement or to “make up” for losses. Instead, they focus on making the right decisions at the right time.
For aspiring traders, the message is simple: slow down. Don’t fall into the trap of thinking that more trades equal more success. Take the time to master one strategy, be patient for quality setups, and stay disciplined in your execution.
Conclusion
Professional forex trading is about precision, not frequency. By trading less often and focusing on high-quality setups, professionals minimize risk and maximize their chances of success. They’ve learned to embrace patience and discipline, understanding that trading isn’t about chasing every move—it’s about waiting for the right opportunities and making the most of them.
If you’re serious about becoming a successful trader, it’s time to rethink the idea that you need to be constantly active. Take a step back, refine your strategy, and remember: the best traders know when to trade and, just as importantly, when not to.
Pride Comes Before the Fall: A Trading Lesson in HumilityIn trading, as in life, pride can be your undoing. The saying “Pride comes before the fall” holds a profound lesson for traders who let overconfidence cloud their judgment. While confidence is an essential trait for success, excessive pride often leads to reckless decision-making, ignored warnings, and ultimately, significant losses.
This post explores the dangers of pride in trading and how maintaining humility can safeguard your capital and enhance your decision-making process.
The Dangers of Pride in Trading
1. Overconfidence in Winning Streaks
Few things inflate a trader's ego like a winning streak. When every trade seems to go in your favor, it's tempting to believe you've mastered the market. However, markets are dynamic and unforgiving.
- Overconfidence may lead you to take larger positions, abandon risk management strategies, or ignore market signals.
- A single unexpected move can erase gains and even wipe out your account.
2. Refusal to Admit Mistakes
Pride can prevent traders from accepting when a trade idea is wrong. This often results in:
- Holding onto losing trades longer than necessary.
- Averaging down into bad positions, magnifying losses.
- Ignoring stop-loss levels because of a belief that the market will "come back."
3. Chasing "Revenge Trades"
After a loss, pride might push you to recover your losses immediately by doubling down on risk. Revenge trading is driven by emotions rather than logic, often leading to bigger losses.
4. Ignoring the Bigger Picture
Pride can blind traders to critical market realities. Instead of adapting to changing conditions, they stubbornly cling to outdated strategies or refuse to learn from others.
How to Keep Pride in Check
1. Treat Every Trade as a Probability Game
The market doesn't owe you anything, and no strategy guarantees success. Every trade involves risk, and outcomes are influenced by factors beyond your control.
- Focus on executing your strategy consistently rather than trying to "win."
- Acknowledge that losses are a natural part of trading.
2. Stick to a Risk Management Plan
Pride can tempt you to exceed your risk limits. Combat this by:
- Using fixed position sizes relative to your account balance.
- Setting stop-loss levels for every trade and respecting them.
3. Practice Continuous Learning
Markets evolve, and so should you. Humility keeps you open to learning new strategies, techniques, and perspectives.
- Analyze your trades, both wins and losses, to identify areas for improvement.
- Seek mentorship or study market history to gain broader insights.
4. Detach Emotionally from Trades
Acknowledge that a single trade doesn't define you as a trader.
- Avoid tying your self-worth to your trading results.
- Focus on the long-term process rather than short-term outcomes.
Conclusion
Pride is one of the most dangerous emotions a trader can harbor. It clouds judgment, promotes reckless behavior, and blinds you to market realities. Trading is not about proving you're right—it's about staying disciplined, managing risk, and adapting to ever-changing conditions.
Remember, humility is your greatest ally in the market. Stay grounded, respect the risks, and you'll be better equipped to navigate the ups and downs of trading without falling victim to the perils of pride.
Pro Tip: Write this on a sticky note and place it near your trading screen: "The market is always right. My job is to listen, adapt, and act accordingly."
Set-and-Forget Trading: A Path to Consistency and FreedomForex trading often feels like a full-time job, demanding constant attention and endless decision-making. However, the set-and-forget trading strategy offers a structured and stress-free alternative, allowing you to trade confidently while enjoying the freedom to focus on other aspects of life. Here, we’ll refine the essence of this strategy and show how it can lead to consistent, profitable results.
What Is Set-and-Forget Trading?
Set-and-forget trading is a disciplined approach where you analyze the market, identify key levels, place your trades with defined parameters, and step away. This method prevents over-trading, minimizes emotional interference, and fosters a calm, calculated mindset.
This strategy is especially appealing for traders balancing other responsibilities, offering the dual benefit of effective trading and time efficiency.
Mastering Key Market Levels
At the core of set-and-forget trading lies the identification of significant price levels, such as support, resistance, and trendlines. These levels act as your map for setting entries, stop-losses, and profit targets. The precision of your analysis at this stage determines the success of your strategy.
Key levels are not random—they are where the market historically reacts, making them the most probable zones for price movement.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls:
While set-and-forget is a powerful approach, it’s not without its challenges. Overanalyzing after placing your trades can lead to unnecessary adjustments, which defeats the purpose of this strategy. Similarly, setting unrealistic expectations can lead to frustration—accept that no strategy is perfect, and focus on long-term profitability. Finally, proper risk management is non-negotiable . Always adhere to your predefined stop-loss and position-sizing rules to protect your capital.
Placing Trades With Confidence
Once you’ve identified the key levels, craft a clear plan for each trade. Define your entry point, stop-loss, and take-profit levels. Limit orders are the cornerstone of this strategy, ensuring your trades are executed precisely at your chosen levels, even when you’re not actively watching the market.
This planning requires discipline but reduces the risk of hasty, emotionally charged decisions.
The Art of Letting Go
Perhaps the most challenging part of set-and-forget trading is stepping away from the charts after placing your trades. However, this step is crucial for maintaining discipline and avoiding impulsive changes to your strategy. Trust your analysis and let the market unfold naturally.
By walking away, you also protect yourself from overanalyzing minor fluctuations, which can lead to emotional and costly adjustments.
Why This Approach Works
The power of set-and-forget lies in its simplicity and alignment with key trading principles:
Emotional Discipline: By predefining trades, you avoid the temptation to deviate from your plan.
Time Efficiency: Spend less time glued to the screen and more time pursuing other goals.
Consistency: Trading from key levels with a clear plan fosters long-term profitability.
Handling Challenges With Grace
Even with set-and-forget, it’s vital to remain realistic. Not every trade will be a winner, and patience is required. Proper risk management, such as adhering to your stop-loss and avoiding excessive position sizes, ensures that even losses are manageable.
Another benefit of this approach is that when trades at key levels don’t hit their targets, price often rebounds or retraces, providing opportunities to minimize losses or exit at breakeven.
Final Thoughts
Set-and-forget trading is a mindset as much as it is a method. It requires patience, discipline, and trust in your strategy. By focusing on key levels, pre-planning trades, and letting the market work for you, you gain not just trading profits but also mental clarity and freedom.
If you’re ready to simplify your trading and embrace consistency, set-and-forget could be the transformative strategy you’ve been seeking.
Lessons from the Hawk Tuah Meme Coin SagaThe recent collapse of the Hawk Tuah meme coin offers several valuable lessons for crypto investors, particularly regarding the risks associated with celebrity-backed tokens and meme coins. Here's a comprehensive look at the event and its implications:
What Happened?
Haliey Welch, a viral internet personality known as the “Hawk Tuah Girl,” launched her cryptocurrency, HAWK, on the Solana blockchain. Initially, the token skyrocketed in value, reaching a market cap of nearly $490 million within hours. However, the excitement was short-lived as the coin's value plummeted by over 90% shortly after its peak, resulting in massive losses for investors.
Investigations revealed suspicious activity, including a small group of wallets controlling 80-90% of the token's supply. These entities quickly sold their holdings after the price surged, a tactic commonly referred to as a Rug- Pull .
Welch has faced accusations of orchestrating the scheme, although she denies any wrongdoing
Key Takeaways for Investors
1. Avoid Hype-Driven Investments
Meme coins often rely on hype rather than fundamentals. The initial surge in HAWK’s value was fueled by Welch’s popularity and aggressive promotion, which masked its lack of intrinsic value.
2. Beware of Celebrity Endorsements
Celebrities frequently endorse or launch crypto projects, but their involvement doesn't guarantee legitimacy. Past incidents with figures like Kim Kardashian and Floyd Mayweather highlight a recurring pattern of failed celebrity-endorsed tokens
3. Understand the Token’s Structure
The dominance of a few wallets in HAWK’s ecosystem made the token vulnerable to manipulation. Always investigate the tokenomics of a project , including the distribution and control of its supply.
Recognize the Signs of a Rug Pull
- Rapid price surges followed by sharp declines
- Concentrated ownership by insiders or “snipers”
- Lack of a clear use case or roadmap
- Exercise Caution with New Tokens
*Newly launched coins are highly volatile and prone to exploitation. In the case of HAWK, the lack of regulatory oversight compounded the risks
Lessons for Regulators
The Hawk Tuah incident underscores the need for stricter oversight of crypto markets, especially celebrity-backed projects. While decentralized finance (DeFi) promotes inclusivity, its openness can be exploited. Regulators like the SEC are already investigating such cases, which may lead to stricter rules on token launches and promotions
Conclusion
The collapse of the Hawk Tuah coin serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of speculative investments in unregulated markets. While the allure of quick profits can be tempting, due diligence, skepticism of promotional tactics, and an understanding of market mechanics are crucial for navigating the crypto space.
Investors should remember: if something sounds too good to be true, it probably is . For long-term success in crypto, focus on projects with robust fundamentals, transparency, and proven utility.
When Investing Turns into GamblingThe distinction between high-risk investing and gambling is a nuanced topic that draws considerable debate among financial experts and everyday investors alike. At what point does a bold investing strategy transition into a gamble? This question is particularly pertinent as more individuals explore the world of trading, often with little experience or understanding of complex financial instruments.
Understanding Gambling
Gambling, at its core, involves wagering something of value on uncertain events with the hope of attaining a greater reward. The term is rooted in the Old English word ‘gamenian,’ which conveys the idea of playfulness or merriment. While this historical context hints at leisure, modern associations with gambling primarily lean towards casino games and sports betting—activities that often prioritize entertainment over profit.
Legally and socially, gambling is characterized by three fundamental elements: consideration (the wager), chance, and prize. It is primarily the element of chance that fundamentally separates gambling from investing as a disciplined practice.
Read Also:
Characteristics of High-Risk Investing
High-risk investing manifests in various forms and is typically characterized by volatile assets, leveraged positions, and intricate financial tools. Examples include CFDs, options trading, and short-selling. While these strategies can yield impressive returns, they come with heightened risks and the possibility of substantial losses, particularly for those who are inexperienced.
The key difference between gambling and investing generally hinges on skill versus chance. Professional CFD traders may acknowledge the unpredictability involved but can also apply strategic approaches to increase their chances of success. This skill component is often what investors cling to, differentiating their methodical approaches from pure gambling.
Read Also:
Psychological Drivers Behind High-Risk Investing
The psychological dynamics involved in high-risk investing bear significant similarities to gambling behaviors. A prominent factor is the dopamine rush associated with successful trades—an exhilarating feeling that can become addictive. While such responses are often embraced in gambling environments, they must be regulated in investing to prevent detrimental decision-making.
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) also plays a crucial role in driving investors toward risky trades. In our social media-saturated era, tales of sudden wealth can instigate impulsive behaviors, propelling individuals into investments without adequate research or risk assessment.
Overconfidence bias is another pitfall; novice investors may overestimate their ability to navigate markets, often resulting in shallow analysis and misguided decisions. Coupled with loss aversion—the tendency to feel losses more acutely than equivalent gains—these cognitive biases can lead to irrational choices, mirroring behaviors common in problem gambling.
Read Also:
Perception vs. Reality
The interplay between perception and reality complicates the discourse around high-risk investing. Many individuals erroneously equate their financial activities solely with mastery over skill and chance. However, overconfidence can mislead beginners into adopting complex strategies without a robust understanding of the underlying mechanics. While they may perceive their actions as investments, outsiders may recognize them as reliance on sheer luck, categorizing such behaviors as gambling.
Emerging asset classes, like cryptocurrencies, add another layer of complexity. Their relative novelty means that market participants often lack the historical data necessary to inform sophisticated strategies, resulting in some deeming these investments as mere gambling.
The Importance of Self-Awareness
Ultimately, self-awareness emerges as a crucial aspect of distinguishing between high-risk investing and gambling. Understanding personal motivations is vital; the riskiness of an asset alone does not dictate its categorization. Allowing emotions to override a carefully charted financial strategy is indicative of gambling-like behavior. Similarly, employing untested or misunderstood strategies can signal a drift away from genuine investment practices toward a gambling mentality.
Read Also:
Final Thoughts
In the realm of finance, it is essential to maintain a clear bifurcation between calculated investing and haphazard gambling. Self-awareness, comprehensive research, and a disciplined approach to risk management are key to ensuring that individuals engage in sound investment practices, rather than crossing over into the unpredictable territory of gambling. Individuals must strive to understand the nuances of their financial choices, recognizing when the line is blurred and committing to informed decision-making. Only then can they navigate the market landscape with confidence and prudence.
Read Also:
✅ Please share your thoughts about this article in the comments section below and HIT LIKE if you appreciate my post. Don't forget to FOLLOW ME; you will help us a lot with this small contribution.
Trading account types explainedForex trading offers exciting opportunities for individuals at various levels of expertise and risk tolerance. One of the first steps to becoming a successful trader is selecting the right type of trading account. Your choice can significantly impact your experience and success in the market. Below, we explore three common types of trading accounts: Cent Account , Demo Account , and Standard Account , based on their features, suitability, and intended users.
1. Cent Account
Ideal for Beginners with Low Risk and Small Deposits
A Cent Account is specifically designed for new traders or those who wish to minimize financial risks while gaining exposure to live market conditions. With balances measured in cents instead of dollars, this account type allows users to trade real money but on a much smaller scale.
Features:
- Requires only a minimal deposit to get started.
- Allows traders to gain real-world trading experience without the fear of losing large sums of
money.
- Provides an opportunity to test strategies and broker conditions with smaller risks.
Who Should Choose This?
- Beginners looking to transition from demo accounts to live trading.
- Traders testing a new strategy or broker platform without risking significant capital.
2. Demo Account
Ideal for Testing Strategies Without Financial Risk
The Demo Account is a virtual trading account that allows users to practice trading without using real money. It mirrors actual market conditions, enabling traders to understand market mechanics, test strategies, and familiarize themselves with trading platforms.
Features:
- No financial risk since all trading is done with virtual funds.
- Simulates real market movements to provide a realistic trading experience.
- Perfect for refining trading skills and strategies before moving to live accounts.
Who Should Choose This?
- Complete beginners who need to learn the basics of forex trading.
- Traders developing or testing new strategies and indicators in a risk-free environment.
3. Standard Account
For Experienced Traders with Higher Risk Tolerance
The Standard Account is designed for experienced traders who are ready to handle larger trades and higher risks. It operates in full dollar amounts, providing access to the full range of trading opportunities offered by forex brokers.
Features:
- Requires a higher initial deposit compared to Cent Accounts.
- Offers higher profit potential but comes with increased risk.
- Grants access to standard lot sizes and advanced trading tools.
Who Should Choose This?
- Experienced traders with a good understanding of market dynamics and risk management.
- Those seeking higher returns and willing to take on the associated risks.
How to Choose the Right Account
When deciding which trading account to open, consider your experience level, risk tolerance, and trading goals:
- If you're new to forex or prefer to trade with minimal risk, a **Cent Account** is a great starting point.
- If you want to practice without financial consequences, a **Demo Account** is the ideal choice.
- If you're confident in your trading abilities and ready for larger stakes, the **Standard Account** may suit your needs.
Remember, the key to successful trading is starting with the right account and gradually progressing as your skills and confidence improve. Always approach trading with a clear strategy and a focus on risk management.
How to recover after a losing streakEven the most seasoned traders—those with decades of experience—encounter losing streaks. These periods can feel discouraging and lead to emotional turbulence that affects decision-making. However, with the right psychological tools, strategies, and perspective, you can regain confidence and emerge stronger. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate this challenging but normal phase of trading.
Psychological Strategies for Regaining Confidence
Acknowledge and Accept Losses
Losing is part of the trading process. Shifting your mindset to view losses as an inevitable part of a long-term strategy can alleviate emotional distress. Experienced traders understand that no strategy guarantees constant wins, and a losing streak doesn’t necessarily mean the strategy is broken.
Step Back and Reassess
When emotions run high after a streak of losses, taking a break is crucial. This pause helps clear your mind, prevent revenge trading, and allows for a fresh perspective. Activities like walking, meditating, or engaging in hobbies can reset your mindset.
Reframe Losses as Learning Opportunities
Use each loss as a tool for growth. Analyze what went wrong—was it the market conditions, your strategy, or emotional decisions? This practice not only helps refine your approach but also rebuilds your confidence through proactive learning.
Visualize Success and Practice Mindfulness
Visualization and mindfulness techniques can help reset your emotional responses to losses. For instance, imagine handling losses calmly or achieving small trading wins. These exercises reprogram your brain to maintain composure under stress.
Reconnect with Your Trading Plan
Revisit your trading strategy to ensure it aligns with your goals and market conditions. A solid, well-tested plan provides psychological assurance and reduces impulsivity during challenging times.
Practical and Tactical Adjustments
Analyze Your Trading Journal
A detailed trading journal is invaluable. It helps you identify patterns in your decisions and pinpoint areas for improvement. For example, are you losing because of emotional entries or overly aggressive position sizes? Journaling fosters accountability and structured recovery.
Trade Smaller Positions
During a losing streak, reduce the size of your trades. Smaller stakes lower emotional pressure and give you room to rebuild confidence through minor wins. A series of small successes can gradually restore your self-belief.
Refine Risk Management
Effective risk management is a cornerstone of consistent trading. Stick to a risk-per-trade limit (commonly 1–2% of your portfolio) and set clear stop-loss orders. These practices minimize damage during downturns and maintain a manageable equity curve.
Adjust Expectations
Recognize that trading success is about probabilities over a series of trades, not individual outcomes. This perspective helps alleviate the emotional weight of single losses and reinforces a focus on long-term performance.
Seek Community Support
Trading can feel isolating, especially during tough times. Engage with mentors, join trading groups, or connect with peers who’ve experienced similar challenges. Sharing experiences can provide valuable insights and emotional support.
The Bigger Picture: Confidence is a Process
Recovering confidence isn’t about eliminating losses; it’s about cultivating resilience. By focusing on disciplined practices, psychological fortitude, and incremental adjustments, you’ll find yourself not only recovering but improving as a trader. Remember, even after 20 years in the markets, encountering losing streaks is part of the journey. What sets successful traders apart is their ability to handle setbacks with composure, adaptability, and a commitment to growth.