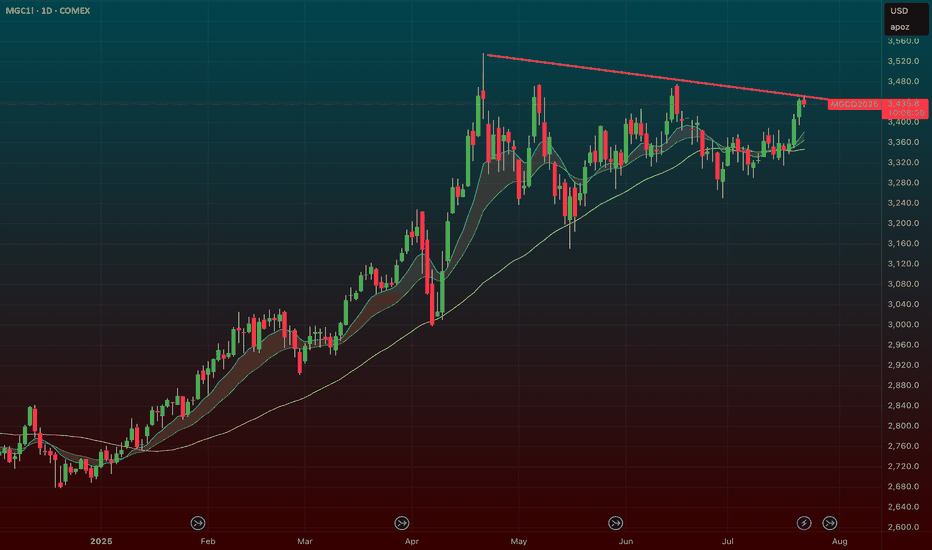
$GLD / $GC – Gold Poised for Breakout as Hard Assets FlexAMEX:GLD / SET:GC – Gold Poised for Breakout as Hard Assets Flex
Gold is setting up for a major breakout, and the broader market is finally catching on to the hard asset trade. Whether it’s inflation ticking up or the never-ending government deficit spending, the market is starting to signal something big.
🔹 Macro Tailwinds:
Inflation pressures + record deficit = a perfect storm for gold.
The dollar is under pressure — metals ( AMEX:GLD , AMEX:SLV , SET:GC ) are responding.
This theme isn’t going away anytime soon.
🔹 Technical Setup:
AMEX:GLD and SET:GC (Gold Futures) are coiled tightly just under breakout levels.
Volume is steady, and momentum is building under the surface.
A move through current resistance could send this entire trade into overdrive.
🔹 My Positioning:
1️⃣ Options: Long AMEX:GLD calls with 1-month expiration — slow mover, but clean structure.
2️⃣ Futures: Trading SET:GC contracts on the breakout side.
3️⃣ Silver Exposure: Still holding partials in AMEX:SLV — it’s following gold’s lead but with more juice.
Why I’m Focused Here:
This is not a one-day theme — hard assets are becoming a rotation trade.
If this confirms, we could see multi-week upside in precious metals.
It’s rare to get clean technicals that align this well with macro.
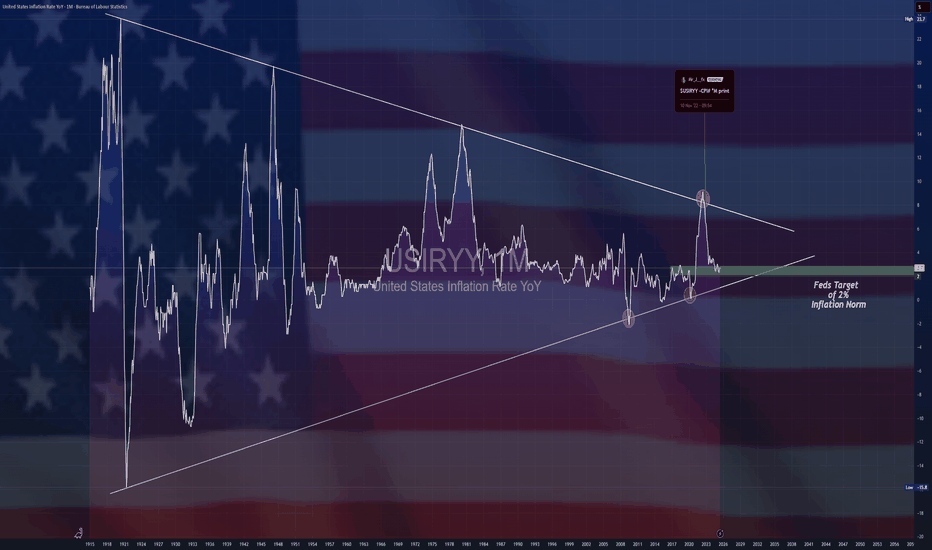
Inflation
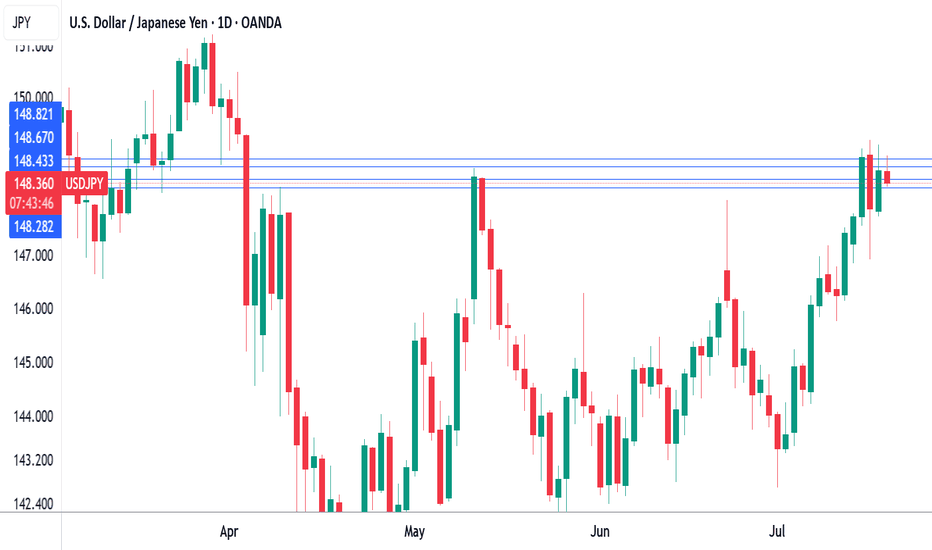
Japan's core CPI cools as expectedThe Japanese yen is showing little movement on Friday. In the North American session, USD/JPY is trading at 148.69, up 0.06% on the day. On the data calendar, Japan's inflation rate eased in June. It's a light day in the US, highlighted by UoM consumer sentiment and inflation expectations.
Inflation in Japan fell in June as expected and the yen is showing little movement today. Headline CPI dropped to 3.3% y/y from 3.5% in May, matching the consensus. This was the lowest level since Nov. 2024, as prices for electricity and gasoline rose more slowly in June. FoodThe inflation numbers come just before an election for Japan's Upper House of Parliament on Sunday. The ruling coalition is in danger of losing its majority, and if that happens, it will likely impact yields and the yen next week.
The Bank of Japan meets next on July 31 and is expected to continue its wait-and-see approach and hold interest rates. The BoJ hiked rates in January but hopes for a series of rate increases were dashed after US President Trump promised and delivered tariffs on many US trading partners, including Japan.
Trade talks between the US and Japan have bogged down and Trump has threatened to hit Japan with 25% tariffs if an agreement isn't reached by Aug. 1. In this uncertain environment, the BoJ isn't likely to raise interest rates. prices were up 7.2%, the most since March, as rice prices soared 100%. Monthly, CPI eased to 0.1%, down from 0.3% in May. Core inflation, which excludes fresh food but includes energy, fell to 3.3% from 3.7%, in line with the consensus and the lowest pace since March.
USD/JPY is testing resistance at 148.66. Above, there is resistance at 1.4882
148.44 and 148.28 are the next support levels
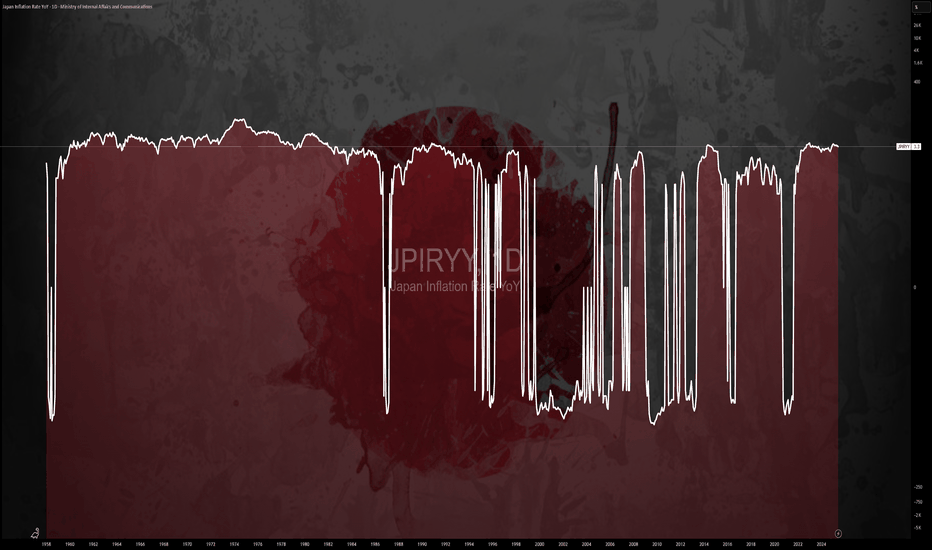
$JPIRYY -Japan Inflation Hits 7-Month Low (June/2025)ECONOMICS:JPIRYY 3.3%
June/2025
source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
-Japan’s annual inflation rate eased to 3.3% in June 2025 from 3.5% in May, marking the lowest reading since last November, as a sharp slowdown in electricity and gas prices offset persistent upward pressure from rice.
Core inflation also matched the headline rate at 3.3%, pointing to a three-month low and aligning with expectations.
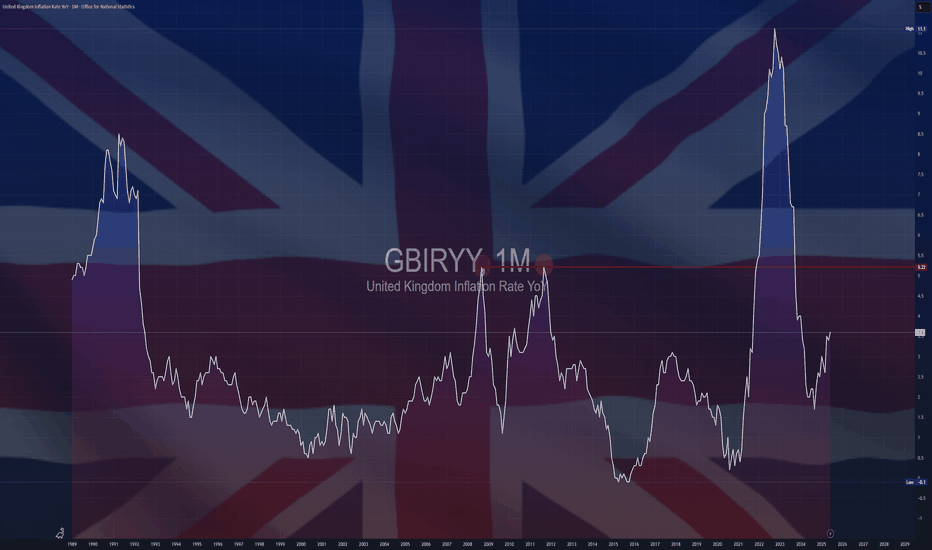
$GBIRYY - U.K Inflation Rises to a 2024 High (June/2025)ECONOMICS:GBIRYY
June/2025
source: Office for National Statistics
- The annual inflation rate in the UK rose to 3.6% in June, the highest since January 2024, up from 3.4% in May and above expectations that it would remain unchanged.
The main upward pressure came from transport prices, mostly motor fuel costs, airfares, rail fares and maintenance and repair of personal transport equipment.
On the other hand, services inflation remained steady at 4.7%.
Meanwhile, core inflation also accelerated, with the annual rate reaching 3.7%.
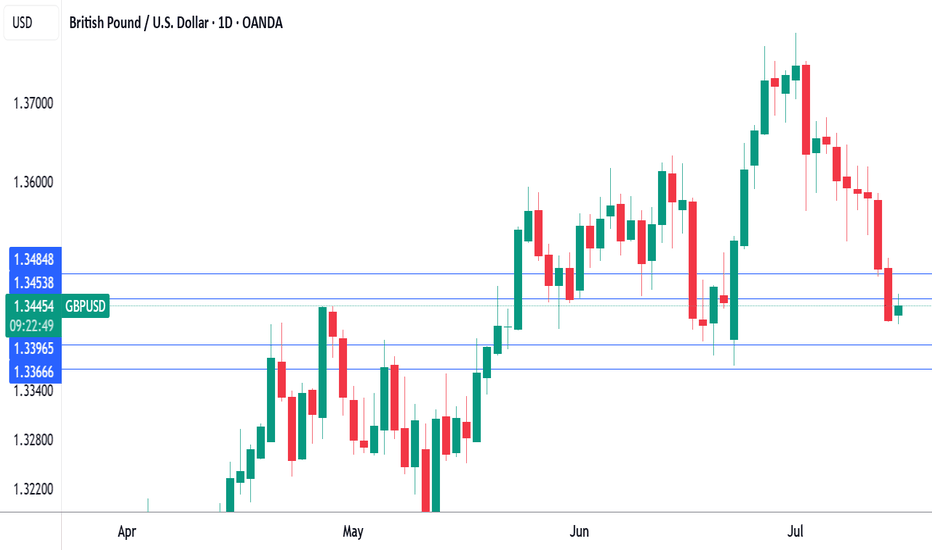
UK inflation heats up, Pound shrugsThe British pound has stabilized on Wednesday and is trading at 1.3389 in the European session, up 0.07% on the day. This follows a four-day losing streak in which GBP/USD dropped 1.5%. On Tuesday, the pound fell as low as 1.3378, its lowest level since June 23.
Today's UK inflation report brought news that the Bank of England would have preferred not to hear. UK inflation in June jumped to 3.6% y/y, up from 3.4% in May and above the market estimate of 3.4%. This was the highest level since January 2024 and is a stark reminder that inflation is far from being beaten. The main drivers of inflation were higher food and transport prices. Services inflation, which has been persistently high, remained steady at 4.7%. Monthly, CPI ticked up to 0.3% from 0.2%, above the market estimate of 0.2%.
It was a similar story for core CPI, which rose to 3.7% y/y from 3.5% in May, above the market estimate of 3.5%. Monthly, core CPI climbed 0.4%, above 0.2% which was also the market estimate.
The hot inflation report will make it more difficult for the BoE to lower interest rates and the money markets have responded by paring expectations of further rate cuts. Still, expectations are that the BoE will cut rates at the August 7 meeting, with a probability of around 80%, despite today’s higher-than-expected inflation numbers.
The UK releases wage growth on Thursday, which is the final tier-1 event prior to the August meeting. Wage growth has been trending lower in recent months and if that continues in the May reading, that could cement an August rate cut.
USD/CAD: Inflation gaps create opportunityIn the U.S., inflation accelerated for a second straight month, with headline CPI reaching 2.7% year-on-year in June as President Trump’s tariffs begin to push up the cost of a range of goods.
Increasing inflation could likely heighten the Federal Reserve’s reluctance to cut its interest rate, in defiance of Trump’s public demand. This could provide upward momentum for USD/CAD if expectations for rate cuts are delayed.
USD/CAD is showing signs of a potential trend reversal after finding strong support around 1.3600 in late June. Price action has since formed a series of higher lows, and the recent breakout attempt above 1.3720 suggests bullish momentum could be building.
Canada’s inflation rate, released at the same time as the US’s, edged up to 1.9%, staying below the Bank of Canada’s 2% target for a third consecutive month. With the BoC already signalling easing bias, this divergence in inflation paths may limit CAD strength.
$USIRYY -U.S Inflation Rate Seen Rising for 2nd Month (June/2025ECONOMICS:USIRYY
June/2025
source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
- The annual inflation rate in the US likely accelerated for the second consecutive month to 2.7% in June, the highest level since February, up from 2.4% in May.
On a monthly basis, the CPI is expected to rise by 0.3%, marking the largest increase in five months.
Meanwhile, core inflation is projected to edge up to 3% from 2.8%. Monthly core CPI is also anticipated to climb 0.3%, up from 0.1% in May, marking its sharpest increase in five months.
Pound under pressure ahead of US, UK inflation reportsThe British pound has edged up higher on Tuesday. In the European session, GBP/USD is trading at 1.3453, up 0.21% on the day. Earlier, GBP/USD touched a low of 1.3416, its lowest level since June 23.
All eyes will be on the UK inflation report for June, which will be released on Wednesday. Headline CPI is expected to remain unchanged at 3.4% y/y, as is core CPI at 3.5%. Monthly, both the headline rates are expected to stay steady at 0.2%.
Has the BoE's battle to lower inflation stalled? The BoE was looking good in March, when inflation eased to 2.6%, but CPI has rebounded to 3.4%, well above the BoE's inflation target of 2%. Services data has been especially sticky, although it dropped to 4.7% in May, down from 5.4% a month earlier.
At 3.4%, inflation is stuck at its highest level since February 2024 and that will complicate plans at the BoE to renew interest rate cuts in order to kick-start the weak UK economy. The central bank has lowered rates twice this year and would like to continue trimming the current cash rate of 4.25%. The Bank meets next on Aug. 7 and Wednesday's inflation data could be a significant factor in the rate decision.
In the US, if June inflation data rises as is expected, fingers will quickly point to President Trump's tariffs as finally having an impact. Recent inflation reports have not shown a significant spike higher due to the tariffs, which were first imposed in April. However, the tariffs may have needed time to filter throughout the economy and could be felt for the first time in the June inflation reading.
The Fed meets next on July 30, with the markets pricing in a 95% chance of a hold, according to CME's FedWatch. For September, the odds of a rate cut stand at 59%. Today's inflation report could cause a shift in these numbers.
GBP/USD tested resistance at 1.3454 earlier. Above, there is resistance at 1.3484
1.3396 and 1.3366 are the next support levels
EUR/CAD: Quant-Verified ReversalThe fundamental catalyst has been triggered. The anticipated strong Canadian CPI data was released as expected, confirming the primary driver for this trade thesis. Now, the focus shifts to the technical structure, where price is showing clear exhaustion at a generational resistance wall. 🧱
Our core thesis is that the confirmed fundamental strength of the CAD will now fuel the technically-indicated bearish reversal from this critical price ceiling.
The Data-Driven Case 📊
This trade is supported by a confluence of technical, fundamental, and quantitative data points.
Primary Technical Structure: The pair is being aggressively rejected from a multi-year resistance zone (1.6000 - 1.6100). This price action is supported by a clear bearish divergence on the 4H chart's Relative Strength Index (RSI), a classic signal that indicates buying momentum is fading despite higher prices.
Internal Momentum Models: Our internal trend and momentum models have flagged a definitive bearish shift. Specifically, the MACD indicator has crossed below its signal line into negative territory, confirming that short-term momentum is now bearish. This is layered with a crossover in our moving average module, where the short-term SMA has fallen below the long-term SMA, indicating the prevailing trend structure is now downward.
Quantitative Probability & Volatility Analysis: To quantify the potential outcome of this setup, we ran a Monte Carlo simulation projecting several thousand potential price paths. The simulation returned a 79.13% probability of the trade reaching our Take Profit target before hitting the Stop Loss. Furthermore, our GARCH volatility model forecasts that the expected price fluctuations are well-contained within our defined risk parameters, reinforcing the asymmetric risk-reward profile of this trade.
The Execution Plan ✅
Based on the synthesis of all data, here is the actionable trade plan:
📉 Trade: Sell (Short) EUR/CAD
👉 Entry: 1.6030
⛔️ Stop Loss: 1.6125
🎯 Take Profit: 1.5850
The data has spoken, and the setup is active. Trade with discipline.
Why Your Orange Juice Costs More?The price of orange juice is surging, impacting consumers and the broader economy. This increase stems from a complex interplay of geopolitical tensions, macroeconomic pressures, and severe environmental challenges. Understanding these multifaceted drivers reveals a volatile global commodity market. Investors and consumers must recognize the interconnected factors that now influence everyday staples, such as orange juice.
Geopolitical shifts significantly contribute to the rising prices of orange juice. The United States recently announced a 50% tariff on all Brazilian imports, effective August 1, 2025. This politically charged move targets Brazil's stance on former President Jair Bolsonaro's prosecution and its growing alignment with BRICS nations. Brazil dominates the global orange juice supply, providing over 80% of the world's trade share and 81% of U.S. orange juice imports between October 2023 and January 2024. The new tariff directly increases import costs, squeezing margins for U.S. importers and creating potential supply shortages.
Beyond tariffs, a convergence of macroeconomic forces and adverse weather conditions amplify price pressures. Higher import costs fuel inflation, potentially compelling central banks to maintain tighter monetary policies. This broader inflationary environment impacts consumer purchasing power. Simultaneously, orange production faces severe threats. Citrus greening disease has devastated groves in both Florida and Brazil. Extreme weather events, including hurricanes and droughts, further reduce global orange yields. These environmental setbacks, coupled with geopolitical tariffs, create a robust bullish outlook for orange juice futures, suggesting continued price appreciation in the near term.
$CNIRYY -China's Inflation Data (June/2025)ECONOMICS:CNIRYY
June/2025
source: National Bureau of Statistics of China
- China’s consumer prices rose by 0.1% yoy in June 2025,
reversing a 0.1% drop in the previous three months and surpassing market forecasts of a flat reading.
It marked the first annual increase in consumer inflation since January, driven by e-commerce shopping events, increased subsidies for consumer goods from Beijing, and easing trade risks with the U.S.
Core inflation, which excludes volatile food and fuel prices, rose 0.7% yoy, marking the highest reading in 14 months and following a 0.6% gain in May.
On a monthly basis, the CPI fell 0.1%, after May's 0.2% drop, pointing to the fourth monthly decline this year.
Australian dollar stabilizes after RBA's surpriseThe Australian dollar is in positive territory after a three-day skid, declining 1.5%. In the North American session, AUD/USD is trading at 0.6532, up 0.50% on the day. The Australian dollar rose as much as 0.95% earlier before retreating.
The Reserve Bank of Australia blindslided the markets on Tuesday as the central bank held the cash rate at 3.85%. The markets had priced in a quarter-point cut at 96%, but the RBA had the last laugh. For the first time, the RBA published the vote tally, which was 6-3 in favor of maintaining the rate.
The rate statement was cautious, as members said "there are uncertainties about the outlook for domestic economic activity and inflation".
Governor Bullock tried to calm the markets, saying that the decision was about "timing rather than direction" and that the Bank would "wait a few weeks" to confirm that inflation was on track to ease and remain sustainably around 2.5%. Bullock said that "we don't want to end up having to fight inflation again".
Inflation is moving in the right direction but the RBA wants to see the second-quarter inflation report on July 30, ahead of the rate decision on Aug. 12. Headline CPI in May eased to 2.1% y/y from 2.4% in April. The core rate dropped to 2.8% from 2.4% in April, the lowest rate since early 2022.
The RBA will be hoping that waiting till August will provide some clarity with regard to US tariff policy. President Trump has pledged new tariffs against various countries but this move is not expected to have much impact on Australia's economy.
AUD/USD is testing resistance at 0.6513. Above, there is resistance at 0.6541
There is support at 0.6463 and 0.6435
$EUIRYY - Europe CPI (June/2025)ECONOMICS:EUIRYY 2%
June/2025
source: EUROSTAT
- Eurozone consumer price inflation rose slightly to 2.0% year-on-year in June 2025, up from May’s eight-month low of 1.9% and in line with market expectations, according to a preliminary estimate.
The figure aligns with the European Central Bank’s official target.
Among major economies, inflation in Germany unexpectedly declined, while France and Spain saw modest increases and Italy’s rate held steady.
S&P 500 Outlook. Best Quarter Since 2023… But What Next?The S&P 500 just logged its best quarterly performance since Q4 2023 , surging on optimism around global trade negotiations and growing expectations that the Fed may begin cutting rates as early as September. US futures are green this morning, thanks to developments like Canada backing off digital taxes, ongoing dialogues with China ahead of the July 9 deadline, and risk-on sentiment is pushing yields and the dollar lower.
But as traders, we need to ask:
Are we witnessing a genuine economic inflection point? Or is this just a liquidity-driven rally that’s pricing in a best-case scenario?
Technical View
Support Zone: 6,150 was just broken through. And 6000, the round number level, coinciding with the 20-day EMA and previous swing level.
Resistance Levels: 6,235 is the next critical ceiling, a clean breakout could see price reach the extension level of 6,415.
Momentum Indicators: RSI remains elevated and is creeping toward the overbought. While momentum is strong, watch out for the possible development of a divergence.
Possible Scenarios
The 'Soft Landing’ Is Now the Base Case
Markets are trading as if the Fed has successfully engineered a soft landing. But that’s now fully priced in, and historically, the most dangerous trades are the ones everyone agrees on. If trade talks stall, inflation re-accelerates, or earnings disappoint, the reversal could be brutal and fast.
Risk-on Sentiment Without Volume Is a Yellow Flag
Despite the price strength, volume has been tapering off. The S&P’s recent leg up occurred on lighter-than-average participation, suggesting institutions may be watching, not chasing. That’s often the case in low-volatility summers, but it also implies that any negative catalyst could cause outsized downside moves.
Macro-Fundamentals May Not Justify Valuation Expansion
Yes, inflation is slowing, and the Fed might cut. But if they do, it’s likely because growth is weakening, not because the economy is roaring. So the very condition that triggers rate cuts could also cap earnings growth!
Projection
Bullish Scenario: A confirmed breakout above 6,280 could carry us toward 6,400–6,500 by mid-Q3, especially if the trade deals progress, July inflation comes in soft, and the Fed signals accommodation.
Bearish Risk: If price fails to hold above 6,120, especially if trade optimism fades, or inflation growth spikes or Fed rhetoric shifts hawkish again, this could then open a quick pullback toward 6,000 or lower, which also aligns with the 50-day SMA.
Key Events to Watch
July 9 Trade Talks Deadline: Any sign of stalling could bring volatility back fast.
June CPI Print (July 10): Crucial for confirming the Fed's next move.
Earnings Season Kickoff (mid-July): Tech-heavy expectations may not be easy to beat after such a strong run.
Conclusion
A record-setting quarter is impressive but not necessarily predictive. This quarter’s rally has been built more on relief and expectations than hard data. When expectations (not earnings) are doing the heavy lifting, any misstep from central banks or geopolitics could unravel gains rapidly.
A rate cut might be delayed, or inflation re-accelerates, or trade talks stall; any of these could leave equities hanging. Remember: the higher the climb without real earnings growth, the harder the fall when sentiment shifts. It's not just about the chart. It is about the narrative behind the price.
What’s your bias for Q3?
Are you buying this breakout or fading the optimism? Drop your thoughts below.
Can PCE data rescue the dollar? JPY, EUR, GBP setup in playThe latest U.S. PCE report is set for release at 8:30am EDT, with both headline and core inflation expected at 0.1% month-on-month.
As the Fed’s preferred inflation measure, today’s figures could influence interest rate expectations. A stronger print may reduce the case for a July rate cut, while a softer result could add pressure on the U.S. dollar.
The dollar has already weakened this week amid speculation over central bank independence (trump is reportedly considering nominating Fed chair Jerome Powell’s successor earlier than normal in order to undermine the current chair).
Pairs to watch include, EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY with symmetrical triangle formations suggesting breakout potential in either direction for all once the data hits.
Australia's CPI slows, raising rate cut expectationsThe Australian dollar is showing limited movement on Wednesday. In the European session, AUD/USD is trading at 0.6495, up 0.08% on the day.
Australia's inflation rate headed lower in May. Headline CPI rose 2.1%, after gains of 2.4% in the previous three months. This was below the market estimate of 2.3%. Monthly, CPI eased to 0.4%, driven by lower petrol and housing costs.
The key core CPI indicator, annual trimmed mean inflation, also dropped sharply, to 2.4% from 2.8%, its lowest level since Nov. 2021.
The soft inflation report has boosted the case for the Reserve Bank of Australia to lower rates at the July meeting. The markets have priced in a 90% probability of a quarter-point cut, up from 81% prior to the inflation release. The markets have priced in three more rate cuts this year, following rate cuts in February and May.
The markets are counting on the RBA to be dovish in the second half of 2025. With inflation not only within the RBA's target of 2-3% but also falling, the markets expect that the RBA will be keen to lower rates in order to preserve economic growth.
Federal Reserve Chair Powell testified before a House Committee on Tuesday and had a cautious message for lawmakers. Powell said that the Fed was committed to keeping inflation contained and that the Fed planned to maintain rates until the impact of tariffs on inflation was more clear and reiterated that inflation still remained above the Fed's 2% target.
Powell has faced blistering criticism from President Trump for not lowering rates. In his testimony, Powell said that Trump's attacks were "having no effects" on Fed policy.
AUD/USD pushed above resistance at 1.3726 and is testing resistance at 1.3727. Above, there is resistance at 1.3750
1.3713 and 1.3702 are the next support levels
Australian dollar jumps on Israel-Iran cease fireThe Australian dollar is up sharply on Tuesday. In the North American session, AUD/USD is trading at 0.6504, up 0.70% on the day.
Investors' risk appetite is higher today after Israel and Iran agreed to a ceasefire in their 12-day war. The markets have reacted favorably to lower oil prices as fears that Iran would close the Straits of Hormuz, which would have disrupted global oil supplies, have diminished. Risk appetite has returned and risk currencies like the Australian dollar have posted strong gains today.
The Israel-Iran war has triggered sharp swings in oil prices and there are fears of an oil price shock if the fragile ceasefire does not hold. An oil price shock would send petrol prices higher and boost inflation, complicating the Reserve Bank of Australia's plans to lower interest rates.
Australia CPI expected to ease to 2.3%
Australia releases the May inflation report early on Wednesday. Headline CPI has been stuck at 2.4% for three consecutive months, within the Reserve Bank of Australia's target of 2-3% and its lowest level since Nov. 2024. The market estimate for May stands at 2.3%. Trimmed Mean CPI, a key core inflation indication, edged up to 2.8% from 2.7% in April.
The Reserve Bank will be keeping a close eye on the inflation report, with the central bank making a rate announcement on July 8. The RBA trimmed rates by a quarter-point in May and has shifted to a more dovish stance - the Board discussed a jumbo half-point cut at the May meeting.
Fred Chair Powell appears before Congress today and Wednesday and is likely to defend the Fed's wait-and-see stance. The Fed is concerned about President Trump's tariffs and the Israel-Iran war threatens stability in the Middle East, hardly the recipe for further rate cuts. Still, there appears to be some dissent within the Fed, as two members, Michelle Bowman and Christopher Waller, have suggested that the Fed could lower rates as early as September.
AUD/USD is testing resistance at 0.6490. Above, there is resistance at 0.6522
There is support at 0.6400 and 0.6342
Yen slides on oil supply jitters after US attack on IranThe Japanese yen has started the week with sharp losses. In the European session, USD/JPY has jumped 1.2% on the day and is trading at 147.82. The yen has fallen to five-week lows against the US dollar.
The fallout from the US attack on Iranian nuclear facilities over the weekend is being felt in the currency markets. The Japanese yen, traditionally a safe-haven currency, continues to depreciate, in response to rising oil prices.
Oil prices rose to their highest level since January on Monday after the US attack on Iranian nuclear facilities. Iran has threatened to close the Straits of Hormuz, a critical trade route through which 20% of the world's oil supply passes through each day. Oil prices have jumped about 10% since the Israel-Iran war started on June 13 and fears of a disruption to oil supply could further boost oil prices.
As oil prices have climbed, the yen has lost ground, declining 3.0% since the Israel-Iran war started. Japan imports almost all of its oil and the rise in oil prices is hurting Japan's trade balance.
Japan's core inflation rate climbed 3.7% y/y in May, up from 3.5% in April. Core CPI has accelerated for a third straight month and hit its highest level since Jan. 2023. This was above the market estimate of 3.6%. Headline inflation ticked lower to 3.5% from 3.6% in April, below the forecast of 3.6%.
The rise in core CPI supports the case for the Bank of Japan to boost interest rates, but the uncertainty over tariffs and the Israel-Iran war will likely mean that the BoJ will stay on the sidelines in the coming months.
There is resistance at 146.91. Next, USD/JPY is testing resistance at 147.61
146.51 and 145.81 are the next support levels
Crude Oil Prices Rocketing amid geopolitical risks
NYMEX:CL1! NYMEX:MCL1! NYMEX:BZ1!
Macro:
Geopolitical tensions remain high and markets are now likely to price in our scenario discussing ongoing air and missile war, given one-off intervention from the US thus far. According to Reuters, the U.S. now assesses that Iranian retaliation could occur within the next two days.What happens next is anybody’s guess but as traders, it is important to navigate these uncertainties with scenario planning and/or reduce risk to account for increased volatility.
We also get Services and Manufacturing PMI data today and PCE Price Index on Friday. Chair Powell is set to testify on Tuesday 9am CT.
Key levels:
Jan 2025 High: 76.57
2025 High: 78.40
2025 CVAH(Composite Value Area High): 75.68
Key LIS zone: 73.50-73.15
We anticipate the following scenarios in crude oil:
Scenario 1:
Prices remain elevated as tensions remain high, despite limited retaliation, however, the situation overall now escalated beyond return to diplomacy.
Scenario 2:
Any push towards de-escalation, unlikely in our analysis, but given the headline risk, crude prices may remain volatile and come off the highs.
Given our key LIS (Line in Sand) zone above, we favor longs above this and shorts below this zone.
$JPIRYY -Japan CPI (May/2025)ECONOMICS:JPIRYY
May/2025
source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
- Japan's annual inflation rate edged down to 3.5% in May 2025 from 3.6% in the previous two months, marking the lowest level since November.
Price growth eased for clothing (2.6% vs 2.7% in April), household items (3.6% vs 4.1%), and healthcare (2.0% vs 2.2%), while education costs fell further (-5.6%). In contrast, inflation held steady for transport (2.7%) and miscellaneous items (1.3%), but accelerated for housing (1.1% vs 1.0%), recreation (3.0% vs 2.7%), and communications (1.9% vs 1.1%).
Meanwhile, prices of electricity (11.3% vs 13.5%) and gas (5.4% vs 4.4%) remained elevated.
On the food side, prices increased by 6.5%, staying at the slowest pace in four months, though rice prices soared over 100%, underscoring the limited impact of government efforts to rein in staple food costs.
Meanwhile, the core inflation accelerated to 3.7% from 3.5% in April, reaching its highest level in over two years, ahead of the summer election.
Monthly, the CPI rose 0.3%, after a 0.1% gain in April.
UK retail sales slide, Pound edges higherThe British pound has gained ground for a second straight day. In the European session, GBP/USD is trading at 1.3496, up 0.22% on the day.
UK retail sales took a tumble in May, falling 2.7% m/m. This followed an upwardly revised 1.3% increase in April and was much worse than the market estimate of -0.5%. This marked the steepest decline since December 2023 and was driven by a sharp drop in food store sales.
Consumers are being squeezed by inflation and are pessimistic about economic conditions - Gfk consumer confidence for June rose slightly to -18 from -20. Annually, retail sales dropped 1.3%, following a 5.0% gain in April and missing the market estimate of 1.7%. This was the weakest reading since April 2024.
The dismal retail sales report reflects the volatile economic landscape and there may not be a light at the end of the tunnel for some time. The Israel-Iran war could lead to oil prices continuing to rise and the uncertainty over US tariffs will only add to the worries of the UK consumer.
The Bank of England held rates on Thursday but the weak retail sales report will add pressure on the central bank to lower rates in the summer. The markets expect one or two rate cuts in 2025, but the main impediment to a rate cut is stubbornly high inflation.
Inflation ticked lower to 3.4% y/y in May from 3.5% a month earlier. The core rate dropped to 3.5% from 3.8% but these numbers are still too high, well above the BoE's target of 2%. Without signs that inflation is easing, it will be difficult for the BoE to justify a rate cut.
GBP/USD is testing resistance at 1.3498. Above, there is resistance at 1.3527
1.3440 and 1.3411 are providing support
$GBINTR - Steady Rates by BoE (June/2025)ECONOMICS:GBINTR
June/2025
source: Bank of England
- The Bank of England voted 6-3 to keep the Bank Rate steady at 4.25% at its June meeting, amid ongoing global uncertainty and persistent inflation.
The central bank noted inflation is expected to remain at current rates for the rest of the year before easing back toward the target next year,
indicating that a gradual and cautious approach to further monetary policy easing remains appropriate.
Pound Steady as BoE holds ratesThe British pound is showing limited movement for a second straight day. In the European session, GBP/USD is trading at 1.3435, up 0.18% on the day.
The Bank of England didn't have any surprises up its sleeve as it held rates at 4.25%. This follows a quarter-point cut at last month's meeting. The MPC vote indicated that six members voted to hold while three voted to lower rates. The markets had projected that the vote would be 7-2 in favor of holding rates.
Today's decision to hold rates was widely expected, but that doesn't mean there aren't economic signals which support a rate cut. The UK economy is in trouble and GDP came in at -0.3% in April, its deepest contraction in 18 months.
The weak economy could desperately use a rate cut, but inflation remains stubbornly high and a rate cut would likely send inflation even higher. Annual CPI remained at 3.4% in May, its highest level in over a year.
The geopolitical tensions, most recently the war between Israel and Iran have led to greater economic uncertainty and complicated any plans to lower rates. The BoE is expected to lower rates one or twice in the second half of the year, with the direction of inflation being a key factor in the Bank's rate path.
The Federal Reserve held rates at Wednesday's meeting for a fourth straight time. The Fed noted that inflation remains higher than the target but said the labor market remains strong. President Trump has pushed hard for the Fed to lower rates but Fed Chair Jerome Powell has stuck to his position and repeated on Wednesday that current policy was the most appropriate to respond to the economic uncertainty.