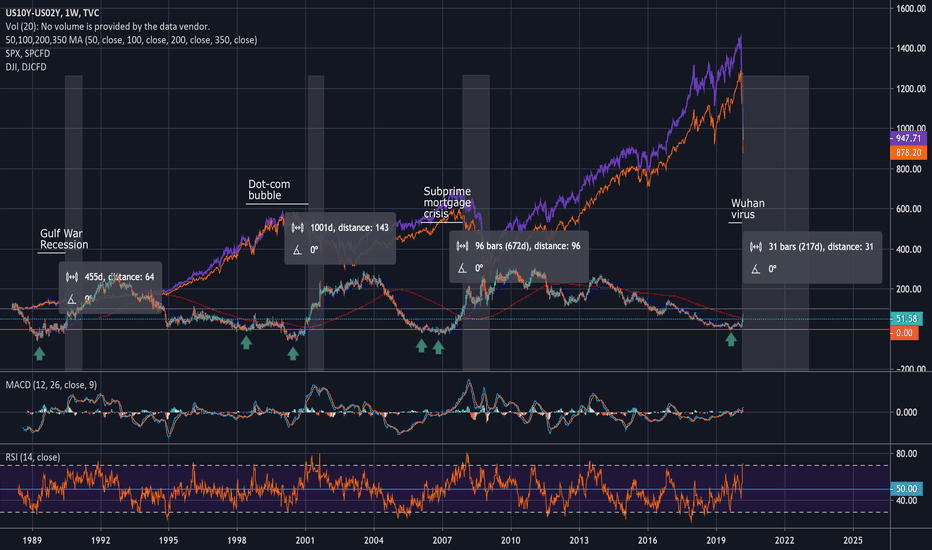
Inverted Yield of 2022 Explained - Till TodayFor our housing loan, many of us, if you are in your 30s today and all the way to 70 years of age, will likely have chosen floating or short-term loan rates rather than longer-term loan rates. However, everything changed in 2022. Now, we are more likely to choose longer-term loan rates over floating rates. Why? Because today, longer-term loan rates are lower than floating rates.
This phenomenon is called an inverted yield curve.
In the 70s and 80s, there was also a period of inverted yields, and different markets moved accordingly as expected. Today, we are seeing an inverted yield once again, and the same markets are moving in a manner similar to those in the 70s and 80s.
We will do a comparison between the 70s and today’s inverted yield. Please let me know what opportunities you see after this tutorial.
2 Year Yield Futures
Ticker: 2YY
Minimum fluctuation:
0.001 Index points (1/10th basis point per annum) = $1.00
10 Year Yield Futures
Ticker: 10Y
Minimum fluctuation:
0.001 Index points (1/10th basis point per annum) = $1.00
Disclaimer:
• What presented here is not a recommendation, please consult your licensed broker.
• Our mission is to create lateral thinking skills for every investor and trader, knowing when to take a calculated risk with market uncertainty and a bolder risk when opportunity arises.
CME Real-time Market Data help identify trading set-ups in real-time and express my market views. If you have futures in your trading portfolio, you can check out on CME Group data plans available that suit your trading needs www.tradingview.com
Invertedyieldcurve
We have a Grey Rhino here - Markets are driven by ignoranceThe US long-term bonds have hit new lows, the yield curve has been inverted for two years now, and inflation remains uncertain, meaning interest rates may not ease at all. Yet, stock markets are reaching new highs.
We have a "grey rhino" in this market. A grey rhino is a large and visible animal that cannot be ignored. Try not to get too close to them because when they start charging, we can never outrun them.
In this market context, we face a big, obvious problem that investors completely ignore until it becomes a crisis. It's different from a "black swan," which is a rare and unpredictable event.
When we recognize that there are problems many do not understand, we have already won half the battle.
U.S. Treasury Bonds Futures & Options
Ticker: ZB
Minimum fluctuation:
1/32 of one point (0.03125) = $31.25
2-Year Yield Futures
Ticker: 2YY
Minimum fluctuation:
0.001 Index points (1/10th basis point per annum) = $1.00
Disclaimer:
• What presented here is not a recommendation, please consult your licensed broker.
• Our mission is to create lateral thinking skills for every investor and trader, knowing when to take a calculated risk with market uncertainty and a bolder risk when opportunity arises.
CME Real-time Market Data help identify trading set-ups in real-time and express my market views. If you have futures in your trading portfolio, you can check out on CME Group data plans available that suit your trading needs www.tradingview.com
What Next For The Inverted Yield Curve?Markets are notorious for exaggerated expectations. They sense a tiger when all they see is a cat. Expectations on rate cuts have been no different. Despite the Fed’s speak on measured changes to policy rates, markets got ahead of themselves since late last year. Markets are now starting to align their expectations with reality.
US economic data from January stands in stark contrast to December readings. Nonfarm payrolls and CPI are higher than expectations. A resilient economy and rebound in inflation have pushed expectations of rate cuts to much later this year.
According to the CME Group FedWatch tool, the probability of a rate cut at the March FOMC policy meeting dropped from 73% on 29 Dec 2023 to merely 8.5% as of 19 Feb 2024. First rate cut is now expected at the 12 June policy meeting this year. Markets are now pricing four rate cuts instead of six cuts as previously anticipated.
Shift in rate cut expectations has led to a rebound in US treasury bond yields. This paper delves into the factors behind the shift in rate expectations. The paper also analyses a hypothetical trade setup using CME Group Yield futures that investors can deploy to harness gains from revised policy path ahead.
RATE CUT EXPECTATIONS IS BECOMING MORE ROOTED IN REALITY NOW
A stream of recent economic data from the US has pointed to a stronger economy and a rebound in inflation, causing rate cut expectations to shift.
January nonfarm payrolls report showed 353k jobs added, exceeding expectations of 333k and the largest build since January 2023. January CPI report showed annual CPI growth slow from its pace of 3.4% in December 2023 to 3.1% in Jan 2024 but still hotter than analyst expectations of 2.9%.
Core CPI was another concern as it stood unchanged at 3.9%. On a monthly basis, CPI jumped 0.3% MoM. 0.6% MoM increase in rent prices and 0.4% increase in food prices were behind the monthly increase.
On the positive front, PPI fell 0.1% MoM in January, with goods prices 0.4% lower. PPI is just 1% higher YoY against an estimate of +1.3% estimate.
January Retail Sales fell sharply by 0.8% MoM in January. December growth was revised lower from +0.6% to +0.4%. This is expected to lead to a lower GDP growth in Q1. GDPNow model from the Atlanta Fed predicts 2.9% growth in Q1, compared to 3.4% before the release.
As a result of the broadly stronger data and higher inflation, expectations of rate cuts at the 20/March FOMC meeting have fallen from their peak of 74% on 29 December 2023 to 8.5% as of 19 February 2024. Expectations for a rate cut by May have also been scaled back. As of 14 Feb 2024, there is just 35% probability of a rate cut at the 01 May FOMC meeting as well.
Source: CME Group FedWatch
FedWatch indicates 50% probability of a rate cut for the meeting on 12 June 2024, which is up from 40% a week ago.
Source: CME Group FedWatch
The increase reflects the recent retail sales and jobless claims data that was stronger than expected. Both have led to a pullback in bond yields from their 2024 highs.
Source: CME Group FedWatch
The CME Group FedWatch tool indicates expectations of four rate cuts in 2024 as of 18/Feb down from six cuts at the start of the year.
The expectations around rate cuts have also shifted in Fed’s messaging. Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic stated that the Federal reserve does not face any urgency in cutting rates due to the current strength in the US economy. Dallas Fed President, Lorie Logan, shares similar sentiments .
Fed Chair Powell echoed the same message. Powell stated the Fed won’t cut rates until it has greater confidence that inflation is moving sustainably to its target. Specifically, he mentioned that a rate cut was unlikely by March. In an interview with “60 Minutes”, Powell suggested that Fed’s base case scenario of 75 basis points of rate cuts in 2024 was unchanged.
As a result of delayed rate cuts expectations, US treasury yields have rebounded.
FOMC MINUTES TO REITERATE HAWKISH POSTURE
Strong economic data and inflation numbers coming in hotter than expected will keep the Fed hawkish in the near term. How long will be anybody's guess?
On 21/Feb (Wed), minutes of the FOMC January meeting will be published. Expectations are for Fed to reiterate its hawkish posture. In anticipation, the 2-year yield futures are up forty-nine basis points (bps) to close at 4.601% as of 16/Feb (compared to 4.112% close of markets on 1/Feb).
Meanwhile, during the same period, the 10-year yield futures jumped forty-five bps to close at 4.295% as of close of markets on 16/Feb.
Taking directional views on the 2-year or the 10-year yields can be difficult when rate expectations are already baked into the yields. Directional views expose the trade to large downside risks vastly reducing reward-to-risk ratio.
In sharp contrast, spread trades enables trades to lock in gains while minimizing downside risks. This paper illustrates a hypothetical treasury spread trade below.
HYPOTHETICAL 10Y-2Y TREASURY SPREAD TRADE
Portfolio managers can better harvest gains from rate moves by trading the closely monitored US Treasury yield spread measuring the gap between yields on 2-year & 10-year Treasury notes. FOMC minutes reiterating a hawkish posture will invert the yield curve even more.
To help traders monitor this spread, the CME Group publishes a Micro Treasury CurveWatch tool which shows daily, weekly, and monthly changes in yields and major yield spreads.
Source: Micro Treasury CurveWatch tool
Portfolio managers can express this view by taking a short position in the CME Group 10-Year Yield Futures (10YG4) and a long position in the CME Group 2-Year Yield Futures (2YYG4).
● Entry: -0.2790 (27.9 bps; enter the spread trade when 10YG4 minus 2YYG4 is -0.2790 bps)
● Target Exit: -0.3690 (36.9 bps)
● Stop Loss: -0.2250 (22.5 bps)
● Profit at Target: USD 90 (9 bps x USD 10)
● Loss at Stop: USD 54 (5.4 bps x USD 10)
● Reward to Risk: 1.66x
MARKET DATA
CME Real-time Market Data helps identify trading set-ups and express market views better. If you have futures in your trading portfolio, you can check out on CME Group data plans available that suit your trading needs www.tradingview.com
DISCLAIMER
This case study is for educational purposes only and does not constitute investment recommendations or advice. Nor are they used to promote any specific products, or services.
Trading or investment ideas cited here are for illustration only, as an integral part of a case study to demonstrate the fundamental concepts in risk management or trading under the market scenarios being discussed. Please read the FULL DISCLAIMER the link to which is provided in our profile description.
Why are investors turning their attention to mid-cap stocks?This will be the 2 questions we will be discussing today
1. So, what is happening on this divergence and its implication?
2. And who is leading who?
a. Large cap leading the mid-to-small cap market? Or
b. The mid-to-small cap leading the large cap market?
The answer: The mid-to-small cap is leading the large cap market and why is it so?
If recession hits, hypothetically mid-to-small cap stocks employing the majority of the work force or employees in United States will be the most affected, this huge workforce is also considered as the mass consumer.
The large cap stocks, their business depends on the mass consumer. If the mass consumers start to tighten their belts, the large cap stocks revenue will also be affected subsequently.
Some reference for traders:
E-mini S&P MidCap 400 & Option:
Outright:
0.10 index points = $10.00
Micro E-mini S&P MidCap 400:
CME ClearPort:
0.05 index points = $0.50
E-mini Russell 2000 & Option:
Outright:
0.10 index points = $5.00
Micro E-mini Russell 200
Outright:
0.10 index points = $0.50
Disclaimer:
• What presented here is not a recommendation, please consult your licensed broker.
• Our mission is to create lateral thinking skills for every investor and trader, knowing when to take a calculated risk with market uncertainty and a bolder risk when opportunity arises.
CME Real-time Market Data help identify trading set-ups in real-time and express my market views. If you have futures in your trading portfolio, you can check out on CME Group data plans available that suit your trading needs www.tradingview.com
Inverted Yield Curve Starts in 2023 - Explained When the yield of the 3-month bond is higher than the 30-year bond yield, this is known as an inverted yield curve. It is a rare and unusual occurrence and we are seeing this today. This signals a potential economic recession in the future.
An inverted yield curve suggests that investors have a pessimistic outlook for the future of the economy. They are willing to accept lower yields on long-term bonds because they anticipate a slowdown in economic growth. In contrast, they demand higher yields on short-term bonds because they expect the central bank to raise interest rates in response to inflationary pressures.
An inverted yield curve can lead to a decrease in borrowing and lending activity, as it can make it more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money. This can result in a reduction in economic growth and can eventually lead to a recession.
Some reference for traders:
Micro Treasury Yields & Its Minimum Fluctuation
Micro 2-Year Yield Futures
Ticker: 2YY
0.001 Index points (1/10th basis point per annum) = $1.00
Micro 5-Year Yield Futures
Ticker: 5YY
0.001 Index points (1/10th basis point per annum) = $1.00
Micro 10-Year Yield Futures
Ticker: 10Y
0.001 Index points (1/10th basis point per annum) = $1.00
Micro 30-Year Yield Futures
Ticker: 30Y
0.001 Index points (1/10th basis point per annum) = $1.00
Disclaimer:
• What presented here is not a recommendation, please consult your licensed broker.
• Our mission is to create lateral thinking skills for every investor and trader, knowing when to take a calculated risk with market uncertainty and a bolder risk when opportunity arises.
CME Real-time Market Data help identify trading set-ups in real-time and express my market views. If you have futures in your trading portfolio, you can check out on CME Group data plans available that suit your trading needs www.tradingview.com
Gold leads inflation by 20 yearsBank run crisis causes the current Fed fund rate to trade higher than the rest of the bond yields, what is its implication?
As US CPI remain high, global equities will continue to be uncertain this year. Investors are now turning their attention to precious metals.
Gold has started to move up since year 2000, it has appreciated more than 700%. However, the inflation and interest rates was stagnated the last 20 years.
What's happening?
Because in those years, I classified it as "Borrowed Time"
A need for easy money policy by:
1) Increasing the money supply
2) Lowering interest rates
Good times may be over, but I am seeing opportunities in the other set of assets - commodities.
For traders -
3 types of gold for trading:
• COMEX Gold
0.10 per troy ounce = $10.00
• E-mini Gold
0.25 per troy ounce = $12.50
• Micro Gold
0.10 per troy ounce = $1.00
Disclaimer:
• What presented here is not a recommendation, please consult your licensed broker.
• Our mission is to create lateral thinking skills for every investor and trader, knowing when to take a calculated risk with market uncertainty and a bolder risk when opportunity arises.
CME Real-time Market Data help identify trading set-ups in real-time and express my market views. If you have futures in your trading portfolio, you can check out on CME Group data plans available that suit your trading needs www.tradingview.com
Japanese have been selling bonds, have Yields peaked for now?One of the reasons US Treasuries, and other bonds, have been selling off is the dumping by Japanese investors.
All duration #YIELDS have done well but more so the shorter term. The Inverted Yield Curve has widened over the last few months but has been significantly lately.
However, today we see the 1 & 10Yr ($TNX) selling off but the 2 Yr is CRATERING! Interesting.
Also interesting is that volume has been waning for investment grade and high yield bonds. Liquidity could be an issue later on if this continues.
Powell's favorite curveA number of news sources reported in the lat 2 days that J Powell's favorite yield curve as a recession indicator is an inverted 3 month and 10 year.
These are now inverted and have only inverted 3 other times according to this data
Before the 2000 crash
Before the Global Financial Crisis
Before Covid lockdowns
Its virtually assured at this point that the US will enter a recession in the near future if we're not in one already.
I have more to say about this and in particular the timing of covid but if you want the tinfoil hat version you'll have to find me on the newsletter...
Good luck out there!
Risk Off: Dollar Up, All Else Falling
CBOT: Micro 10-Year Yield ( CBOT_MINI:10Y1! )
Last Friday, U.S. stocks plunged again as soaring interest rates and FX market turmoil fueled investor fears of a global recession.
The Dow fell below 30,000 and closed at 29,590, down 486 or -1.6%. S&P 500 broke through 3700 and settled at 3,697, down 1.72%. Nasdaq Composite lost nearly 200 points and closed at 10,868, down 1.80%. Russell 2000 finished at 1,679, down 2.48%.
On Wednesday, the Fed raised Fed Funds Rate by 75 basis points to 3.00-3.25% range. Market expected two more rate hikes totaling 125 bps in the November and December FOMC meetings, bringing it to 4.25-4.50% by year end.
U.S. Treasury yields surged this week after the Fed's move, with 2-year rate topping 4.2%, a 15-year high. 10-year Treasury yield is currently quoted at 3.687%.
Meanwhile, US dollar index ( ICEUS:DXY ) exceeded 113 points, its highest level since April 2002. Euro currency fell to 0.9688 against the dollar, a 20-year low. British pound closed at $1.08, a new low in more than three decades.
Global Market in a Risk-Off Mode
On August 29th, I pointed out that global financial markets are in a paradigm shift triggered by runaway inflation and high interest rate. All major assets would undergo “repricing”. The recent US CPI data and Fed rate hike help speed up this process.
The title chart at the top of this analysis shows year-to-date returns from major financial assets:
• US Dollar Index ( ICEUS:DXY ): +17.73%, at 20-year high
• S&P 500 ( SP:SPX ): -22.72%, in a bear market territory
• WTI Crude Oil ( NYMEX:CL1! ): +3.05%. In March, crude oil gained 60% in response to geopolitical crisis. It turned south ever since the Fed began raising interest rate
• Gold ( COMEX:GC1! ): -8.95%. Under a strong dollar, gold has become a risky asset being disposed off by investors.
• Euro ( CME:6E1! ): -14.07%. With geopolitical risk compounding a recession, the economic outlook of the Euro-Zone countries is very gloomy
• High Grade Copper ( COMEX:HG1! ): -23.77%. Copper demand will decline in the event of global recession. Futures market has fully priced this in
• Soybean ( CBOT:ZS1! ): +6.54%. Corn futures was up 25% in June. But the gain was largely given away as the fear of recession outweighed the risk of food crisis
In a “flight to safety”, investors shift their assets out of stocks, bonds and commodities, into US dollars instead. With strong exchange rate and high interest rate, US dollar appears to be the only “safe haven” in market turmoil.
How to Invest in Dollar?
If you are holding financial assets in foreign currency, converting them into US dollar is a logical first step.
A risk-averted investor may put dollars into a flowing rate bank account, or purchase money market fund. In a defensive move, you park money in US dollar account until market stabilizes and new investment opportunities emerge. Don’t tie up your money in long-duration deposit, as interest rate is almost certainly going to rise.
An active investor may consider trading risk-free US treasury bonds. Other dollar bonds such as corporate bond, convertible bond and municipal bond are subject to repricing.
Bond price and bond yield are inversely related. As we expect yield to go up, a trade could be constructed by shorting a cash treasury bond, or shorting CBOT treasury bond futures.
CBOT Micro Yield Futures list for two consecutive months. They are more intuitive to trade. If you hold the view that treasury yield would rise, long the micro yield futures. November contract will begin trading next week.
Why do I prefer 10-Year ( CBOT_MINI:10Y1! ) over 2-Year ( CBOT_MINI:2YY1! )? We are currently in an Inverted Yield Curve environment. October 2-Year Yield (2YYV2) is quoted at 4.196%, but the 10-year contract (10YV2) is quoted at 3.739%, 457 points lower. In my opinion, rate hikes are fully priced in on the 2YY quote, but 10Y may still have some upside potential.
The next FOMC meeting is November 1-2, and the rate decision would be announced at 2PM eastern time on November 2nd. The 10Y November contract may trade till the end of November.
Financial market is extremely volatile this year. Getting an information edge increases your odds of success in managing risk. I suggest leveraging real-time market data for a better gauge of market situation. TradingView users already have access to delayed data. A Pro user could upgrade to real-time CME market data for only $4 a month, a huge discount at the time of high inflation.
Happy Trading.
Disclaimers
*Trade ideas cited above are for illustration only, as an integral part of a case study to demonstrate the fundamental concepts in risk management under the market scenarios being discussed. They shall not be construed as investment recommendations or advice. Nor are they used to promote any specific products, or services.
The yield curve has inverted, how to overcome this?Content:
• Difference between interest rate and yield?
• Why it is important to note of yield curve inversion?
• How to tell when Yields are inverted?
• What is the long-term trend for interest rates and yields
• How to manage a rising yield?
Disclaimer:
• What presented here is not a recommendation, please consult your licensed broker.
• Our mission is to create lateral thinking skills for every investor and trader, knowing when to take a calculated risk with market uncertainty and a bolder risk when opportunity arises.
1. Difference between interest rate and yield?
i. Interest rates are a benchmark for borrowers and
ii. Yields are for lenders. For eg. investors to the U.S. government
iii. Both interest rates and yields move in tandem together
3. Why is it important to note yield inversion?
i. For eg. - when the return on a 30-years yield is lower than the 2-year yield, that indicates a
ii. For lenders or investors – a pessimistic outlook, a reluctance to commit their money to the longer-term bond, they prefer short-term deposits as the market is unclear in the long-term.
iii. For borrowers – most individuals or companies have shorter-term borrowing, for eg a 2 years fixed rate or a bridging loan. When the yields are inverted, suddenly they find them paying more on interest rates repayment.
Since interest rates and yields move in tandem, expect the shorter-term lending rates to go higher. This will hurt companies and individuals who have higher leverage items on their books.
If you are into shorter-term trading, do look into the market with live feed data.
I am starting an inflation series, in the next video tutorial, we will discuss why inflation is happening not just in U.S. but all around the world.
Micro 10 Years Yield Futures
0.001 = US$1
3.488 = 3488 x US$1 = US$3,488
3188 to 3488 = 300 x US$1 = US$300
Huge Recession WarningWith the 2022 recession ever coming closer, more hints that it’s nearing appear. One of those hints include this graph, which shows the 1 year bond surpassing the 4% mark, and it’s more than any other bond. For the first time in more than 15 years, the 1 year bond surpasses 4%. The yield curve has been inverted for more than 1 month, and it’s still inverted. At any point Black Monday can happen and crash the market. I believe the recession that is about to happen will be worse than even the 2008 recession. It’s more of a depression, not a recession. The 1 year bond didn’t reach as high back then before the recession.
TVC:US01Y
SP:SPX
The Real Cost of Fed Rate HikesCBOT_MINI:10Y1! CBOT_MINI:2YY1!
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is scheduled to meet on July 26-27. Market widely expects a 75-basis-points (bps) Fed Funds rate increase, from current target of 1.50%-1.75% to 2.25%-2.50%. The call for a 100-point hike, while still feasible, is weakened after U.S. gasoline price dropped 70 cents per gallon in the past month. New data hints that the runaway inflation may be contained.
Federal funds Rate is the interest rate that banks charge each other to borrow or lend excess reserves overnight. It is the most important global interest rate benchmark, as it directly or indirectly influences the borrowing cost for governments, corporations, and households. By the end of July, Fed Funds would have gone up by 2.25% (assuming 75 bps hike in July) from zero before March. The Fed is not afraid of raising rate even higher until inflation moves back to its 2% policy target.
How much will a higher interest rate cost for government, business, or household? I will illustrate the impact of 100bps rate increase in this analysis. All data comes from either the Fed or USdebtclock.org, unless otherwise noted.
Total Debt : By the end of Q1 2022, the total debt outstanding in the U.S. by both public and private sectors is $90.1 trillion. Mind-boggling. What does the number mean?
• U.S. GDP was $23.0 trillion in 2021. Debt-to-GDP ratio is 3.92. It would take all Americans four years to pay off their debt, without spending or paying interest.
• US population is 332,403,650 as of January 2022 per US Census Bureau. Debt per capita is $270,949. Each time a baby is born, he or she already owes more than a quarter million dollar.
US National Debt : $30.6 trillion based on USdebtclock.org real-time calculation. This is just the debt owed by Federal government and various federal agencies.
• National Debt to GDP ratio: 133%.
• Federal tax revenue is estimated at $4.4 trillion in 2022. If our government just levies taxes and does nothing else, it will take seven years to pay off the debt.
• Federal budget is $6.0 trillion in 2022, with budget deficit running at $1.6 trillion. Interest on debt is $440 billion, the fourth largest budget item. If interest rate goes up 100 bps across the yield curve, federal government will have to come up with $306 billion extra to service the debt.
• Federal budget in 2022: $6.0 trillion
o budget deficit $1.6 trillion
o Interest on debt $440 billion (4th largest budget item)
o Remark: $306 billion extra to service the debt, if interest rate goes up by 100bps
• When all the rate hikes are over, annual debt interest payment could be over $1.0 trillion. It would become the 3rd largest budget item, behind Medicare ($1.4 trillion), Social Security ($1.0 trillion) and ahead of Defense ($751 billion)!
State and Local Government debt : $3.3 trillion, of which $2.1 trillion from state governments and $1.2 trillion from local governments.
• If interest rate goes up by 100 bps, state and local governments will have to come up with $33 billion extra to service their debt.
• We may expect tax hikes from state and local governments, while public services may be cut back at the same time.
US Corporate Debt : $11 trillion, which includes all debt issued by non-financial corporations domiciled in the U.S.
• If interest rate goes up by 100 bps, American businesses will have to come up with $110 billion extra to service their debt.
• We may expect higher prices for goods and services, as businesses pass on the interest cost to consumers.
• Companies with high debt ratio may increase the chance of delinquency.
US Household Debt : $23.5 trillion. This includes mortgage, auto loan, credit card loan and student loan, etc.
• Personal debt per citizen is $70,304. If interest rate goes up by 100 bps, each person will have to come up with $703 extra a year to service their debt.
• American families are fighting with a higher cost-of-living on multiple fronts. If the U.S. falls into a recession, their financial situation will worsen significantly.
• Mortgage delinquency is expected to rise significantly.
The remainder, approximately $21 trillion, is outstanding balance of credit instruments issued by banks and other financial institutions.
Believe it or not, we have only just scrubbed the surface of our mounting debt problem. Most government liabilities are unfunded or underfunded. Each year, the Federal Government borrows new money to pay off the maturing debt.
Medicare, Medicaid, and Social Security are pay-as-you-go programs. Government taxes current workers to pay for the benefits of retirees, without any money saving up for current workers. No one has a crystal ball if the benefits are still there when they reach retirement.
With such a depressing future ahead of us, are there any trading opportunities? The answer is yes. I am counting on the inverted yield curve to return to historical normal.
Yield curve plots the interest rates on government bonds with different maturity dates, notably three-month Treasury Bills, two-year and 10-year Treasury Notes, 15-year and 30-year Treasury Bonds. Bond investors expect to be paid more for locking up their money for a long stretch, so interest rates on long-term debt are higher than those on short-term. Plotted out on a chart, the various yields for bonds create an upward sloping line.
Sometimes short-term rates rise above long-term ones. That negative relationship is called yield curve inversion. An inversion has preceded every U.S. recession for the past half century, so it’s seen as a leading indicator of economic downturn.
On July 21st, the yield on two-year Treasury notes stood at 3.00 percent, above the 2.91 percent yield on 10-year notes. By comparison, two-year yields were one percentage point lower than the 10-year yields a year ago.
Why are we seeing yield curve inversion now? Short-term yield directly responded to Fed rate hikes. It has gone up 225 bps in five months. Longer term yields are determined by credit market supply and demand. The prospect of an upcoming recession held off lending by businesses and households alike, keeping the yields relatively stable.
In my opinion, yield curve inversion could not sustain for long. Borrowers would flock to lower rate debt, pushing up demand for longer term credit. Market force would revert the yield curve to a normal one with interest rates on long-term debts higher than those on short-term ones.
Are there any instruments we could leverage to trade the reversal of yield curve inversion? Long the Spread of CBOT Micro 10-Year Yield (10Y) and 2-Year Yield (2YY) .
Traditional Treasury Futures are quoted in Treasury Notes price, which can be viewed as the present value of future payments that bondholder will receive – interest payment every six months and the return of principal at par value at maturity.
Micro Yield Futures are more intuitive. They are quoted in yield directly. On July 22nd, August 10Y Yield Futures (10YQ2) was settled at 2.819. August 2Y Yield Futures (2YYQ2) was settled at 3.06. The 10Y-2Y spread is -0.241.
The 10Y-2Y spread has been positive in recent years. It turned negative in the beginning of July as we experienced the inverted yield curve. I expect the spread to return to historic normal - a positive number, in the coming months.
To trade Micro Yield futures, margins are $240 for 10Y and $330 for 2YY. A long spread can be constructed by a Long 10Y and a Short 2YY positions.
The great thing about a spread trade lies with the fact that you don’t have to be right in predicting the direction of interest rates. Spread will be widened if 10Y rises faster than 2YY. Even in a falling rate environment, if 10Y fell less than 2YY, the spread will be enlarged too.
Happy Trading.
Disclaimers
*Trade ideas cited above are for illustration only, as an integral part of a case study to demonstrate the fundamental concepts in risk management under the market scenarios being discussed. They shall not be construed as investment recommendations or advice. Nor are they used to promote any specific products, or services.
Opportunity to buy US Treasuries and a failing fiat system?The 2/10 treasury yield spread is approaching an inversion.
All of the previous yield curve inversions were associated with catastrophic event many of which stemming out of a fiat monetary system that seems very obviously to be failing.
We are seeing the failing fiat monetary system if we look at the amount of money being created out of thin air by the FED (and ECB, Bank of England, Bank of Japan).
The FED is expected to raise interest rates at its May 3-4, 2022 meeting.
More rate hikes are expected to follow, with the goal of reducing inflation.
The markets anticipate that the federal funds rate will exceed 3% by early 2023.
The dollar is showing great strength across other leading currencies.
If you invest in treasury you can get a fair interest rate of 3% (and assuming with more rate hikes even more), as US treasuries bond are available at a great rebate.
Do consider the currency devaluation possible if your base living currency is not the USD.
Recession Risk IncreasingWidespread economic data reflecting unhealthy market indicating significant risk of total market correction (stagflation/recession)
1. Inflation (CPI, PPI) sharly rising at levels not seen in 4 decades
2. Leading indicator: New Home Sales declining, with increasing housing supply
3. Lagging Indicator: Durable Goods month over month and year over year declined
4. Commodity prices rising sharply including oil closing in on all time high
5. Money supply at volumes far above sustainable levels
6.Overnight Reverse Repo currently at $1.7 Trillion
7. Gold monthly chart reflects bullish cup and handle pattern formed from 2011 to present with price target of $2.5k
Labor market is realizing extreme shortage, with decreasing labor availability in a trend that the BLS has identified for years. Competition for scarce labor increasing as there are more jobs than total workforce available to fill them even at 100% employment. This trend is predicted to continue for the remainder of this decade.
Federal Reserve lacks credibility with current regime losing ability to sway markets. FOMC communicated tightening policies with incremental 25 bps rate hike and the markets responded with the healthiest week of growth in over 2 years.
FYI - Will Stock market History Repeat itself? From 10-8-2019 CNBC Article
The father of the yield curve indicator says now is the time to prepare for a recession.
The yield for the 3-month Treasury has been above the 10-year since May, a condition known as an inverted yield curve that has predicted the past seven recessions.
“This is the time where you need to reflect upon your strategy."
“It’s way better to have a plan to go by than to find yourself in a situation where the recession hits and you have to improvise.”
My opinion: Need to be extra ready to get out of the market when the yield curve crosses above zero.
Source: www.cnbc.com