How Will Uncle Sam Strike Back? – U.S. Treasuries on the Edge📉 How Will Uncle Sam Strike Back? – U.S. Treasuries on the Edge
After covering leveraged loans ( BKLN ), junk bonds ( HYG ), and investment-grade corporates ( LQD ), we now focus on the most important piece of the U.S. credit puzzle: Treasuries.
Specifically, the long end of the curve — tracked by TLT .
📊 What the Chart Shows
Left Panel (3D Chart)
• All-time highs in Feb 2020 at $179.80
• Long-term trendline going back to 2004
• Critical support was broken in 2022 — a structural breakdown
Right Panel (8H Chart)
• Clear descending channel since 2020
• Price has rejected from the channel top multiple times
• Recent bounces off the lower channel suggest a potential final flush
🧠 What Happened in 2022? (can't blame Trump for that...)
This wasn’t politics — it was policy.
• The Fed's fastest hiking cycle in decades
• Liquidity evaporated
• Long-duration bonds were abandoned
• The key trendline that had held for years was finally lost
That line — once support — is now resistance.
📐 My Technical Expectation
I expect one final slide before a reversal.
• Channel base sits at ~$76.32
• My projection targets $71.30 or even $68
• That would mark new all-time lows for TLT
🟡 After that? I expect a macro reversal , targeting:
• 🔼 $101 – mid-channel reversion
• 🔼 $112–115 – former support zone (2019–2022), now resistance
🔍 Macro Context
This chart isn’t just about price.
It reflects how markets are pricing confidence in U.S. debt .
And right now?
That confidence is shaky . With Trump turning 'orange' and taking it out against almost everyone else: China but also his allies(EU, Canada, Japan, etc )
🔄 Recap of the Series So Far:
• BKLN – record leveraged loan outflows
• HYG – junk bonds bounced at historical support
• LQD – investment grade bonds holding steady
• TLT – U.S. Treasuries under pressure, and possibly breaking down
📌 Next up?
🟧 CRYPTOCAP:BTC
Because when the world begins to question Treasuries , the search for alternative stores of value begins.
One Love,
The FXPROFESSOR 💙
ps. wait for the next posts...they might be epic!
Treasurybonds
Economic Red Alert: China Dumps $8.2T in US BondsThe Great Unwinding: How a World of Excess Supply and Fading Demand Is Fueling a Crisis of Confidence
The global financial system, long accustomed to the steady hum of predictable economic cycles, is now being jolted by a dissonant chord. It is the sound of a fundamental paradigm shift, a tectonic realignment where the twin forces of overwhelming supply and evaporating demand are grinding against each other, creating fissures in the very bedrock of the world economy. This is not a distant, theoretical threat; its tremors are being felt in real-time. The most recent and dramatic of these tremors was a stark, headline-grabbing move from Beijing: China’s abrupt sale of $8.2 trillion in U.S. Treasuries, a move that coincided with and exacerbated a precipitous decline in the U.S. dollar. While the sale itself is a single data point, it is far more than a routine portfolio adjustment. It is a symptom of a deeper malaise and a powerful accelerant for a crisis of confidence that is spreading through the arteries of global finance. The era of easy growth and limitless demand is over. We have entered the Great Unwinding, a period where the cracks from years of excess are beginning to show, and the consequences will be felt broadly, from sovereign balance sheets to household budgets.
To understand the gravity of the current moment, one must first diagnose the core imbalance plaguing the global economy. It is a classic, almost textbook, economic problem scaled to an unprecedented global level: a glut of supply crashing against a wall of weakening demand. This imbalance was born from the chaotic response to the COVID-19 pandemic. In 2020 and 2021, as governments unleashed trillions in fiscal stimulus and central banks flooded the system with liquidity, a massive demand signal was sent through the global supply chain. Consumers, flush with cash and stuck at home, ordered goods at a voracious pace. Companies, believing this trend was the new normal, ramped up production, chartered their own ships, and built up massive inventories of everything from semiconductors and furniture to automobiles and apparel. The prevailing logic was that demand was insatiable and the primary challenge was overcoming supply-side bottlenecks.
Now, the bullwhip has cracked back with a vengeance. The stimulus has faded, and the landscape has been radically altered by the most aggressive coordinated monetary tightening in modern history. Central banks, led by the U.S. Federal Reserve, hiked interest rates at a blistering pace to combat the very inflation their earlier policies had helped fuel. The effect has been a chilling of economic activity across the board. Demand, once thought to be boundless, has fallen off a cliff. Households, their pandemic-era savings depleted and their purchasing power eroded by stubborn inflation, are now contending with cripplingly high interest rates. The cost of financing a home, a car, or even a credit card balance has soared, forcing a dramatic retrenchment in consumer spending. Businesses, facing the same high borrowing costs, are shelving expansion plans, cutting capital expenditures, and desperately trying to offload the mountains of inventory they accumulated just a year or two prior.
This has created a world of profound excess. Warehouses are overflowing. Shipping rates have collapsed from their pandemic peaks. Companies that were once scrambling for microchips are now announcing production cuts due to a glut. This oversupply is deflationary in nature, putting immense downward pressure on corporate profit margins. Businesses are caught in a vise: their costs remain elevated due to sticky wage inflation and higher energy prices, while their ability to pass on these costs is vanishing as consumer demand evaporates. This is the breeding ground for the "cracks" that are now becoming visible. The first casualties are the so-called "zombie companies"—firms that were only able to survive in a zero-interest-rate environment by constantly refinancing their debt. With borrowing costs now prohibitively high, they are facing a wave of defaults. The commercial real estate sector, already hollowed out by the work-from-home trend, is buckling under the weight of maturing loans that cannot be refinanced on favorable terms. Regional banks, laden with low-yielding, long-duration bonds and exposed to failing commercial property loans, are showing signs of systemic stress. The cracks are not isolated; they are interconnected, threatening a chain reaction of deleveraging and asset fire sales.
It is against this precarious backdrop of a weakening U.S. economy and a global supply glut that China’s sale of U.S. Treasuries must be interpreted. The move is not occurring in a vacuum. It is a calculated action within a deeply fragile geopolitical and economic context, and it carries multiple, overlapping meanings. On one level, it is a clear continuation of China’s long-term strategic objective of de-dollarization. For years, Beijing has been wary of its deep financial entanglement with its primary geopolitical rival. The freezing of Russia’s foreign currency reserves following the invasion of Ukraine served as a stark wake-up call, demonstrating how the dollar-centric financial system could be weaponized. By gradually reducing its holdings of U.S. debt, China seeks to insulate itself from potential U.S. sanctions and chip away at the dollar's status as the world's undisputed reserve currency. This $8.2 trillion sale is another deliberate step on that long march.
However, there are more immediate and tactical motivations at play. China is grappling with its own severe economic crisis. The nation is battling deflation, a collapsing property sector, and record-high youth unemployment. In this environment, its primary objective is to stabilize its own currency, the Yuan, which has been under intense downward pressure. A key strategy for achieving this is to intervene in currency markets. Paradoxically, this intervention often requires selling U.S. Treasuries. The process involves the People's Bank of China selling its Treasury holdings to obtain U.S. dollars, and then selling those dollars in the open market to buy up Yuan, thereby supporting its value. So, while the headline reads as an attack on U.S. assets, it is also a sign of China's own domestic weakness—a desperate measure to defend its own financial stability by using its vast reserves.
Regardless of the primary motivation—be it strategic de-dollarization or tactical currency management—the timing and impact of the sale are profoundly significant. It comes at a moment of peak vulnerability for the U.S. dollar and the Treasury market. The dollar has been extending massive losses not because of China’s actions alone, but because the underlying fundamentals of the U.S. economy are deteriorating. Markets are increasingly pricing in a pivot from the Federal Reserve, anticipating that the "cracks" in the economy will force it to end its tightening cycle and begin cutting interest rates sooner rather than later. This expectation of lower future yields makes the dollar less attractive to foreign investors, causing it to weaken against other major currencies.
China’s sale acts as a powerful accelerant to this trend. The U.S. Treasury market is supposed to be the deepest, most liquid, and safest financial market in the world. It is the bedrock upon which the entire global financial system is built. When a major creditor like China becomes a conspicuous seller, it sends a powerful signal. It introduces a new source of supply into a market that is already struggling to absorb the massive amount of debt being issued by the U.S. government to fund its budget deficits. This creates a dangerous feedback loop. More supply of Treasuries puts downward pressure on their prices, which in turn pushes up their yields. Higher Treasury yields translate directly into higher borrowing costs for the entire U.S. economy, further squeezing households and businesses, deepening the economic slowdown, and increasing the pressure on the Fed to cut rates, which in turn further weakens the dollar. China’s action, therefore, pours fuel on the fire, eroding confidence in the very asset that is meant to be the ultimate safe haven.
The contagion from this dynamic—a weakening U.S. economy, a falling dollar, and an unstable Treasury market—will not be contained within American borders. The cracks will spread globally, creating a volatile and unpredictable environment for all nations. For emerging markets, the situation is a double-edged sword. A weaker dollar is traditionally a tailwind for these economies, as it reduces the burden of their dollar-denominated debts. However, this benefit is likely to be completely overshadowed by the collapse in global demand. As the U.S. and other major economies slow down, their demand for raw materials, manufactured goods, and services from the developing world will plummet, devastating the export-driven models of many emerging nations. They will find themselves caught between lower debt servicing costs and a collapse in their primary source of income.
For other developed economies like Europe and Japan, the consequences are more straightforwardly negative. A rapidly falling dollar means a rapidly rising Euro and Yen. This makes their exports more expensive and less competitive on the global market, acting as a significant drag on their own already fragile economies. The European Central Bank and the Bank of Japan will find themselves in an impossible position. If they cut interest rates to weaken their currencies and support their exporters, they risk re-igniting inflation. If they hold rates firm, they risk allowing their currencies to appreciate to levels that could push their economies into a deep recession. This currency turmoil, originating from the weakness in the U.S., effectively exports America’s economic problems to the rest of the world.
Furthermore, the instability in the U.S. Treasury market has profound implications for every financial institution on the planet. Central banks, commercial banks, pension funds, and insurance companies all hold U.S. Treasuries as their primary reserve asset. The assumption has always been that this asset is risk-free and its value is stable. The recent volatility and the high-profile selling by a major state actor challenge this core assumption. This forces a global repricing of risk. If the "risk-free" asset is no longer truly risk-free, then the premium required to hold any other, riskier asset—from corporate bonds to equities—must increase. This leads to a tightening of financial conditions globally, starving the world economy of credit and investment at the precise moment it is most needed.
In conclusion, the abrupt sale of $8.2 trillion in U.S. Treasuries by China is far more than a fleeting headline. It is a critical data point that illuminates the precarious state of the global economy. It is a manifestation of the Great Unwinding, a painful transition away from an era of limitless, debt-fueled demand and toward a new reality defined by excess supply, faltering consumption, and escalating geopolitical friction. The underlying cause of this instability is the deep imbalance created by years of policy missteps, which have left the world with a glut of goods and a mountain of debt. The weakening U.S. economy and the resulting slide in the dollar are the natural consequences of this imbalance. China’s actions serve as both a symptom of this weakness and a catalyst for a deeper crisis of confidence in the U.S.-centric financial system. The cracks are no longer hypothetical; they are appearing in the banking sector, in corporate credit markets, and now in the bedrock of the system itself—the U.S. Treasury market. The tremors from this shift will be felt broadly, ushering in a period of heightened volatility, economic pain, and a fundamental reordering of the global financial landscape.
US10Y Big downside potentialThe U.S. Government Bonds 10YR Yield (US10Y) has been since last week on a 1D MA50 (blue trend-line) rebound, consistently rising since the April 04 Low (Support 1). The presence of the Lower Highs trend-line just above it, puts strong selling pressure long-term.
As a result, either now or upon a Lower Highs contact, we expect the US10Y to turn bearish and Target 3.860% (Support 1).
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
** Please LIKE 👍, FOLLOW ✅, SHARE 🙌 and COMMENT ✍ if you enjoy this idea! Also share your ideas and charts in the comments section below! This is best way to keep it relevant, support us, keep the content here free and allow the idea to reach as many people as possible. **
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
💸💸💸💸💸💸
👇 👇 👇 👇 👇 👇
China is about to decided whether retailiate or not. Donald Trump and hes administration went to far and to many direction.
EU and China at the same time is just too much but tretening the whole world is just an enormous startegic error.
He made woke up not1 but 170 bear at the same time while the bears were sleeping and dreaming. And the dream ended. The USA not enymore realiable, trustworty, and therefore friendly country. The bears are dissapointed and angrys.
They dont wanna have does fals dreams at the next time, and its seems that Trump is in a deadend roed.
Honestly this story can be continued for pages but lets just speak about the an abnormal situation.
BONDS UP 10Y 5Y - trough agressive selling of US debt which is really will tied up the FED hands if the inflation does not happen due to the lack of the tarrifs. 10Y is at the 4,3
The questions can china put the USA in a situation then interest rate cat wount help on the longrun since China and may some of their contries under their influence reaching high detach in a US10Y 5Y and interest rate relation and sending US in to debt cicle.
The slow one is that that will slowly sell as much debt of US that they are cancelling the fed rate cuts.
The fast one is sending aup rates by at least 6% and making the big boys on the stock market to capitulate.
I will update and elaborate this idea better , but I hope if someone reads gets some hints.
iShares 20 Year Treasury Bond | TLT | Long in the $80sFor the patient, one of the "safest" investments is in long-term treasury bonds (specifically NASDAQ:TLT ). For those who may not understand why, bond prices move inversely to yields. If interest rates drop (which the Federal Reserve has stated is going to happen this year), NASDAQ:TLT will rise. If interest rates rise (like what happened in early 2022), NASDAQ:TLT will fall. But all information from the Federal Reserve points to interest rate cuts starting this year *or* in the near future.
As of April 1st, 2025, the dividend yield for NASDAQ:TLT is 4.52%. That interest rate beats the vast majority of savings accounts right now. I don't think we will see NASDAQ:TLT prices in the $80's longer than a year or two. A contrarian may argue "inflation is rising!", but the data continue to point to it actually stabilizing. Yes, prices are higher compared to 4-5 years ago for just about everything... but the higher prices are "stable". Tariffs may put a slight wrinkle in this stability in the near-term, but I think the economy is already slowing and the Federal Reserve will be pressured to start dropping interest rates sooner than later.
I believe a global economic bust is inevitable - but no one knows when. Anyone who says they can time it is a charlatan. If/when a global economic bust occurs, the Federal Reserve will drop interest rates (like what happened in 2020) to get the economy juiced up again. NASDAQ:TLT will double in price or go further.
My general point is I *believe* NASDAQ:TLT is nearing a low and any future declines (especially below $80) are personal opportunities for buy-and-hold. It's a solid hedge with a good dividend. Options don't give you that and timing events is a guessing game for every retail trader. So, as someone who tries to think beyond the "now", I am gathering shares, enjoying the dividend, and not touching them until a global economic bust occurs. Currently holding positions at $85, $86, $87, and $90.
Targets:
2027: $100.00
2028: $105.00
2029: $110.00
2030: $115.00
Bust (unknown timing): $170+
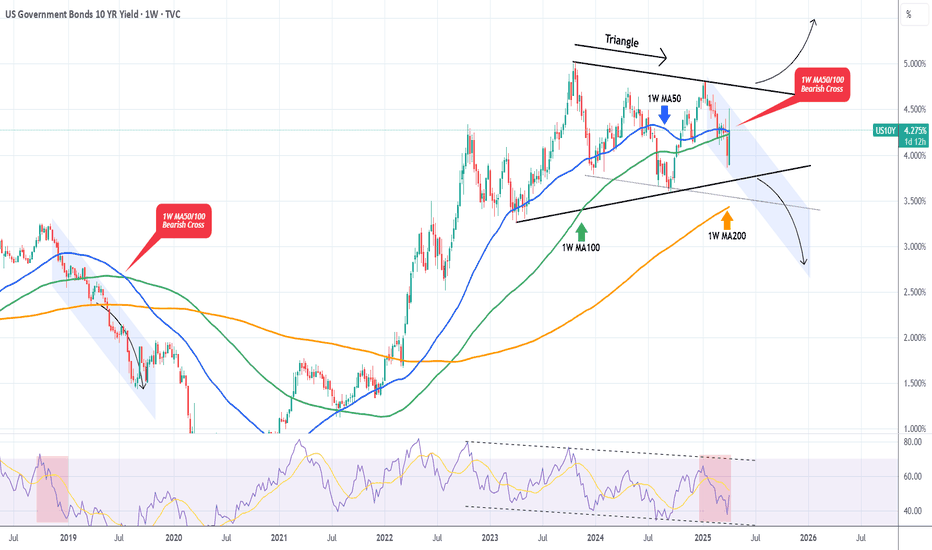
US10Y This break-out will be massive.The U.S. Government Bonds 10YR Yield (US10Y) is trading within a 2-year Triangle pattern and following this week's trade events, got back on its 1W MA50 (blue trend-line). A potential break-out either way from this long-term pattern will be massive.
We do believe though that there are higher probabilities for a bearish break-out as the 1W MA50 is about to cross below the 1W MA100 and form the first 1W MA50/100 Bearish Cross since July 22 2019. Interestingly enough, that was following the last Trade War between the U.S. and China.
At the same time, the 1W RSI has been within a Channel Down since late 2022, indicating a huge Bearish Divergence.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
** Please LIKE 👍, FOLLOW ✅, SHARE 🙌 and COMMENT ✍ if you enjoy this idea! Also share your ideas and charts in the comments section below! This is best way to keep it relevant, support us, keep the content here free and allow the idea to reach as many people as possible. **
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
💸💸💸💸💸💸
👇 👇 👇 👇 👇 👇
TLT Short Term OutlookHere we have TLT moving according to our previously published chart. We think TLT will move sideways, consolidating in the near future before finding direction. Although the outlook for TLT and the Bond Market is positive, in the near short term we may see a decline in the bonds market and choppy movements. We anticipate a zigzag move followed by a possible price retest of near $85 before bouncing back up.
TLT Analysis: Bonds in Turmoil Amid Tariff ChaosThis week, we've witnessed a dramatic shift as equities and U.S. government bonds cratered simultaneously. Trump, facing intense market backlash, notably reversed his aggressive tariff stance—forced by China's strategic response and market realities. At the start of the week, the yield on 10-year U.S. Treasuries stood at 4.00%, skyrocketing to 4.51% in just a matter of days—a massive jump by typical investor standards. This rapid rise significantly impacts mortgage rates, car loans, and credit card borrowing, reflecting broader financial stress.
The sharp rise in bond yields resembles the forced-selling reaction to Liz Truss and Kwasi Kwarteng's mini-budget crisis in 2022. Trump's tariff-induced inflation fears and notably weak demand in recent U.S. Treasury auctions further intensified bond selling pressure.
Technical Levels & Analysis for TLT
Hourly Chart
TLT has clearly broken crucial support levels, highlighting significant bearish momentum:
• Resistance Zone: $90.00 - $90.50
• Current Trading Zone: Approximately $88.50
• Support Zone: $86.50 - $87.00 (critical level to watch)
Daily Chart
The daily perspective confirms bearish sentiment with substantial price drops and increasing volatility:
• Major Resistance Area: $92.50 - $93.50 (strong overhead resistance where trapped longs may reside)
• Immediate Support Area: $86.50 - $87.00
Trade Ideas & Scenarios
Bearish Scenario (primary):
• Entry Trigger: A confirmed break below the immediate support at $86.50.
Profit Targets:
• Target 1: $85.00 (short-term follow-through)
• Target 2: $83.50 (potential deeper continuation)
• Stop Loss: Above $88.50, limiting risk in case of unexpected bullish reversal.
Bullish Scenario (counter-trend play):
• Entry Trigger: Strong recovery and hold above $89.00.
Profit Targets:
• Target 1: $90.50 (initial resistance)
• Target 2: $92.50 (secondary resistance level)
• Stop Loss: Below recent lows near $86.50 to tightly manage risk.
The rapid shifts in bond yields and tariffs are causing heightened market volatility. Investors must remain vigilant and maintain strict risk management. Watch these key TLT levels closely, especially amid ongoing tariff news and bond market reactions.
US10Y: 10-Year Treasury Yield – Safe Bet or Yield Trap?(1/9)
Good morning, everyone! ☀️ US10Y: 10-Year Treasury Yield – Safe Bet or Yield Trap?
With the 10-year yield at 4.358%, is it time to lock in safety or wait for better rates? Let’s break it down! 🔍
(2/9) – YIELD PERFORMANCE 📊
• Current Yield: 4.358% as of Mar 25, 2025 💰
• Historical Context: Above pandemic lows (~1-2%), below early 2000s (5-6%), per data 📏
• Sector Trend: Inverted yield curve signals caution, per economic reports 🌟
It’s a mixed bag—let’s see what’s cooking! ⚙️
(3/9) – MARKET POSITION 📈
• Safe Haven: U.S. Treasuries are risk-free ⏰
• Income Appeal: 4.358% yield draws income seekers 🎯
• Potential Upside: If rates fall, bond prices rise 🚀
Firm in safety, with growth potential! 🏦
(4/9) – KEY DEVELOPMENTS 🔑
• Inverted Yield Curve: 2-year yield higher, hinting at slowdown, per data 🌍
• Fed Outlook: Expected rate cuts later in 2025, per posts on X 📋
• Market Reaction: Investors balancing income with economic risks 💡
Navigating through uncertainty! 💪
(5/9) – RISKS IN FOCUS ⚡
• Interest Rate Risk: If rates rise, bond prices drop 🔍
• Inflation Risk: Erodes real returns if inflation outpaces yield 📉
• Opportunity Cost: Missing higher returns from stocks ❄️
It’s a trade-off—risks are real! 🛑
(6/9) – SWOT: STRENGTHS 💪
• Risk-Free: No default risk, backed by U.S. government 🥇
• Liquidity: Active market for trading, per data 📊
• Tax Benefits: Interest exempt from state, local taxes 🔧
Got solid foundations! 🏦
(7/9) – SWOT: WEAKNESSES & OPPORTUNITIES ⚖️
• Weaknesses: Interest rate and inflation risks, per economic reports 📉
• Opportunities: Capital gains from falling rates, diversification benefits 📈
Can it deliver both income and growth? 🤔
(8/9) – POLL TIME! 📢
US10Y at 4.358%—your take? 🗳️
• Bullish: Buy now, rates will fall soon 🐂
• Neutral: Hold, wait for more clarity ⚖️
• Bearish: Wait for higher yields or better opportunities 🐻
Chime in below! 👇
(9/9) – FINAL TAKEAWAY 🎯
US10Y offers a steady yield with safety, but with an inverted curve, caution is advised. Gem or bust?
US10Y Strong sell signal below the 1D MA50.The U.S. Government Bonds 10YR Yield (US10Y) has been trading within a Channel Down since the October 23 2023 High. In the past 2 months it has been on a downtrend, which is the technical Bearish Leg of the pattern.
The 1D MACD is on its 2nd Bullish Cross on a decline, very similar with the previous Bearish Leg of the Channel Down. We are again on the 0.5 Fibonacci level and as long as any rebound gets rejected below or on the 1D MA50 (blue trend-line), the long-term bearish pattern remains intact.
We expect a similar Bearish Leg of -24% overall to target 3.685%.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
** Please LIKE 👍, FOLLOW ✅, SHARE 🙌 and COMMENT ✍ if you enjoy this idea! Also share your ideas and charts in the comments section below! This is best way to keep it relevant, support us, keep the content here free and allow the idea to reach as many people as possible. **
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
💸💸💸💸💸💸
👇 👇 👇 👇 👇 👇
t-bonds x alt season.t-bonds are primed for lift-off.
we just witnessed the largest decline in the history of the treasury. since march 2020, t-bonds have looked like they’re in a correction. most are calling it five waves down, signaling a deeper bear market. but they’re seeing the surface, not the structure.
i'm building a case that says otherwise.
the five-wave drop from all-time highs? that wasn’t the start of the bear market.
it was the end of wave c in an expanded flat that began in 2016.
most think the t-bond bear market started in 2020.
i’m saying it started in 2016,,,
and if i’m right, it just ended.
---
as the market prices-in future interest rate cuts, fueled by artificial suppression of gas prices and inflation stabilisation, t-bond values will climb throughout this next year.
normally, stocks and bonds move inverse to each other.
not this time.
this time, they move together. 1:1.
why? because the us dollar is about to get wrecked.
quantitative easing is coming back.
liquidity will expand.
the global liquidity index will rise.
the way we make that happen is by crushing the dxy.
---
tldr;
- rate cuts incoming
- making t-bonds go up
- quantitative easing
- nukes the dxy
- making stocks go up
- risk-on environment returns
- risk assets go parabolic
- alt season is triggered.
🌙
US10Y: Buy signal on the 1D MA50.The U.S. Government Bonds 10 YR Yield is neutral on its 1D technical outlook (RSI = 54.381, MACD = 0.046, ADX = 33.861) as it is on a bearish wave insde the long term Channel Up pattern. The last HL bottom was priced on the 1D MA50. That is the most efficient buy entry to target the 4.0 Fibonacci extension (TP 5.100).
## If you like our free content follow our profile to get more daily ideas. ##
## Comments and likes are greatly appreciated. ##
100 Years of 100% ProbabilityThis Chart shows the normalized Bollinger Band Width for the US Ten Year Treasury Bond Yield.
Basis = 10 Year SMA
Upper and Lower Bollinger Bands = 3.0 Standard Deviations from Basis
Normalized BB Width = (Upper - Lower) / Basis
For the last century, 100% of the time that US Ten Year Yields extended 3 Standard Deviations above their 10 Year SMA while their normalized Bollinger Band width reached this 100 year long trend, rates experienced a sharp and meaningful correction.
*** During World War II, width reached the trend line but rates remained at the 10 year average and did not extend 3 Standard Deviations above it.
US10Y going lower as Fed has no choice but to continue cutting.More than 1 year ago (November 7 2023, see chart below), we made a bold (for the time being) call on the U.S. Government Bonds 10YR Yield (US10Y), as against the prevailing market sentiment we gave a sell signal, right after what turned out to be a top:
Today we revisit this pattern, following yesterday's Rate Cut by the Fed primarily because of their statements that instead of 4, they will only proceed to 2 more cuts in 2025. We believe this to be false and expect the Fed to quickly resume the previous outlook.
The chart shows that the 1M RSI Lower Highs have are consistent with the previous Bearish Reversal on the US10Y price, similar to 2006 - 2007. We are expecting to hit the 0.382 Fibonacci retracement level at 2.100%, as the Fed's Cut Cycle will be accelerated in order to meet within 12-18 months their 2% inflation target and stabilize.
For better illustration we have plotted also the U.S. Interest Rate (red trend-line), where you can clearly see that the fractal we compare to today, is right before cuts started in August 2007. Also it is a natural consequence for the US10Y to fall when rate cut cycles start, evident also in June 2019, December 2000, May 1995, May 1989 September 1984, May 1981 etc.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
** Please LIKE 👍, FOLLOW ✅, SHARE 🙌 and COMMENT ✍ if you enjoy this idea! Also share your ideas and charts in the comments section below! This is best way to keep it relevant, support us, keep the content here free and allow the idea to reach as many people as possible. **
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
💸💸💸💸💸💸
👇 👇 👇 👇 👇 👇
Trump Presidency Ignites Bond Yields on Inflation ExpectationsThe “Make America Great Again” ethos has set the greenback on fire. Donald Trump's re-election has the US dollar surging 2%, extending its rally since early October to a total gain of 5%.
This resurgence is despite the anticipated 25 basis points (“bps”) rate cut at the November FOMC meeting. Dollar rally is driven by expectations of potential policy changes by the Trump Presidency.
HIGHER INFLATION EXPECTATIONS UNDER TRUMP 2.0
Trump’s election victory, combined with the Republican sweep of the Senate and the House of Representatives, gives the party the leverage to enact swift and substantial legislative changes.
His policies, such as corporate-friendly tax cuts & light-touch regulations, are expected to amplify corporate growth. These policies, combined with import tariff imposition, are expected to drive inflation higher. Rising inflation will curtail the pace of rate cuts by the Fed.
Rate cut expectations have eased since election. On November 6 (election day), projections pointed to rates reaching 350-375 bps on election day (6/Nov) per CME FedWatch tool. Now, they are expected to reach 375-400 bps.
Trump has previously pushed the Fed towards accommodative rate environment. Fed Chair Powell re-iterated that the Fed remains independent and data driven.
Source: CME FedWatch
Trump's proposed tariff policy will further strengthen the dollar. In August 2023, Trump announced plans for a universal 10% tariff on all U.S. imports, reiterating that tariffs on Chinese goods could be even higher, potentially reaching 60%-100%.
Such tariffs are expected to drive inflation higher. It will raise consumer prices and provoke retaliatory actions from trading partners, worsening inflation. Trump aims for these tariffs to revitalize American manufacturing and reduce reliance on imports which collectively support a stronger dollar.
STRONGER DOLLAR TRIGGER BOND YIELD SURGE
The resurgent dollar has contributed to the sharp rally in bond yields. The yield rally since October has resulted in the 10Y yield rising by 60 bps. Yields initially surged after the election result but partially reversed the following day after the FOMC meeting.
It currently stands 5 bps higher than the pre-election level.
Unlike the yield, the yield spread has remained flat since October. Higher for longer rates act to push this spread lower.
The Federal Reserve reaffirmed (at its Nov meeting) its dovish tone as Powell pointed to signs of an easing job market and slowing inflation. However, its impact on curbing bond yields was limited.
According to a JP Morgan report , while Fed Chair Powell has consistently conveyed a dovish tone over the years, the Fed's actual decisions have often skewed hawkish.
Although Powell’s dovish statements have initially brought bond yields down, the hawkish policy actions and Fed’s wait and watch approach that followed have typically led to renewed yield increases. This explains why yields continue to rise despite Powell’s dovish remarks at the November meeting.
HYPOTHETICAL TRADE SETUP
Treasury bond yields have been on the rise since October and Trump’s win has supercharged the rally. Investors are expecting higher inflation due to Republican policies which favour corporate growth.
Import tariff, if enacted, would have an even larger impact on the dollar and bond yields. However, actual policy plans remain uncertain for now.
While yields initially surged after the elections, they partially reversed shortly after as the Fed signalled a dovish stance. Despite this, the 10Y-2Y yield spread has remained unchanged.
Resurgent inflation will lead to the Fed slowing the pace of rate cuts. The recent reversal in yield spreads may be unsustainable given the expectation for slower rate cuts. When Trump administration announces policy plans, yields could surge even more strongly.
This week’s CPI release is anticipated to influence bond market movements. Analysts expect October’s YoY inflation to remain steady at 2.4%. If inflation holds at this level, it may have minimal impact, aligning with the Fed’s "watch and wait" strategy. However, a sharper-than-expected drop in inflation could reinforce expectations of quicker Fed rate cuts.
With the impact of inflation most apparent on the longer-tenor yields, investors can focus the position on the 10Y-2Y spread.
CME Yield Futures are quoted directly in yield with a 1 basis-point change representing USD 10 in one lot of Yield Future contract. This simplifies spread calculations with a 1 bps change in spread representing profit & loss of USD 10.
The individual margin requirements for 2Y and 10Y Yield futures are USD 330 and USD 320, respectively. However, with CME Group’s 50% margin offset for the spread, the required margin drops to USD 325 as of 12/Nov, making this trade even more capital efficient.
A hypothetical long position on the CME 10Y yield futures and a short position on the 2Y yield futures offers a reward to risk ratio of 1.3x is described below.
Entry: 6.2 basis points
Target: -11.5 basis points
Stop Loss: 20 basis points
Profit at Target: USD 177 ((6.2 - (-11.5)) x 10)
Loss at Stop: USD 138 ((6.2 - 20) x 10)
Reward to Risk: 1.3x
MARKET DATA
CME Real-time Market Data helps identify trading set-ups and express market views better. If you have futures in your trading portfolio, you can check out on CME Group data plans available that suit your trading needs tradingview.com/cme .
DISCLAIMER
This case study is for educational purposes only and does not constitute investment recommendations or advice. Nor are they used to promote any specific products, or services.
Trading or investment ideas cited here are for illustration only, as an integral part of a case study to demonstrate the fundamental concepts in risk management or trading under the market scenarios being discussed. Please read the FULL DISCLAIMER the link to which is provided in our profile description.
Yield Curve Reinverts on Easing Rate Cut ExpectationsFed sets the rates. Rates guide treasury yields. Fed remains data dependent. Incoming data creates nuanced shifts in yield spreads.
The September jobs report revealed 254,000 jobs added, significantly exceeding expectations of 147,000, with August figures also revised upward. This strong report, along with the JOLTS data from earlier in the week, indicates that the job market remains strong and not as weak as previously anticipated.
Despite the strong jobs data, the yield curve has inverted once again. While Mint Finance has previously highlighted that recession risks can lead to the yield curve inverting, that is not the only reason. This time around, the inversion is being driven by delay in rate cut expectations. CME’s Yield Futures enables investors to deftly express their views on the path of rates ahead.
JOB MARKET SHOWS MIXED SIGNS OF RECOVERY
The latest JOLTS figures showed U.S. job openings rising from 7.711 million to 8.090 million in August, with the previous month's numbers revised up by 38,000. Although job openings remain near a two-year low, the increase is a positive sign.
Rise in job openings was primarily due to increase in construction jobs (+138k), which are often seasonal, and government jobs (+103k). However, the overall report paints a mixed picture. Hiring fell by 99k from the previous month, and while total separations dropped by 317,000, the largest contributor was a 159,000 contraction in quits.
With fewer hires and a large drop in quits, the data suggests the job market is not particularly strong, as workers hesitate to leave their current positions with fewer being hired into new roles.
The Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) showed 254,000 jobs added in September, with health care, social assistance, and leisure and hospitality sectors leading the gains. As a result of these additions, the unemployment rate eased to 4.1%. Hourly earnings grew by 4% YoY, with the previous month's figures revised upward to 3.9%.
RATE CUT EXPECTATIONS TEMPER
Further rate cuts are still expected, but the anticipated pace has slowed. Before the PCE inflation report on September 27, CME FedWatch indicated a cumulative 75 basis point reduction over the next two FOMC meetings in November and December.
Source: CME FedWatch
CME FedWatch tool also indicated a high probability of 100 basis-point cuts last month. However, after the encouraging PCE report, which showed inflation easing to 2.2%—its lowest level since 2021 and close to the Fed's target—the probability of a cumulative 50 basis-point cut has steadily risen.
Following the jobs report last week, the probability of cumulative 50 basis-points cuts surged to 80%.
The trend suggests that market participants are increasingly expecting a soft landing, with inflation easing and the job market remaining strong. A soft landing reduces the urgency for aggressive rate cuts, giving the Fed more flexibility to monitor the effects of previous rate hikes and lower rates more gradually.
Source: CME FedWatch
Crucially, Fed Chair Jerome Powell has suggested a similar outlook for rate trajectory. While speaking at the National Association for Business Economics, he suggested that if the economy continues on its current trajectory, he expects two more smaller rate cuts this year, or cumulative rate cuts of 50 basis points at the next two meetings. FOMC projections also signalled a similar rate outlook for 2024 as signalled by the dot plot below.
Source: FOMC
YIELD CURVE RE-INVERTS
Bond yields have increased sharply to their highest level since August on tempered rate cut expectations.
Crucially, the increase has been much sharper for the 2-year yields indicating near-term expectations of elevated rates for longer.
The result has been a re-inversion in the yield spread with 2-year & 10-year treasury yields now on par. Notably, the yield futures spread has declined more sharply than the treasury yield spread.
HYPOTHETICAL TRADE SETUP
Recent economic data points to rising likelihood of a soft landing. Expectations of rapid rate cuts have tempered accordingly. While rates are expected to continue declining, the pace is expected to slow with a cumulative 50 basis points (“bps”) of further cuts in 2024 likely.
As rates remain elevated for an extended period, the yield curve has begun to invert again. With current inflation easing, the inflation premium on long-term treasuries has diminished.
FOMC projections suggest a gradual path toward rate normalization, suggesting a potential near-term yield curve inversion before it eventually normalizes. Investors can express views on this outlook through CME yield futures.
Further, the yield futures spread is trading at a (~5bps) premium to the treasury yield spread, as the futures contracts approaches expiry on October 31, the futures spread will converge towards the treasury yield spread which further benefits the short position.
CME Yield Futures are quoted directly in yield with a 1 basis point (“bp”) change representing USD 10 in one lot of Yield Future contract. This simplifies spread calculations with a 1 bp change in spread representing profit & loss of USD 10. The individual margin requirements for 2Y and 10Y Yield futures are USD 330 and USD 320, respectively. However, with CME’s 50% margin offset for the spread, the required margin drops to USD 325 as of October 8, making this trade even more compelling.
A hypothetical trade setup comprising of long 2Y yield October futures and short 10Y yield October futures with reward to risk ratio of 1.5x is described below.
Entry: 13.5 bps
Target: -1.5 bps
Stop Loss: 23.5 bps
Profit at Target: USD 150 (15 bps x 10)
Loss at Stop: USD 100 (10 bps x 10)
Reward/Risk: 1.5x
MARKET DATA
CME Real-time Market Data helps identify trading set-ups and express market views better. If you have futures in your trading portfolio, you can check out on CME Group data plans available that suit your trading needs tradingview.com/cme .
DISCLAIMER
This case study is for educational purposes only and does not constitute investment recommendations or advice. Nor are they used to promote any specific products, or services.
Trading or investment ideas cited here are for illustration only, as an integral part of a case study to demonstrate the fundamental concepts in risk management or trading under the market scenarios being discussed. Please read the FULL DISCLAIMER the link to which is provided in our profile description.
Chart Analysis of 10-Year U.S. Treasury Bond Yields
Based on current chart patterns and Elliott Wave Theory, it appears we are in Wave 4 of a higher-degree cycle for the 10-year U.S. Treasury bond yields. Wave 4 is typically a corrective phase following a strong trending Wave 3, suggesting that this phase may involve consolidation or retracement.
Key Levels to Watch:
38% Retracement (Lower Orange Line) : If yields bottom near this retracement level, it may indicate a potential support zone where Wave 4 could complete its correction.
61% Retracement (Upper Orange Line) : Should the yields find support at the 38% level, they might subsequently target the 61% retracement level of Wave 3, suggesting a potential upward move.
Market Implications : If the bond yields continue to rise and reach these retracement levels, we could witness a significant bearish trend in the broader market. However, it's crucial to recognize that market conditions are dynamic and can affect these projections.
Disclaimer : This analysis is based on the current technical chart patterns and Elliott Wave Theory. Market conditions are subject to change, and unforeseen factors can impact outcomes. Therefore, it's essential to stay informed and consult with a financial advisor before making investment decisions.
Regards
US10Y going lower with the Fed having no choice but to cut.Almost 10 months ago (November 7 2023, see chart below), we made a bold (for the time being) call on the U.S. Government Bonds 10YR Yield (US10Y), as against the prevailing market sentiment we gave a sell signal, right after what turned out to be a top:
Today's revisit to this pattern shows that the 1M RSI Lower Highs have already started to form a Bearish Reversal on the US10Y price, similar to 2006 - 2007. We are expecting to hit the 0.382 Fibonacci retracement level at 2.100% as its first Target, on the Fed's first wave of rate cutting and gradually hit the lower Fib targets as the rates stabilize.
For better illustration we have plotted also the U.S. Interest Rate (red trend-line), where you can clearly see that the fractal we compare to today, is right before cuts started in August 2007. Also it is a natural consequence of US10Y falling when rate cut cycles start, evident also in June 2019, December 2000, May 1995, May 1989 September 1984, May 1981 etc.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
** Please LIKE 👍, FOLLOW ✅, SHARE 🙌 and COMMENT ✍ if you enjoy this idea! Also share your ideas and charts in the comments section below! This is best way to keep it relevant, support us, keep the content here free and allow the idea to reach as many people as possible. **
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
💸💸💸💸💸💸
👇 👇 👇 👇 👇 👇
GOVT ETF: Bullish Reversal on the Horizon?The GOVT ETF, representing U.S. Treasury Bonds, shows signs of a potential bullish reversal, according to our proprietary QuantEdge Momentum System.
Key Indicators:
Z-Score:
The Z-Score has surged to 1.60, signaling an overextension to the downside in the past months. This indicates that the recent downward momentum might be exhausted, leading to a possible trend reversal.
Z-Score of RSI:
The Z-Score of RSI at 1.72 shows a significant bullish momentum shift. This suggests that the asset might be gaining strength, with buyers stepping in to push prices higher. The crossing above 0 confirms that bullish sentiment is currently prevailing.
Cumulative Volume Delta (CVD):
The CVD indicator reflects a strong buying pressure, as demonstrated by the marked shift from deep negative territory (-451,481,504) towards a less pronounced negative reading. This shift suggests that the selling pressure has weakened, and buyers are beginning to dominate the market.
Price Action:
The price has broken above the green momentum cloud, signaling a potential shift from a downtrend to an uptrend. Given the alignment of other indicators, this could be the beginning of a bullish phase for GOVT.
Projection:
Over the next quarter, GOVT is likely to experience a bullish correction, driven by strong buying momentum. The ETF could target resistance levels in the $25.00-$26.00 range if the current momentum continues. The Z-Score and RSI suggest that the upside could be substantial as the ETF looks to recover from recent losses.
However, caution is warranted if the Z-Score or RSI starts to diverge negatively, as it could indicate the potential for a correction or consolidation before resuming the uptrend. Monitoring these indicators will be crucial to confirm the strength of the reversal.
Based on the proprietary QuantEdge Momentum System, GOVT appears poised for a bullish quarter. Investors looking to capitalize on U.S. Treasury Bonds might find this an opportune time to consider GOVT as a potential buy.
10-Year T-Note vs. 10-Year Yield Futures: Which One To Trade?Introduction:
The 10-Year T-Note Futures and 10-Year Yield Futures are two prominent instruments in the financial markets, offering traders unique opportunities to capitalize on interest rate movements. This video compares these two products, focusing on their key characteristics, liquidity, and the differences in point and tick values, ultimately helping you decide which one to trade.
Key Characteristics:
10-Year T-Note Futures represent a contract based on the value of U.S. Treasury notes with a 10-year maturity, while 10-Year Yield Futures are based on the yield of these notes. The T-Note Futures contract size is $100,000, while the 10-Year Yield Futures contract size is based on $1,000 per index point, reflecting a $10 DV01 (dollar value of a one basis point move).
Liquidity Comparison:
Both 10-Year T-Note Futures and 10-Year Yield Futures are highly liquid, with substantial daily trading volumes and open interest. This high liquidity ensures tight spreads and efficient trade execution, providing traders with confidence in entering and exiting positions in both markets.
Point and Tick Values:
Understanding the point and tick values is crucial for effective trading. For 10-Year T-Note Futures, each tick is 1/32nd of a point, worth $31.25 per contract. The 10-Year Yield Futures have a tick value of 0.001 percent, worth $1.00 per contract. These values influence trading costs and profit potential differently and are essential for precise strategy formulation.
Margin Information:
The initial margin requirement for 10-Year T-Note Futures typically ranges around $1,500 per contract, while the maintenance margin is slightly lower. For 10-Year Yield Futures, the initial margin is approximately $500 per contract, reflecting its lower notional value and DV01. Maintenance margins for yield futures are also marginally lower, providing traders with flexible capital management options.
Trade Execution:
We demonstrate planning and placing a bracket order for both products. Using TradingView charts, we set up entry and exit points, showcasing how the different tick values and liquidity levels impact trade execution and potential outcomes.
Risk Management:
Effective risk management is vital when trading futures. Utilizing stop-loss orders and hedging techniques can mitigate potential losses. Avoiding undefined risk exposure and ensuring precise entries and exits help maintain a balanced risk-reward ratio, which is essential for long-term trading success.
Conclusion:
Both 10-Year T-Note Futures and 10-Year Yield Futures offer unique advantages. The choice depends on your trading strategy, risk tolerance, and market outlook. Watch the full video for a detailed analysis and insights on leveraging these products in your trading endeavors.
When charting futures, the data provided could be delayed. Traders working with the ticker symbols discussed in this idea may prefer to use CME Group real-time data plan on TradingView: www.tradingview.com This consideration is particularly important for shorter-term traders, whereas it may be less critical for those focused on longer-term trading strategies.
General Disclaimer:
The trade ideas presented herein are solely for illustrative purposes forming a part of a case study intended to demonstrate key principles in risk management within the context of the specific market scenarios discussed. These ideas are not to be interpreted as investment recommendations or financial advice. They do not endorse or promote any specific trading strategies, financial products, or services. The information provided is based on data believed to be reliable; however, its accuracy or completeness cannot be guaranteed. Trading in financial markets involves risks, including the potential loss of principal. Each individual should conduct their own research and consult with professional financial advisors before making any investment decisions. The author or publisher of this content bears no responsibility for any actions taken based on the information provided or for any resultant financial or other losses.
10yr Treasury Yields Consolidate at Key 4.32% LevelThe world’s most important market, the 10yr US Treasury, is trading directly at a critical level. Going back years, the 4.32% level has served as reliable support/resistance, and today’s drop after peeking above that level yesterday has only emphasized the importance of that key level.
At the same time, the 10yr Treasury yield has put in a series of lower highs and higher lows dating back to Q4 of last year, creating a symmetrical triangle pattern that could lead to an outbreak of volatility in the coming weeks. A bullish breakout above 4.60% would hint at a possible retest of 5.00% (and likely weigh on risk assets like stocks and higher-yielding currencies), whereas a bearish breakdown in yields would open the door for a drop toward the December lows near 3.80%.
-MW
TLT Is Coming Into Key Support Within A Corrective DeclineTreasury bond TLT has been trading lower since the start of 2024, but after an impulsive rally at the end of 2023, we believe it's just making and finishing a deep A-B-C corrective decline. It's actually now coming into key strong support zone at 61,8% - 78,6% Fibo. retracement and channel support line, from where we should be aware of bounce, recovery and continuation higher back to 2024 highs. Just keep in mind that bullish confirmation is only above channel resistance line near 92.00 region, while invalidation level remains at 82.45.