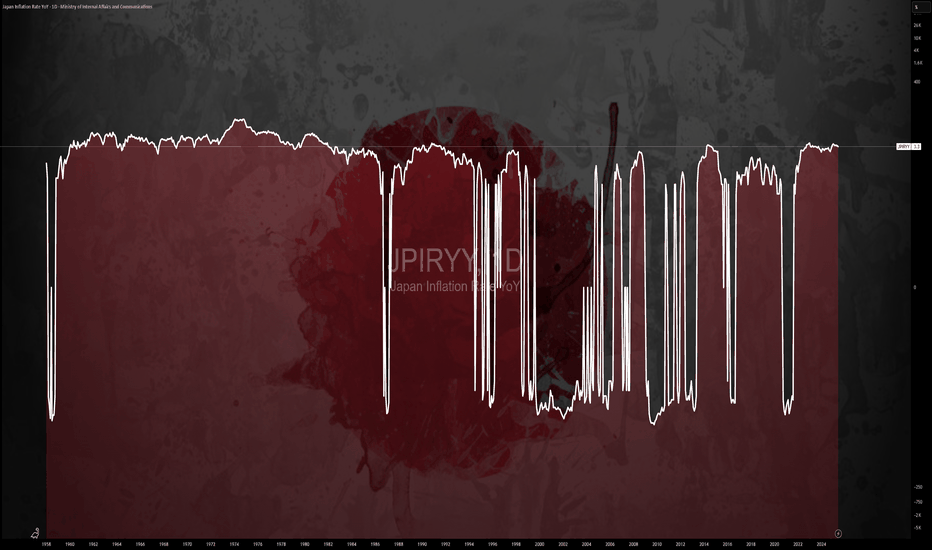
$JPIRYY -Japan Inflation Hits 7-Month Low (June/2025)ECONOMICS:JPIRYY 3.3%
June/2025
source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
-Japan’s annual inflation rate eased to 3.3% in June 2025 from 3.5% in May, marking the lowest reading since last November, as a sharp slowdown in electricity and gas prices offset persistent upward pressure from rice.
Core inflation also matched the headline rate at 3.3%, pointing to a three-month low and aligning with expectations.
JPIRYY trade ideas
$JPIRYY -Japan CPI (May/2025)ECONOMICS:JPIRYY
May/2025
source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
- Japan's annual inflation rate edged down to 3.5% in May 2025 from 3.6% in the previous two months, marking the lowest level since November.
Price growth eased for clothing (2.6% vs 2.7% in April), household items (3.6% vs 4.1%), and healthcare (2.0% vs 2.2%), while education costs fell further (-5.6%). In contrast, inflation held steady for transport (2.7%) and miscellaneous items (1.3%), but accelerated for housing (1.1% vs 1.0%), recreation (3.0% vs 2.7%), and communications (1.9% vs 1.1%).
Meanwhile, prices of electricity (11.3% vs 13.5%) and gas (5.4% vs 4.4%) remained elevated.
On the food side, prices increased by 6.5%, staying at the slowest pace in four months, though rice prices soared over 100%, underscoring the limited impact of government efforts to rein in staple food costs.
Meanwhile, the core inflation accelerated to 3.7% from 3.5% in April, reaching its highest level in over two years, ahead of the summer election.
Monthly, the CPI rose 0.3%, after a 0.1% gain in April.
$JPIRYY -Japan's CPI (April/2025)ECONOMICS:JPIRYY 3.6%
April/2025
source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
- Japan's annual inflation rate stood at 3.6% in April 2025,
unchanged from March while remaining at its lowest print since December.
Food prices rose the least in four months (6.5% vs 7.4% in March) even as rice costs jumped 94.8% y-o-y, hitting a new record for the 7th straight month due to poor harvests and rising demand from record tourist numbers.
Price growth also eased for clothing (2.7% vs 3.0%) and household items (4.1% vs 4.5%).
Cost of education fell much steeper (-5.6% vs -1.2%).
In contrast, inflation was stable for transport (at 2.7%) while accelerating for housing (1.0% vs 0.8%), healthcare (2.2% vs 2.0%), recreation (2.7% vs 2.0%), communications (1.1% vs 1.0%), and miscellaneous items (1.3% vs 1.1%).
Prices of electricity (13.5% vs 8.7% ) and gas (4.4% vs 2.4%) rose the most in three months, as the impact of government subsidies faded.
Core inflation climbed to an over 2-year high of 3.5% from 3.2% in March.
Monthly, the CPI rose 0.1%, easing from a 0.3% gain in March.
$JPIRYY -Japan's Inflation Rate (February/2025)ECONOMICS:JPIRYY
February/2025
source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
- The annual inflation rate in Japan fell to 3.7% in February 2025 from a 2-year high of 4.0% in the prior month, amid a sharp slowdown in prices of electricity (9.0% vs 18.0% in January )and gas (3.4% vs 6.8%) following the government's reinstatement of energy subsidies.
Also, food prices rose slightly slower after hitting a 15-month high in January (7.6% vs 7.8%).
Further, inflation eased for healthcare (1.7% vs. 1.8%), recreation (2.1% vs. 2.6%), and miscellaneous items (1.1% vs. 1.4%).
At the same time, education costs continued to fall (-1.1% vs. -1.1%).
In contrast, inflation remained steady for housing (at 0.8%) and clothing (at 2.8%), while accelerating for transport (2.4% vs. 2.0%) and furniture and household items (4.0% vs. 3.4%), and bouncing back for communications (0.1% vs. -0.3%).
The core inflation rate dropped to 3.0% from January's 19-month top of 3.2%, above forecasts of 2.9%.
Monthly, the CPI dropped 0.1%, the first fall since September, after a 0.5% gain in January.
$JPIRYY -Japan's Inflation Rate (CPI)ECONOMICS:JPIRYY 4%
(January/2025)
source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
- The annual inflation rate in Japan climbed to 4.0% in January 2025 from 3.6% in the prior month, marking the highest reading since January 2023.
Food prices rose at the steepest pace in 15 months (7.8% vs 6.4% in December), with fresh vegetables and fresh food contributing the most to the upturn.
Further, electricity prices (18.0% vs 18.7%) and gas cost (6.8% vs 7.8%) remained elevated with the absence of energy subsidies since May 2024.
Additional upward pressure also came from housing (0.8% vs 0.8%), clothing (2.8% vs 2.9%), transport (2.0% vs 1.1%), furniture and household items (3.4% vs 3.0%), healthcare (1.8% vs 1.7%), recreation (2.6% vs 4.0%), and miscellaneous items (1.4% vs 1.1%).
In contrast, prices continued to fall for communication (-0.3% vs -2.1%) and education (-1.1% vs -1.0%).
The core inflation rate rose to a 19-month high of 3.2%, up from 3.0% in December and topping consensus of 3.1%.
Monthly, the CPI increased by 0.5%, after December's 14-month top of 0.6% rise.
$JPIRYY -Japan Inflation Rate Highest in Near 2 YearsECONOMICS:JPIRYY 3.6%
(December/2024)
source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
- The annual inflation rate in Japan jumped to 3.6% in December 2024 from 2.9% in November,
marking the highest reading since January 2023 as food prices rose the most in a year.
Meanwhile, the core inflation rate climbed to a 16-month peak of 3%, in line with estimates.
$JPIRYY -Japan's CPI (November/2024)ECONOMICS:JPIRYY
(November/2024)
source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
- The annual inflation rate in Japan climbed to 2.9% in November 2024 from 2.3% in the prior month, marking the highest reading since October 2023.
The core inflation rate rose to a 3-month high of 2.7% in November,
up from 2.3% in October and surpassing estimates of 2.6%.
Monthly, the CPI increased by 0.6%, the highest figure in 13 months.
$JPIRYY -Japan's Inflation Rate (October/2024)ECONOMICS:JPIRYY 2.3%
October/2024
source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
-The annual inflation rate in Japan fell to 2.3% in October 2024 from 2.5% in the prior month, marking the lowest reading since January.
Electricity prices saw the smallest increase in six months (4.0% vs 15.2% in September), as the effects of the energy subsidy removal in May diminished.
Also, gas prices rose more slowly (3.5% vs 7.7%).
In addition, costs slowed for furniture and household utensils (4.4% vs. 4.8%) and culture (4.3% vs. 4.8%).
Moreover, prices dropped further for communication (-3.5% vs -2.6%) and education (-1.0% vs. -1.0%).
On the other hand, prices edged higher for food (3.5% vs 3.4%) and housing (0.8% vs. 0.7%). Meanwhile, transport prices jumped (0.5% vs. 0.1%) amid faster rises in cost of clothing (2.8% vs 2.6%), healthcare (1.7% vs 1.5%), and miscellaneous items (1.1% vs 0.9%).
The core inflation rate hit a six-month low of 2.3%, down from September's 2.4% but above estimates of 2.2%.
Monthly, the CPI increased by 0.4%, a reversal from a 0.3% fall in September.
$JPIRYY -Japan's CPI (September/2024)ECONOMICS:JPIRYY 2.5%
(September/2024)
source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
- The annual inflation rate in Japan fell to 2.5% in September 2024 from 3.0% in the prior month, marking the lowest reading since April.
Electricity prices increased the least in three months as the impact of energy subsidy removal in May waned (15.2% vs. 26.2% in August), and the cost of gas rose much more slowly (7.7% vs. 11.1%).
Moreover, costs moderated for food (3.4% vs. 3.6%), furniture & household utensils (4.8% vs. 5.2%), transport (0.1% vs. 0.2%), and culture (4.3% vs. 4.8%).
Additionally, prices fell further for communication (-2.6% vs. -2.4%) and education (-1.0% vs. -1.0%).
On the other hand, inflation remained unchanged for housing (0.7%) and healthcare (1.5%), while edging higher for clothes (2.4% vs. 2.3%) and miscellaneous (0.9% vs. 0.8%).
Meanwhile, the core inflation rate hit a five-month low of 2.4%, down from August's 2.8%, compared with the consensus of 2.3%.
On a monthly basis, the CPI declined by 0.3%, pointing to the first drop since February 2023.
$JPIRYY -Japan Inflation Rate YoYECONOMICS:JPIRYY (March/2024)
The annual inflation rate in Japan ticked lower to 2.7% in March 2024 from February's 3-month peak of 2.8%, matching market consensus.
There were slowdowns in prices of transport (2.9% vs 3.0% in February), clothes (2.0% vs 2.6%), furniture & household utensils (3.2% vs 5.1%), healthcare (1.5% vs 1.8%), communication (0.2% vs 1.4%), and culture & recreation (7.2% vs 7.3%).
At the same time, inflation was stable for food (at 4.8%), housing (at 0.6%), education (at 1.3%), and miscellaneous (at 1.1%).
Meanwhile, prices of fuel, and light dropped the least in a year (-1.7% vs -3.0%), with electricity (-1.0% and -2.5%) and gas (-7.1% vs -9.4%) falling at softer paces as energy subsidies from the government would fully end in May.
The core inflation rate fell to 2.6% from a four-month top of 2.8%, slightly below forecasts of 2.7%. Monthly, consumer prices rose by 0.2% in March, the most since last October, after being flat in the prior two months.
source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
Japan Currency Crash After Rate Hike - Inflation cycle begin A brand-new cycle for the Japanese economy is in the making with a higher inflation to come and a weaker yen.
When the Bank of Japan hiked interest rates for the first time in 17 years, the Japanese Yen instead of strengthening, it crashed.
Micro Japanese Yen Futures
Ticker: MJY
Minimum fluctuation:
0.000001 per JPY increment = $1.25
Japanese Yen Futures & Options
Ticker: 6J
Minimum fluctuation:
0.0000005 per JPY increment = $6.25
Disclaimer:
• What presented here is not a recommendation, please consult your licensed broker.
• Our mission is to create lateral thinking skills for every investor and trader, knowing when to take a calculated risk with market uncertainty and a bolder risk when opportunity arises.
CME Real-time Market Data help identify trading set-ups in real-time and express my market views. If you have futures in your trading portfolio, you can check out on CME Group data plans available that suit your trading needs www.tradingview.com
$JPIRYY -CPI (YoY)ECONOMICS:JPIRYY Japan Inflation Rate Lowest in A Year
The annual inflation rate in Japan fell to 3.0% in September 2023 from 3.2% in August, pointing to the lowest reading since September 2022.
Meantime, core inflation rate dropped to a 13-month low of 2.8%,
slightly above market consensus of 2.7% while staying outside the Bank of Japan's 2% target for the 18th month.
Core inflation rate dropped to a 13-month low of 2.8%, slightly above consensus of 2.7% while staying outside the Bank of Japan's 2% target for the 18th month. On a monthly basis, consumer prices rose 0.3% in September, after a 0.2% gain in August. source: Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
source:
Ministry of Internal Affairs & Communications
The Bank of Japan can’t let goThis week financial markets were dominated by central banks policy decisions. While the Federal Reserve (Fed) and Bank of England (BOE) kept rates on hold, the policy board of the Bank of Japan (BOJ) decided to further increase the flexibility in its yield curve control policy.
The BOJ previously set a strict cap of 1.0% for the 10-year Japanese Government Bond (JGB) yield. But it has now decided that 1% should be a “reference” (not a strict cap), which effectively allows the yield to rise above 1% when the BOJ thinks it is appropriate. The upper bound of 1% appears to be a level they can’t let go of. By doing so, the BOJ is choosing an exit path that gives them the maximum flexibility but minimum volatility around the Yen. We view this as a dovish move as consensus expectations were for the BOJ to move the cap to 1.25% rather than 1%.
Japan’s remains on a narrow path
One of the reasons holding back the BOJ from normalisation of policy rates, is they still believe Japan’s recovery since the re-opening in October 2022 remains on a narrow path as it relies heavily on tourism, while the broader services sectors have yet to pick up significantly and manufacturing activity has been hampered by soft exports. Japan’s flash PMI readings for October showed us a bifurcated economy where the services sector is stronger than the manufacturing sector. Manufacturing PMI clocked in at 47.6, which is in contraction territory. Services PMI was 51.1, which is down from last month’s reading of 53.8 but is still in expansion territory, no doubt helped by fiscal stimulus and the accommodative monetary policy environment.
BOJ on the lookout for an intensified virtuous cycle between wages and prices
BOJ governor Ueda indicated that the BoJ will be monitoring the upcoming spring union-employer wage negotiations. A strong outcome could catalyse the earlier attainment of sustained inflation in Japan, but overall, Japan’s recovery isn’t strong enough yet for employers, especially small enterprises, to meaningful support wage hikes in the broad economy. While headline inflation bolted north of 4% in January 2023, it appears to have peaked and has begun receding. While core inflation remains around the 4% mark. The Producer Price Index (PPI) slowed to 2% annually in September suggesting a stabilization or even drop in CPI ahead.
The BOJ revised its outlook for core inflation (all items less fresh food and energy) to 3.8% in FY23, 1.9% for FY24 and 1.9% for FY25. The BoJ stated that the inflation uptick “needs to be accompanied by an intensified virtuous cycle between wages and prices”.
The Yen is unlikely to appreciate under BOJ’s policy change owing to the large gap in interest rates between the US and Japan. The direction of the Yen matters for Japanese equities owing to Japan high export tilt. The exporters stand to benefit amidst a weaker Yen.
Fire power abounds for Japanese equities
Japanese equities had a strong first half in 2023, attaining 33-year highs. Yet valuations at 15.7x price to earnings ratio (P/E), still trade at a 30% discount to its 15-year average providing room to catch up. More importantly, earnings revision estimates in Japan are currently the highest among the major economies. Earnings yield at 4.07% for the Nikkei 225 Index has been trending above bond yields 0.947% for 10 Year JGBs , keeping the well-known TINA (There is no Alternative) trade alive in favour of Japanese equities.
Tailwind from corporate governance reforms
Tokyo Stock Exchange’s (TSE) call for listed companies to focus on achieving sustainable growth and enhancing corporate value is beginning to bear fruit. The call was aimed at companies with a price to book (P/B) ratio below one. Those companies were asked to develop a plan for improvement, disclose and then implement and track its progress. The progress has been encouraging with 31% of companies on the prime market making a disclosure of their plan .
Large companies with a price to book ratio below one have been more proactive with disclosure. Historically cash-heavy Japanese companies face increasing pressure to improve their numbers, possibly by funnelling historically high excess cash reserves into increased buybacks or dividends.
Conclusion
Inflation has been missing in Japan for more than a decade. So now that it has arrived aided by the post pandemic pick up of the Japanese economy, policy makers are not in a rush to obliterate it. With wage growth lagging behind inflation, the Bank of Japan does not appear ready to wean itself from Yield Curve Control until a more intensified virtuous cycle is observed between wages and prices. The BOJ’s policy decision this week is unlikely to allow the appreciation of the Yen, which should continue to provide a competitive advantage to Japanese exporters.
This material is prepared by WisdomTree and its affiliates and is not intended to be relied upon as a forecast, research or investment advice, and is not a recommendation, offer or solicitation to buy or sell any securities or to adopt any investment strategy. The opinions expressed are as of the date of production and may change as subsequent conditions vary. The information and opinions contained in this material are derived from proprietary and non-proprietary sources. As such, no warranty of accuracy or reliability is given and no responsibility arising in any other way for errors and omissions (including responsibility to any person by reason of negligence) is accepted by WisdomTree, nor any affiliate, nor any of their officers, employees or agents. Reliance upon information in this material is at the sole discretion of the reader. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance.