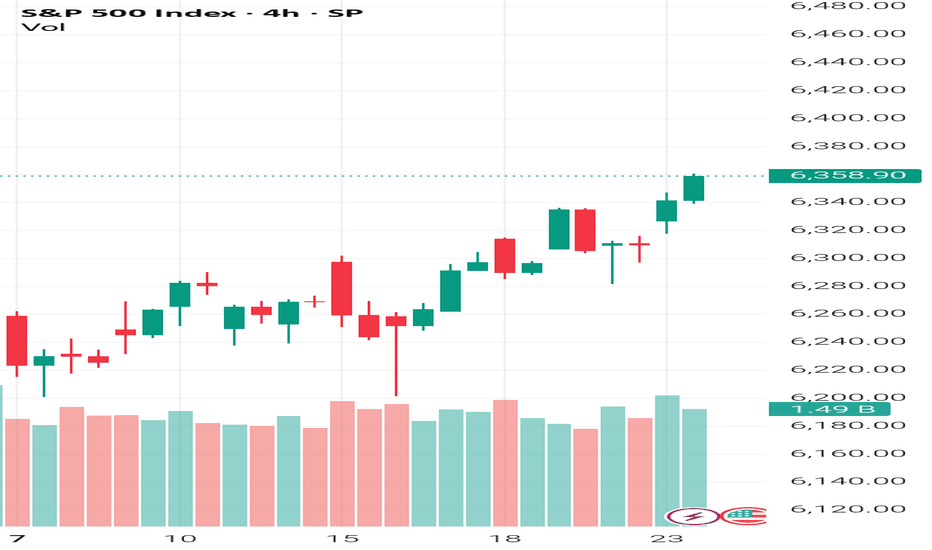
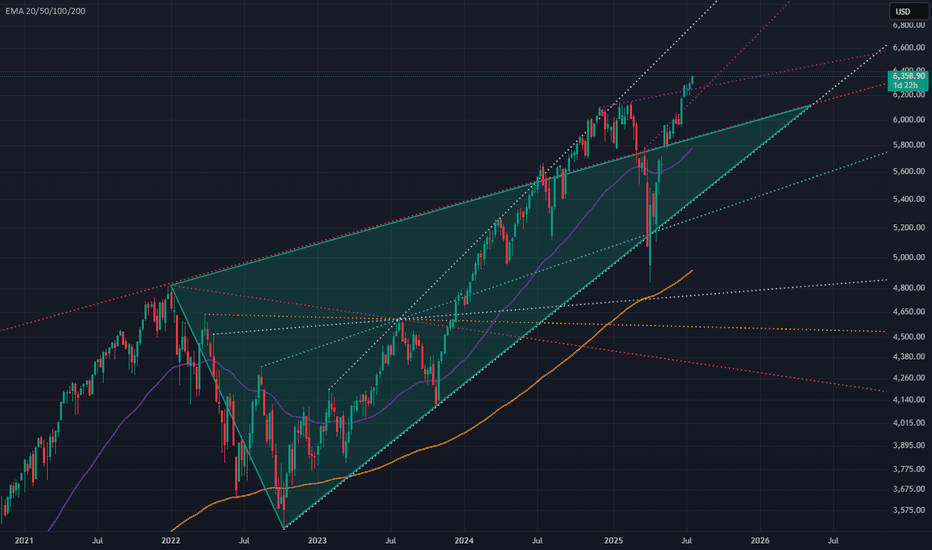
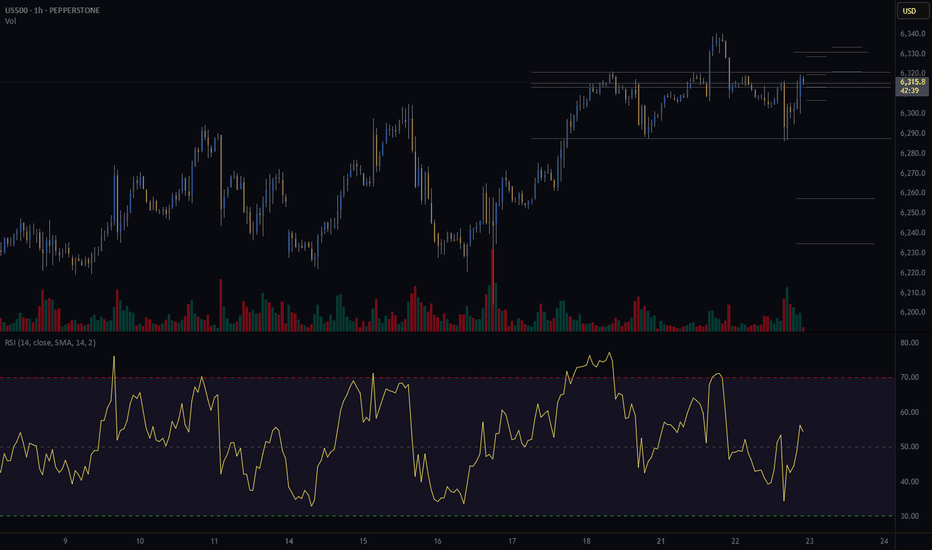
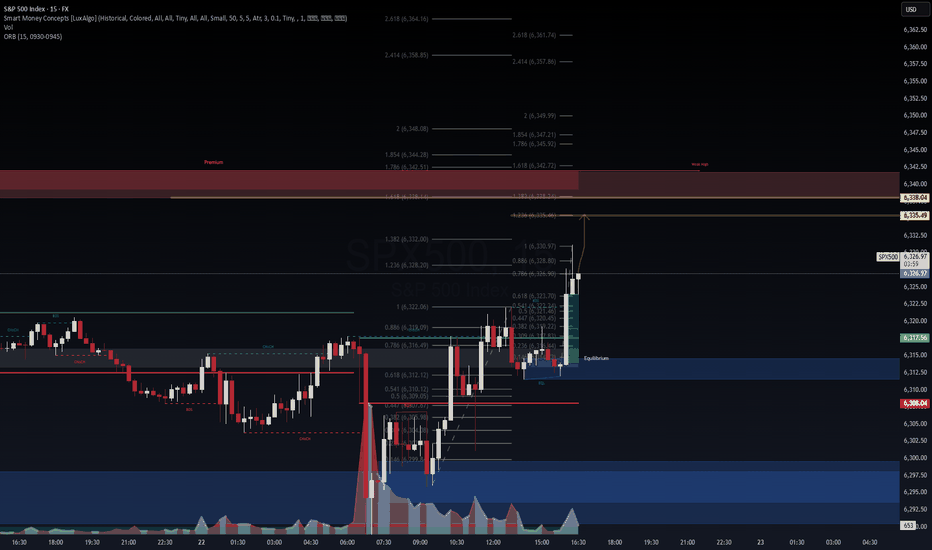
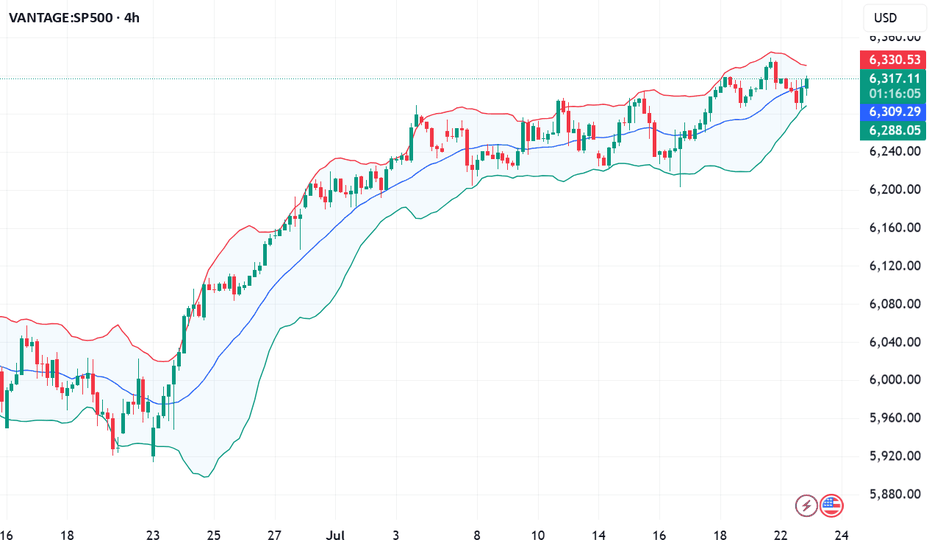
S&P500 push to new ATH? Key Developments:
AI Drives Earnings Momentum
Alphabet reported strong results, but flagged surging AI infrastructure costs, signaling increased capex ahead.
SK Hynix posted record earnings and committed to expanding AI-related investments, reinforcing the sector’s critical growth role.
Investor sentiment remains AI-positive, with capital rotation favoring tech and semiconductors despite margin compression risks.
Banking Sector Boosted by Tariff-Driven Volatility
Deutsche Bank’s FIC (Fixed Income & Currencies) trading revenue jumped 11% to €2.28B, its best Q2 since 2007, aided by global trade uncertainty.
BNP Paribas also beat earnings estimates, continuing the strong showing from European banks amid market volatility.
Trade & Tariff Watch
The EU and US are nearing a deal on a 15% standard tariff rate, potentially stabilizing trade flows and market pricing.
Trump’s broader reciprocal tariff push remains in focus, especially after the US-Japan deal. Investors are watching for signs of escalation or resolution with other partners like the EU and Canada.
Fed in the Political Spotlight
Trump visited the Fed’s construction site, criticizing costs and maintaining pressure on Chair Jerome Powell.
Speculation about Fed leadership changes and political interference is unsettling, though markets have largely shrugged this off for now.
Meanwhile, House Republicans are drafting a follow-up tax-and-spending plan, which could shape future fiscal policy and market expectations.
Conclusion: S&P 500 Trading Outlook
The S&P 500 remains buoyed by strong earnings, particularly from AI-linked sectors and financials, while geopolitical risks and tariff volatility are being absorbed as catalysts for trading profits rather than panic.
Bullish factors: Strong corporate earnings (Alphabet, SK Hynix, Deutsche Bank), potential trade de-escalation (EU-US tariff deal), and AI momentum.
Risks to monitor: Rising AI capex (impact on margins), political tension around the Fed, and tariff uncertainty.
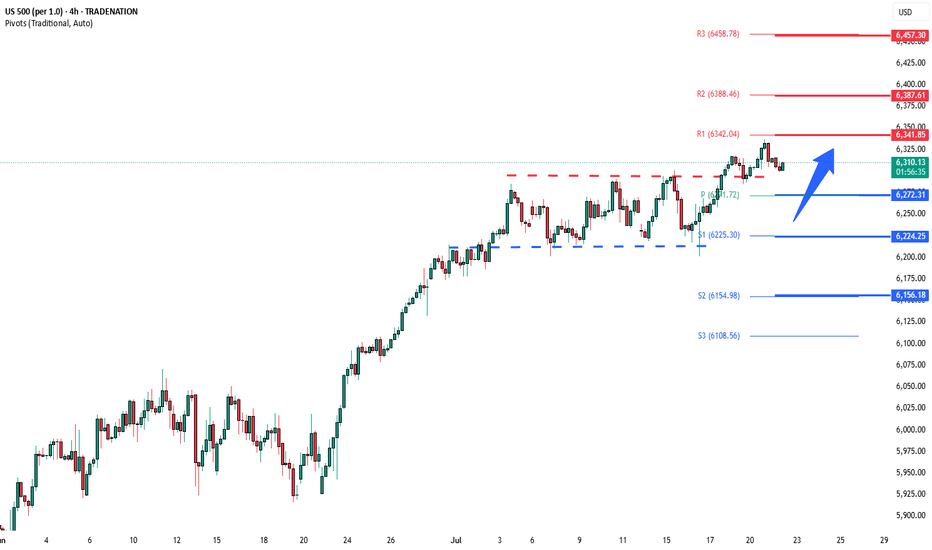
Key Support and Resistance Levels
Resistance Level 1: 6387
Resistance Level 2: 6457
Resistance Level 3: 6502
Support Level 1: 6272
Support Level 2: 6224
Support Level 3: 6156
This communication is for informational purposes only and should not be viewed as any form of recommendation as to a particular course of action or as investment advice. It is not intended as an offer or solicitation for the purchase or sale of any financial instrument or as an official confirmation of any transaction. Opinions, estimates and assumptions expressed herein are made as of the date of this communication and are subject to change without notice. This communication has been prepared based upon information, including market prices, data and other information, believed to be reliable; however, Trade Nation does not warrant its completeness or accuracy. All market prices and market data contained in or attached to this communication are indicative and subject to change without notice.
US500 trade ideas
ECB on the agenda: The ECB is on the agenda today. I don't envision a particularly volatile event, although a continuation of the 'limited further cuts narrative' should see the EUR supported, particularly given growing thoughts of a US / EUR trade deal.
All in all, with the S&P still climbing, I continue to hold the view that 'risk on' trades are viable, especially since the announcement of the US / JAPAN trade deal. It's just a case of choosing whether to short the JPY or USD.
In other news, 'soft' SERVICE PMI data from the UK puts a little more pressure on the BOE to cut rates, arguably creating a GBP short 'catalyst' trade for anyone at the charts in that moment.
Also, a relatively hawkish speech from the RBA'S BULLOCK, keeps the AUD high on my 'to long list'.
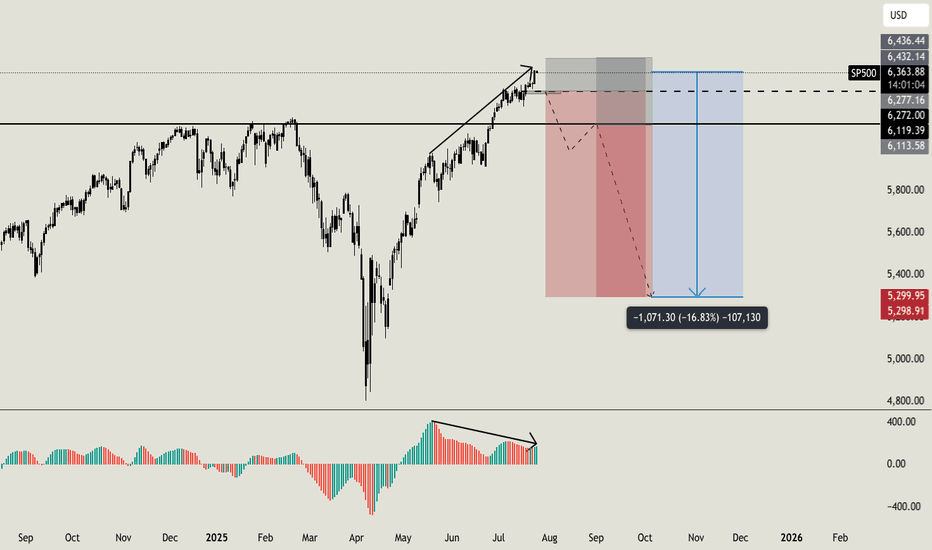
Do you want to keep buying SP500?Hello all. I usually love to work analyzing volumes, times and key level, i am not used to check the standard indicators, but this time i'll made an exception. Lot of indicators (AO, MACD, RSI, OBV) are showing weakness on higher timeframe with a strong bearish divergence (like the one i am sharing now on AO). On smaller timeframe i usually ignore this signals, because they can result in a little retrace, but on higher timeframe like this one can be a strong reversal indicator. But this is not the only things that let me open this position. Going deeper into my analysis, i have a first key level at $6270. Once we will break below this level, i'll open my first sell order with a stoploss a little higher than ATH. If price will break below my second key level at $6120 i'll open my second short order. My main and final target is $5300 (around -16% from now) but i will consider to secure profits before this level. I'll update you guys, and let me know if you are agree with me or not. Cheers
Well...... I have no words to say, lets see what happens now. The Last Breath of Bulls
They came with horns of thunder,
hooves pounding gold from earth,
a decade’s dance in roaring winds,
each sunrise glinting mirth.
They charged through fields of candlesticks,
green banners held aloft,
dreams stacked on dreams, layer by layer,
voices rising, soft to rough.
But markets tire as all beasts do,
the grass runs dry and thin,
greed’s fattened calves now restless,
as silence crowds the din.
A tremor in the trading halls,
screens blinking red, then grey,
the bulls look up at iron clouds,
no dawn in this new day.
They stand, bewildered, heavy,
in fields now tinged with frost,
the horns that once carved futures bright,
bowed under the cost.
The end comes not with fury,
but a quiet pulling thread,
the bullish songs that once were sung,
now whispers of the dead.
Yet even as the bulls lie down,
the soil still holds the sun,
for from the hush of fallen hooves,
new seasons will be spun.
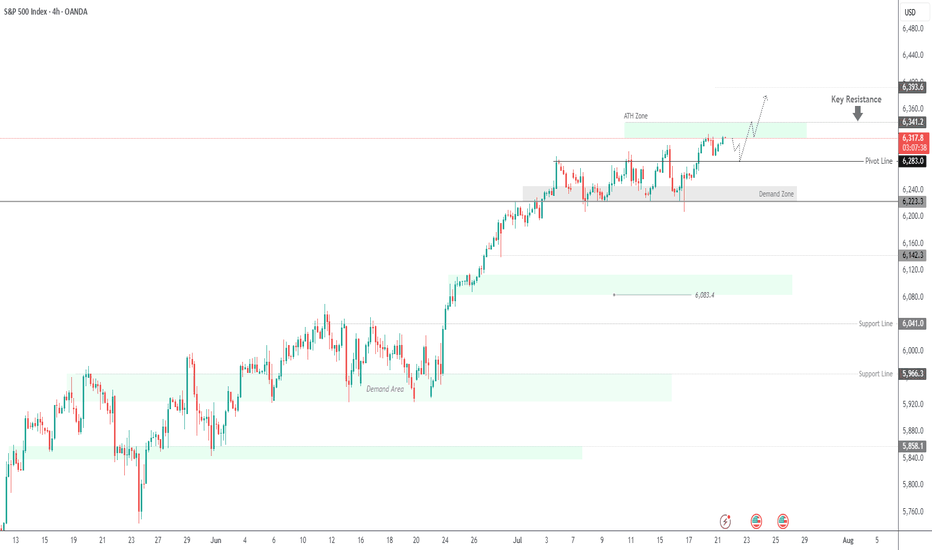
SPX500 Near ATH | Earnings Week Could Fuel Next MoveSPX500 | Weekly Outlook
The S&P 500 continues its bullish run, trading at record highs as investors await a critical week of tech earnings. Reports from Alphabet and Tesla could be key in justifying the lofty valuations driven by the AI boom.
Technical Outlook:
The price is expected to consolidate between 6341 and 6283 before any decisive move. A short-term bearish correction may occur initially, but if the price holds above the support zone, a push toward a new ATH at 6341 is likely. A breakout above this level could extend gains toward 6375 and 6393.
However, a break below 6283 would indicate weakness, potentially driving the price toward the demand zone near 6250 and 6224.
Support: 6283 · 6250 · 6224
Resistance: 6341 · 6375 · 6393
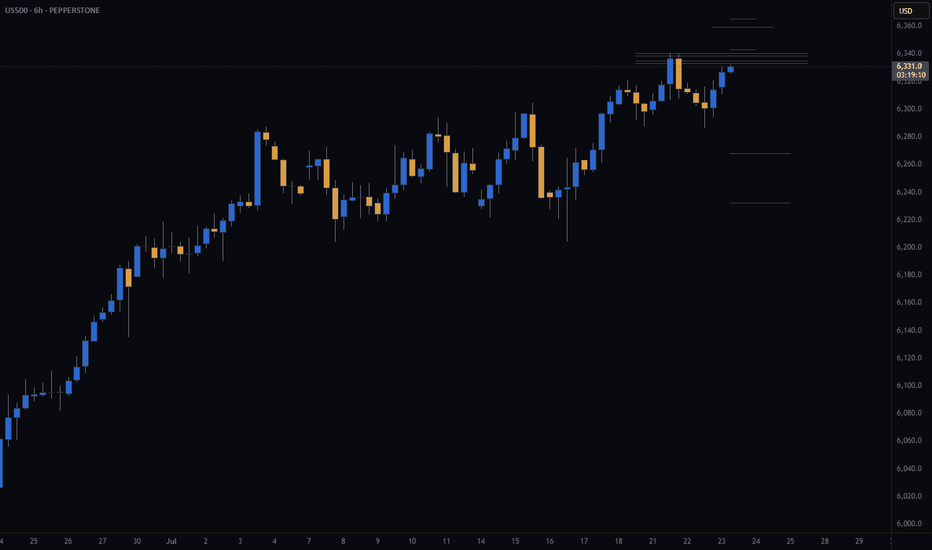
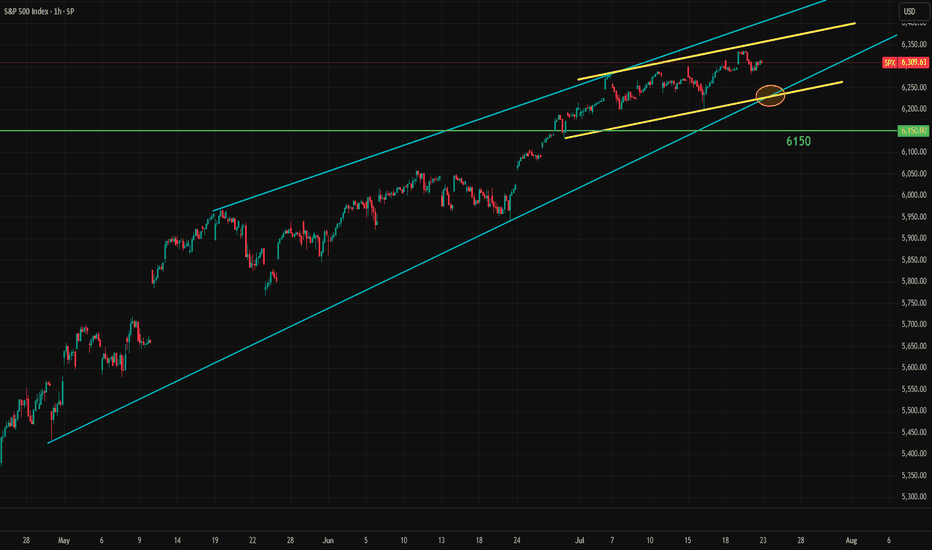
Market Breadth Flashes Warning, but S&P 500 Still Holds SteadyThe S&P 500 continues its slightly positive movement. However, the momentum has been slowing, forming a long, wedge-like pattern. These long wedges have been a recurring feature in the stock market for years. From the monthly timeframe to the 1-hour chart, the market often forms wedges.
Wedge formations tend to break to the downside but can persist for a long time before doing so. The S&P 500 typically makes a sharp correction selloff, then recovers in a "V" shape, followed by the formation of another wedge. This pattern appears to be repeating once again. Still, there are some negative signals that traders should be aware of:
1- The impact of tariffs on growth remains a major unknown. Most tariff deals have not been finalized yet. While the Japan agreement is a positive step, negotiations with the EU will be more significant.
2- Many earnings reports will be released in the coming weeks, potentially shaping market sentiment. These earnings will reflect some of the tariff effects. AI and tech remain the key market drivers, so their results will be especially important.
3- Some breadth indicators are showing early warning signs. One of the most useful is the "percentage of stocks above the 200-day moving average." This metric shows whether the market is broadly participating in the rally or being driven by a few large-cap names. Typically, when the market weakens, traders rotate into mega caps. The rounded numbers below shows the weakness:
March 2024 Top: 5250 - Percantege Above 200 MA: 85%
July 2024 Top: 5675 - Percantege Above 200 MA: 80%
December 2024 Top: 6100 - Percantege Above 200 MA: 74%
July 2025 Current: 6309 - Percantege Above 200 MA: 66%
This shows that fewer and fewer stocks are managing to stay above their 200-day moving average while S&P making new highs. This is not an immediate red flag, but the weakening is apparent.
In summary, the slightly positive outlook remains intact for now and is expected to continue until the wedge breaks with some early warning signs. If that happens, a sharp selloff may follow, creating both selling and buying opportunities. In the short term, 6280 is the immediate support level to watch.
People don't like the truth! Let's be honest, people don't like honesty. They prefer ideas that affirm their own beliefs.
When I read articles and posts from newer traders, it's often from a place of "all in" diamond hands and the notion that things go up forever.
I've been a trader for over 25 years now, and the game isn't about making a quick buck, it's about making money over and over again. This got me thinking, the issue is when you deal with a small account you require leverage, small timeframes and of course the "shit" or bust mindset. If you lose a thousand dollars, $10,000 even $100,000 - what does it matter? That's no different than a game of poker in Vegas.
The idea of being 80% in drawdown, is alien to me. The idea of one trade and one win is also a crazy notion.
Instead of playing with the future, there is an easier way to work. This isn't about slow and boring, it's about psychology and discipline. 10% returns on a million-dollar account isn't all that difficult. Instead of aiming for 300x returns on an alt coin (due to the account size being tiny) You can make less of a percentage gain with a larger account size.
In terms of psychology - the word " HOPE " is used, way too often, it's used when you hope a stock or the price of Bitcoin goes up, it's used when you hope the position comes back in your favour, it's used when you want your 10,000 bucks to double.
This isn't trading, it's gambling.
The truth is, it's not the winners that make you a good trader. It's the way you deal with the losses.
Once you learn proper risk management, a downtrend in a market move is a 1-2% loss coupled with a new opportunity to reverse the bias.
As a disciplined trader, the game is played differently.
Let's assume you don't have $100k spare - prop firms are a great option, OPM = other people's money.
Remove the risk and increase the leverage, all whilst trading with discipline.
The market goes through many phases, cycles and crashes.
You don't always need something as catastrophic to take place, but if you are all in on a position. You need to understand that losses can be severe and long-lasting.
When everyone sees an oasis in the desert, it's often a mirage.
You only have to look at the Japanese lesson in 1989, when the Nikkei was unstoppable-until it wasn't. For that short space in time, everyone was a day trader, housewives to taxi drivers.
Everyone's a genius in a Bull market.
Then comes the crash. The recovery time on that crash?
34-years!!!
I have covered several aspects of psychology here on TradingView;
When it comes to trading, if you are able to keep playing. It's a worthwhile game. If you are gambling, it's a game whereby the house often wins.
Right now, stocks are worth more than their earnings. Gold is up near all-time highs, crypto, indices the same.
All I am saying is if you are all in. Be careful!
Disclaimer
This idea does not constitute as financial advice. It is for educational purposes only, our principal trader has over 25 years' experience in stocks, ETF's, and Forex. Hence each trade setup might have different hold times, entry or exit conditions, and will vary from the post/idea shared here. You can use the information from this post to make your own trading plan for the instrument discussed. Trading carries a risk; a high percentage of retail traders lose money. Please keep this in mind when entering any trade. Stay safe.
Wall Street takes off: 5 secret growth engines for #S&P500 Record closes for the indices on July 21 came from a powerful combo: a surge in #Google , a strong start to the earnings season, gains in #Apple (+0.6%), #Amazon (+1.4%), plus #Microsoft, #Meta Platforms, and #Nvidia . This momentum, coupled with market bets on imminent Fed rate cuts and hopes for a softening US-EU tariff conflict, pushed #S&P500 and #NQ100 to new all-time highs.
5 mega drivers that could keep #S&P500 and #NQ100 on the runway through 2025:
• AI capex and monetization: Top cloud providers are ramping up spending in computing clusters and generative AI solutions. The growing lineup of paid AI products (Google Gemini, Microsoft Copilot+ Apps, Amazon Bedrock) is starting to generate significant revenue, boosting profit estimates for the “Magnificent 7.”
• Fed policy easing: If inflation keeps drifting towards 2%, we may see the first rate cut of the cycle between July and September. Historically, every 25 bps drop in 10-year UST yields adds ~2% to the #NQ100 ’s valuation multiple.
• Record buybacks and dividends: #S&P500 companies hold $3.5 trillion in cash. After tax relief on repatriated foreign earnings earlier this year, several megacap boards approved accelerated buybacks — mechanically supporting stock prices.
• Easing tariff risks: Potential trade deals between the US and EU, and the US and Mexico, would remove the threat of 20–50% tariffs priced into valuations, unlocking CAPEX in manufacturing and semiconductors — sectors with a heavy #NQ100 weight.
• Resilient consumers and services: Unemployment remains near 4%, and household spending is growing 2–3% YoY. This supports e-commerce, streaming, and platform advertising — together making up ~40% of #NQ100 and ~28% of #S&P500 .
The current highs of #S&P500 and #NQ100 aren’t a random spike — they result from strong corporate earnings, expectations of Fed cuts, and hopes of trade détente. If even some of these five drivers materialize, the indices have a strong chance to stay elevated and set new records by year-end. FreshForex analysts believe current prices could spark a new rally, with today’s market conditions offering plenty of entry points in both indices and stock CFDs.
The Empirical Validity of Technical Indicators and StrategiesThis article critically examines the empirical evidence concerning the effectiveness of technical indicators and trading strategies. While traditional finance theory, notably the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH), has long argued that technical analysis should be futile, a large body of academic research both historical and contemporary presents a more nuanced view. We explore key findings, address methodological limitations, assess institutional use cases, and discuss the impact of transaction costs, market efficiency, and adaptive behavior in financial markets.
1. Introduction
Technical analysis (TA) remains one of the most controversial subjects in financial economics. Defined as the study of past market prices and volumes to forecast future price movements, TA is used by a wide spectrum of market participants, from individual retail traders to institutional investors. According to the EMH (Fama, 1970), asset prices reflect all available information, and hence, any predictable pattern should be arbitraged away instantly. Nonetheless, technical analysis remains in widespread use, and empirical evidence suggests that it may offer predictive value under certain conditions.
2. Early Empirical Evidence
The foundational work by Brock, Lakonishok, and LeBaron (1992) demonstrated that simple trading rules such as moving average crossovers could yield statistically significant profits using historical DJIA data spanning from 1897 to 1986. Importantly, the authors employed bootstrapping methods to validate their findings against the null of no serial correlation, thus countering the argument of data mining.
Gencay (1998) employed non-linear models to analyze the forecasting power of technical rules and confirmed that short-term predictive signals exist, particularly in high-frequency data. However, these early works often omitted transaction costs, thus overestimating potential returns.
3. Momentum and Mean Reversion Strategies
Momentum strategies, as formalized by Jegadeesh and Titman (1993), have shown persistent profitability across time and geographies. Their approach—buying stocks that have outperformed in the past 3–12 months and shorting underperformers—challenges the EMH by exploiting behavioral biases and investor herding. Rouwenhorst (1998) confirmed that momentum exists even in emerging markets, suggesting a global phenomenon.
Conversely, mean reversion strategies, including RSI-based systems and Bollinger Bands, often exploit temporary price dislocations. Short-horizon contrarian strategies have been analyzed by Chan et al. (1996), but their profitability is inconsistent and highly sensitive to costs, timing, and liquidity.
4. Institutional Use of Technical Analysis
Contrary to the belief that TA is primarily a retail tool, it is also utilized—though selectively—by institutional investors:
Hedge Funds: Many quantitative hedge funds incorporate technical indicators within multi-factor models or machine learning algorithms. According to research by Neely et al. (2014), trend-following strategies remain a staple among CTAs (Commodity Trading Advisors), particularly in futures markets. These strategies often rely on moving averages, breakout signals, and momentum filters.
Market Makers: Although market makers are primarily driven by order flow and arbitrage opportunities, they may use TA to model liquidity zones and anticipate stop-hunting behavior. Order book analytics and technical levels (e.g., pivot points, Fibonacci retracements) can inform automated liquidity provision.
Pension Funds and Asset Managers: While these institutions rarely rely on TA alone, they may use it as part of tactical asset allocation. For instance, TA may serve as a signal overlay in timing equity exposure or in identifying risk-off regimes. According to a CFA Institute survey (2016), over 20% of institutional investors incorporate some form of technical analysis in their decision-making process.
5. Adaptive Markets and Conditional Validity
Lo (2004) introduced the Adaptive Markets Hypothesis (AMH), arguing that market efficiency is not a binary state but evolves with the learning behavior of market participants. In this framework, technical strategies may work intermittently, depending on the ecological dynamics of the market. Neely, Weller, and Ulrich (2009) found technical rules in the FX market to be periodically profitable, especially during central bank interventions or volatility spikes—conditions under which behavioral biases and structural inefficiencies tend to rise.
More recent studies (e.g., Moskowitz et al., 2012; Baltas & Kosowski, 2020) show that momentum and trend-following strategies continue to deliver long-term Sharpe ratios above 1 in diversified portfolios, particularly when combined with risk-adjusted scaling techniques.
6. The Role of Transaction Costs
Transaction costs represent a critical variable that substantially alters the net profitability of technical strategies. These include:
Explicit Costs: Commissions, fees, and spreads.
Implicit Costs: Market impact, slippage, and opportunity cost.
While early studies often neglected these elements, modern research integrates them through realistic backtesting frameworks. For example, De Prado (2018) emphasizes that naive backtesting without cost modeling and slippage assumptions leads to a high incidence of false positives.
Baltas and Kosowski (2020) show that even after accounting for bid-ask spreads and market impact models, trend-following strategies remain profitable, particularly in futures and FX markets where costs are lower. Conversely, high-frequency mean-reversion strategies often become unprofitable once these frictions are accounted for.
The impact of transaction costs also differs by asset class:
Equities: Higher costs due to wider spreads, especially in small caps.
Futures: Lower costs and higher leverage make them more suitable for technical strategies.
FX: Extremely low spreads, but high competition and adverse selection risks.
7. Meta-Analyses and Recent Surveys
Park and Irwin’s (2007) meta-analysis of 95 studies found that 56% reported significant profitability from technical analysis. However, profitability rates dropped when transaction costs were included. More recent work by Han, Yang, and Zhou (2021) extended this review with data up to 2020 and found that profitability was regime-dependent: TA performed better in volatile or trending environments and worse in stable, low-volatility markets.
Other contributions include behavioral explanations. Barberis and Thaler (2003) suggest that TA may capture collective investor behavior, such as overreaction and underreaction, thereby acting as a proxy for sentiment.
8. Limitations and Challenges
Several methodological issues plague empirical research in technical analysis:
Overfitting: Using too many parameters increases the likelihood of in-sample success but out-of-sample failure.
Survivorship Bias: Excluding delisted or bankrupt stocks leads to inflated backtest performance.
Look-Ahead Bias: Using information not available at the time of trade leads to unrealistic results.
Robust strategy development now mandates walk-forward testing, Monte Carlo simulations, and realistic assumptions on order execution. The growing field of machine learning in finance has heightened these risks, as complex models are more prone to fitting noise rather than signal (Bailey et al., 2014).
9. Conclusion
Technical analysis occupies a contested but persistent role in finance. The empirical evidence is mixed but suggests that technical strategies can be profitable under certain market conditions and when costs are minimized. Institutional investors have increasingly integrated TA within quantitative and hybrid frameworks, reflecting its conditional usefulness.
While TA does not provide a universal arbitrage opportunity, it can serve as a valuable tool when applied adaptively, with sound risk management and rigorous testing. Its success ultimately depends on context, execution discipline, and integration within a broader investment philosophy.
References
Bailey, D. H., Borwein, J. M., Lopez de Prado, M., & Zhu, Q. J. (2014). "The Probability of Backtest Overfitting." *Journal of Computational Finance*, 20(4), 39–69.
Baltas, N., & Kosowski, R. (2020). "Trend-Following, Risk-Parity and the Influence of Correlations." *Journal of Financial Economics*, 138(2), 349–368.
Barberis, N., & Thaler, R. (2003). "A Survey of Behavioral Finance." *Handbook of the Economics of Finance*, 1, 1053–1128.
Brock, W., Lakonishok, J., & LeBaron, B. (1992). "Simple Technical Trading Rules and the Stochastic Properties of Stock Returns." Journal of Finance, 47(5), 1731–1764.
Chan, L. K. C., Jegadeesh, N., & Lakonishok, J. (1996). "Momentum Strategies." Journal of Finance, 51(5), 1681–1713.
De Prado, M. L. (2018). Advances in Financial Machine Learning, Wiley.
Fama, E. F. (1970). "Efficient Capital Markets: A Review of Theory and Empirical Work." Journal of Finance, 25(2), 383–417.
Gencay, R. (1998). "The Predictability of Security Returns with Simple Technical Trading Rules." Journal of Empirical Finance, 5(4), 347–359.
Han, Y., Yang, K., & Zhou, G. (2021). "Technical Analysis in the Era of Big Data." *Review of Financial Studies*, 34(9), 4354–4397.
Jegadeesh, N., & Titman, S. (1993). "Returns to Buying Winners and Selling Losers: Implications for Stock Market Efficiency." *Journal of Finance*, 48(1), 65–91.
Lo, A. W. (2004). "The Adaptive Markets Hypothesis: Market Efficiency from an Evolutionary Perspective." *Journal of Portfolio Management*, 30(5), 15–29.
Moskowitz, T. J., Ooi, Y. H., & Pedersen, L. H. (2012). "Time Series Momentum." *Journal of Financial Economics*, 104(2), 228–250.
Neely, C. J., Weller, P. A., & Ulrich, J. M. (2009). "The Adaptive Markets Hypothesis: Evidence from the Foreign Exchange Market." *Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis*, 44(2), 467–488.
Neely, C. J., Rapach, D. E., Tu, J., & Zhou, G. (2014). "Forecasting the Equity Risk Premium: The Role of Technical Indicators." *Management Science*, 60(7), 1772–1791.
Park, C. H., & Irwin, S. H. (2007). "What Do We Know About the Profitability of Technical Analysis?" *Journal of Economic Surveys*, 21(4), 786–826.
Rouwenhorst, K. G. (1998). "International Momentum Strategies." *Journal of Finance*, 53(1), 267–284.
Zhu, Y., & Zhou, G. (2009). "Technical Analysis: An Asset Allocation Perspective on the Use of Moving Averages." *Journal of Financial Economics*, 92(3), 519–544.
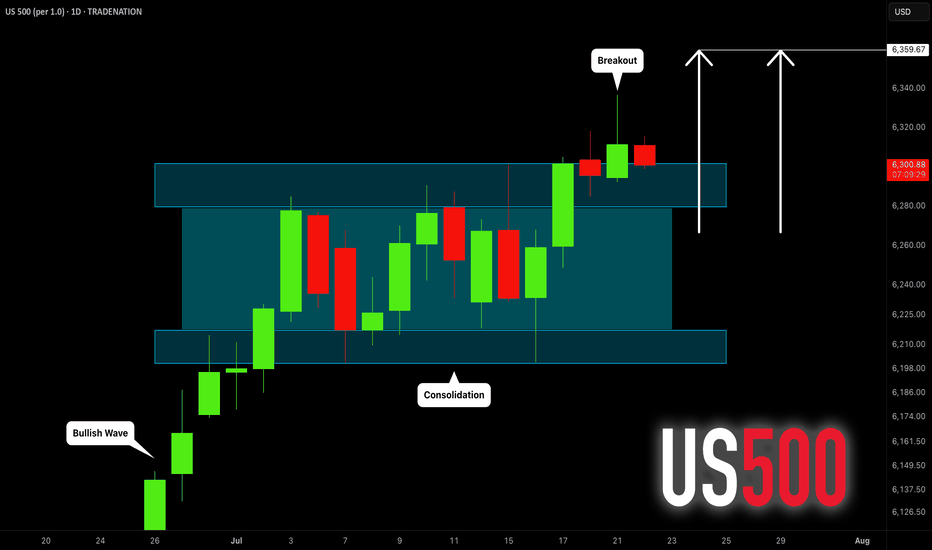
S&P500 INDEX (US500): Bullish Trend Continues
US500 updated a higher high this week, breaking a resistance
of a bullish flag pattern on a daily time frame.
I think that the market will rise even more.
Next goal for the bulls - 6359
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
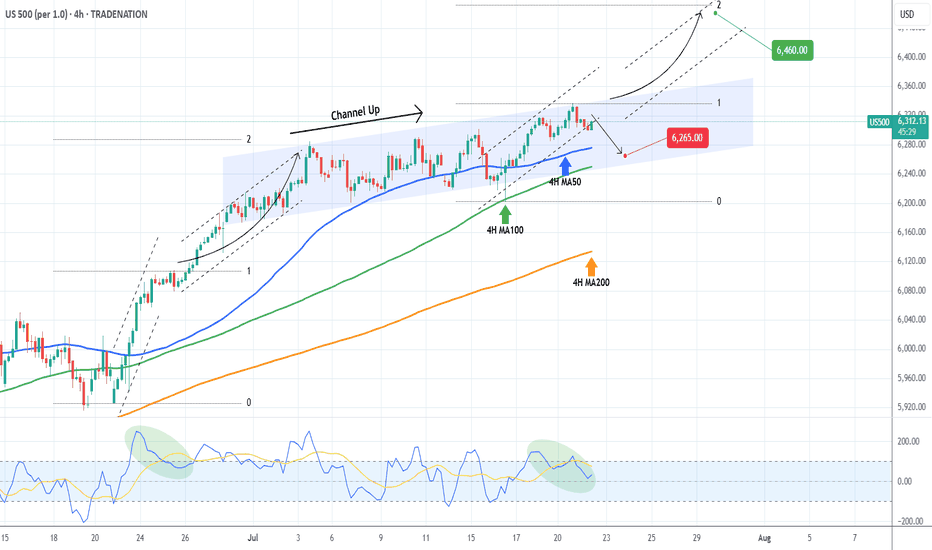
S&P500 Critical short-term crossroads.The S&P500 index (SPX) has been trading within a Channel Up since for the entirety of July and right now is ahead of important crossroads. It either breaks out above the pattern or pulls back to price a new Higher Low.
Based on the 4H CCI and the similarities with the June 24 - 25 consolidation, there are higher probabilities to break upwards. That fractal reached the 2.0 Fibonacci extension after it broke out. We will wait for confirmation and if it's delivered, we will buy the break-out and target 6460 (just below Fib 2.0 ext).
Until then, being so close to the Channel Up top, makes a solid short opportunity targeting a Higher Low (bottom). The previous one was priced exactly on the 4H MA100 (green trend-line) so that's our target or 6250 if it comes earlier.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
** Please LIKE 👍, FOLLOW ✅, SHARE 🙌 and COMMENT ✍ if you enjoy this idea! Also share your ideas and charts in the comments section below! This is best way to keep it relevant, support us, keep the content here free and allow the idea to reach as many people as possible. **
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Disclosure: I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
💸💸💸💸💸💸
👇 👇 👇 👇 👇 👇
If we want a 2020-2021 style run, we need a seasonal pullbackUS 500 Index SP:SPX AMEX:SPY AMEX:VOO August seasonal scenario: institutional participation remains light, being outperformed by leveraged dip buying retail. How long can they remain on the sidelines, missing opportunities for their clients, before FOMO kicks in? Remember that institutions aren't emotionally driven, unlike their retail counter parts. That being said, they're itching to get in. What will compel them? IMO, a 5% pull back will incentivize them to buy. The August seasonal pull back may provide just that opportunity. If it comes, what happens in late Q3 and the rest of Q4 will likely be similar to 2020-2021. The deeper the pull back, the more impulsive it will likely be, as retail and institutions will be temporarily in tandem. SP:SPX PEPPERSTONE:US500 AMEX:SPY AMEX:VOO
S&P500 sideways consolidation breakoutKey Developments:
Fed Politics: Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent called for a review of the Fed’s $2.5B HQ renovation, continuing political pressure on Jerome Powell. This adds to the uncertainty around Fed independence and rate path.
Meme Stock Surge:
Opendoor soared 121% amid a retail-driven frenzy.
Major institutional investors are also chasing the rally, pushing broader equities to record highs.
However, upcoming Alphabet and Tesla earnings could be a turning point for momentum.
Corporate News:
Hewlett Packard Enterprise suffered a $985M loss in the Autonomy case—corporate governance and M&A risks in spotlight.
Sarepta paused drug shipments amid backlash—biotech volatility rising.
LA Times plans IPO—media valuations may resurface.
Crypto Moves:
Trump Media bought $2B in Bitcoin and related assets, aiming to become a crypto treasury.
JPMorgan may lend against crypto, signaling broader institutional adoption.
Tech & AI:
MIT’s Andrew Lo predicts AI will make real investment decisions in 5 years.
OpenAI–Oracle to expand US data center capacity by 4.5 GW—significant tech infrastructure tailwind.
Conclusion for S&P 500 Trading:
The S&P 500 remains supported by strong risk appetite, AI optimism, and crypto momentum, but faces near-term tests from key tech earnings (Alphabet, Tesla). Political noise around the Fed and signs of speculative froth (meme stocks) could introduce volatility. Stay bullish with caution—watch earnings and Fed commentary closely for market direction.
Key Support and Resistance Levels
Resistance Level 1: 6340
Resistance Level 2: 6390
Resistance Level 3: 6457
Support Level 1: 6270
Support Level 2: 6224
Support Level 3: 6156
This communication is for informational purposes only and should not be viewed as any form of recommendation as to a particular course of action or as investment advice. It is not intended as an offer or solicitation for the purchase or sale of any financial instrument or as an official confirmation of any transaction. Opinions, estimates and assumptions expressed herein are made as of the date of this communication and are subject to change without notice. This communication has been prepared based upon information, including market prices, data and other information, believed to be reliable; however, Trade Nation does not warrant its completeness or accuracy. All market prices and market data contained in or attached to this communication are indicative and subject to change without notice.
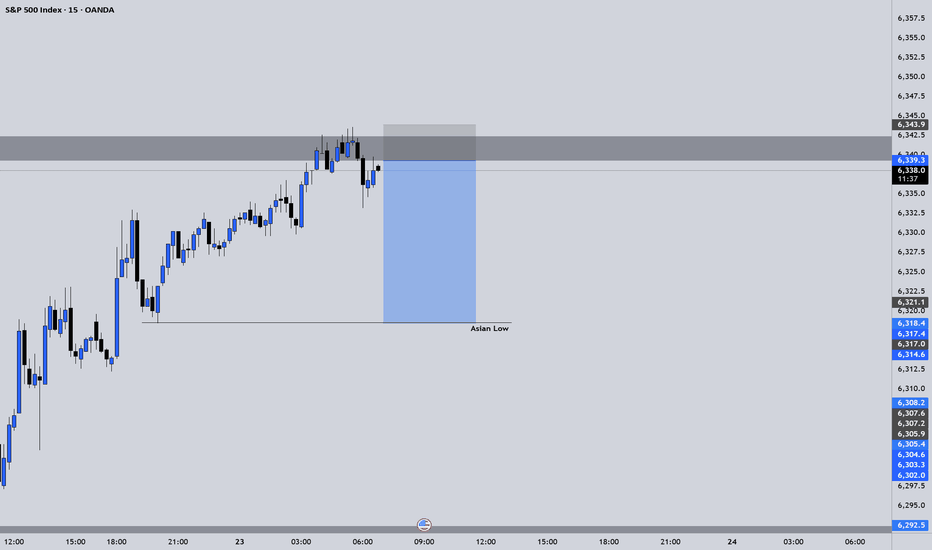
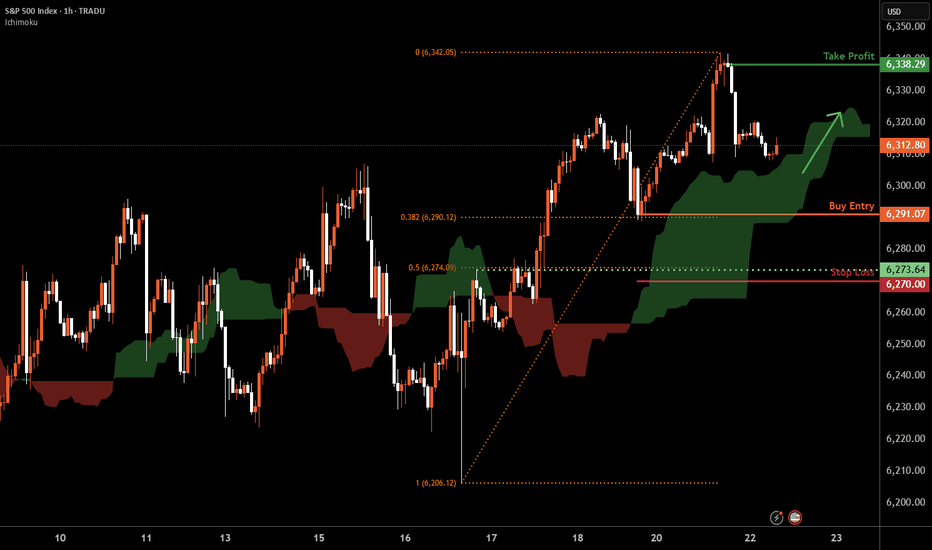
S&P 500 H1 | Swing-low support at 38.2% Fibonacci retracementThe S&P 500 (SPX500) is falling towards a swing-low support and could potentially bounce off this level to climb higher.
Buy entry is at 6,291.07 which is a swing-low support that aligns with the 38.2% Fibonacci retracement.
Stop loss is at 6,270.00 which is a level that lies underneath a pullback support and the 50% Fibonacci retracement.
Take profit is at 6,338.29 which is a swing-high resistance.
High Risk Investment Warning
Trading Forex/CFDs on margin carries a high level of risk and may not be suitable for all investors. Leverage can work against you.
Stratos Markets Limited (tradu.com ):
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 66% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
Stratos Europe Ltd (tradu.com ):
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 66% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
Stratos Global LLC (tradu.com ):
Losses can exceed deposits.
Please be advised that the information presented on TradingView is provided to Tradu (‘Company’, ‘we’) by a third-party provider (‘TFA Global Pte Ltd’). Please be reminded that you are solely responsible for the trading decisions on your account. There is a very high degree of risk involved in trading. Any information and/or content is intended entirely for research, educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute investment or consultation advice or investment strategy. The information is not tailored to the investment needs of any specific person and therefore does not involve a consideration of any of the investment objectives, financial situation or needs of any viewer that may receive it. Kindly also note that past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results. Actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in forward-looking or past performance statements. We assume no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of any of the information and/or content provided herein and the Company cannot be held responsible for any omission, mistake nor for any loss or damage including without limitation to any loss of profit which may arise from reliance on any information supplied by TFA Global Pte Ltd.
The speaker(s) is neither an employee, agent nor representative of Tradu and is therefore acting independently. The opinions given are their own, constitute general market commentary, and do not constitute the opinion or advice of Tradu or any form of personal or investment advice. Tradu neither endorses nor guarantees offerings of third-party speakers, nor is Tradu responsible for the content, veracity or opinions of third-party speakers, presenters or participants.
Waiting for a Clear Signal: Too Early to Short the IndexNothing interesting is forming on the index so far.
My outlook remains neutral.
I previously attempted to short it, but those attempts were unsuccessful. Now I need to wait for a more reliable entry point — the chart will show the way.
For now, I’m staying on the sidelines.
Historically, the start of the Fed’s rate-cutting cycle has always coincided with the beginning of a decline in the stock market. I believe this time won’t be an exception — but for now, it’s too early to short.
SPX - Time for a correction? To make it very simple,
Prices have been going up very nicely those last few weeks and months.
Everyone is happy but as we know that can't last.
NASDAQ:OPEN seems to be the latest pump and dump and it's just another sign of a coming correction imho.
Most stocks I've been following have reached resistance zone, levels where profit taking is very likely.
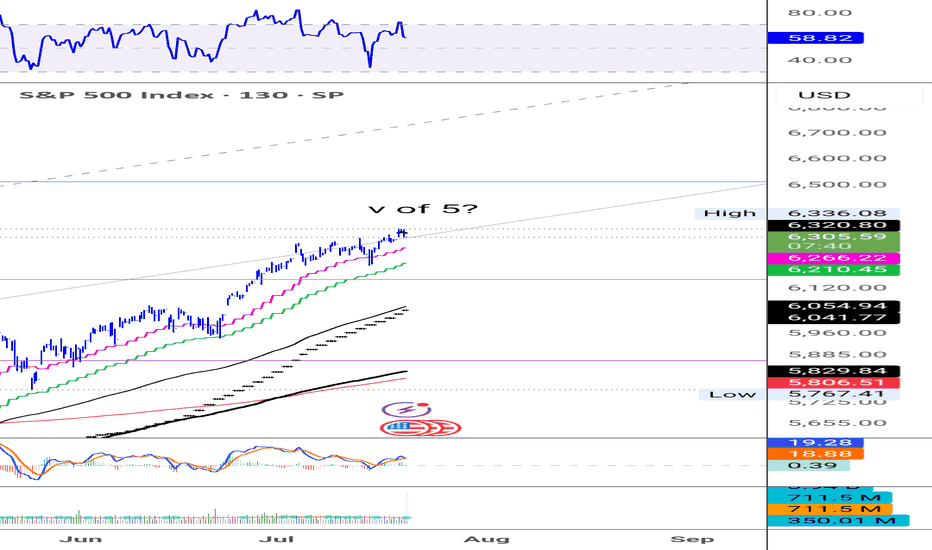
$S&P500 seems to have made a fifth wave, RSI divergence is present and confirming that.
It's difficult to pinpoint the exact top of course so I'm giving myself some leeway and use a small 1% stop loss in this case.