Falling Wedge Trading Pattern: Unique Features and Trading RulesFalling Wedge Trading Pattern: Unique Features and Trading Rules
Various chart patterns give an indication of possible market direction. A falling wedge is one such formation that indicates a possible bullish reversal. This FXOpen article will help you understand whether the falling wedge pattern is bullish or bearish, what its formation signifies about the market direction, and how it can be used to spot trading opportunities.
What Is a Falling Wedge Pattern?
Also known as the descending wedge, the falling wedge technical analysis chart pattern is a bullish formation that typically occurs in the downtrend and signals a trend reversal. It forms when an asset's price drops, but the range of price movements starts to get narrower. As the formation contracts towards the end, the buyers completely absorb the selling pressure and consolidate their energy before beginning to push the market higher. A falling wedge pattern means the end of a market correction and an upside reversal.
How Can You Spot a Falling Wedge on a Price Chart?
This pattern is usually spotted in a downtrend, which would indicate a possible bullish reversal. However, it may appear in an uptrend and signal a trend continuation after a market correction. Either way, the falling wedge provides bullish signals. The descending formation generally has the following features.
- Price Action. The price trades lower, forming lower highs and lower lows.
- Trendlines. Traders draw two trendlines. One connects the lower highs, and the other connects the lower lows. Finally, they intersect towards a convergence point. Each line should connect at least two points. However, the greater the number, the higher the chance of the market reversal.
- Contraction. The contraction in the price range signals decreasing volatility in the market. As the formation matures, new lows contract as the selling pressure decreases. Thus, the lower trendline acts as support, and the price consolidating within the narrowing range creates a coiled spring effect, finally leading to a sharp move on the upside. The price breaks through the upper trendline resistance, indicating that sellers are losing control and buyers are gaining momentum, resulting in an upward move.
- Volume. The trading volume ideally decreases as the pattern forms, and the buying volume increases with the breakout above the upper trendline, reflecting a shift in momentum towards the buyers.
Falling and Rising Wedge: Differences
There are two types of wedge formation – rising (ascending) and falling (descending).
An ascending wedge occurs when the highs and lows rise, while a descending wedge pattern has lower highs and lows. In an ascending formation, the slope of the lows is steeper and converges with the upper trendline at some point, while in a descending formation, the slope of the highs is steeper and converges with the support trendline at some point.
Usually, a rising wedge indicates that sellers are taking control, resulting in a downside breakdown. Conversely, a descending wedge pattern indicates that buyers are gaining momentum after consolidation, generally resulting in an upside breakout.
The Falling Wedge: Trading Rules
Trading the falling wedge involves waiting for the price to break above the upper line, typically considered a bullish reversal. The pattern’s conformity increases when it is combined with other technical indicators.
- Entry
According to theory, the ideal entry point is after the price has broken above the wedge’s upper boundary, indicating a potential upside reversal. Furthermore, this descending wedge breakout should be accompanied by an increase in trading volume to confirm the validity of the signal.
The price may retest the resistance level before continuing its upward movement, providing another opportunity to enter a long position. However, the entry point should be based on the traders' risk management plan and trading strategy.
- Take Profit
It is essential to determine an appropriate target level. Traders typically set a profit target by measuring the height of the widest part of the formation and adding it to the breakout point. Another approach some traders use is to look for significant resistance levels above the breakout point, such as previous swing highs.
- Stop Loss
Traders typically place their stop-loss orders just below the lower boundary of the wedge. Also, the stop-loss level can be based on technical or psychological support levels, such as previous swing lows. In addition, the stop-loss level should be set according to the trader's risk tolerance and overall trading strategy.
Trading Example
In the chart above, there is a falling wedge. A trader opened a buy position on the close of the breakout candlestick. A stop loss was placed below the wedge’s lower boundary, while the take-profit target was equal to the pattern’s widest part.
Falling Wedge and Other Patterns
Here are chart patterns that can be confused with a falling wedge.
Falling Wedge vs Bullish Flag
These are two distinct chart formations used to identify potential buying opportunities in the market, but there are some differences between the two.
A descending wedge is a bullish setup, forming in a downtrend. It is characterised by two converging trendlines that slope downward, signalling decreasing selling pressure. A breakout above the upper trendline suggests a bullish move.
A bullish flag appears after a strong upward movement and forms a rectangular shape with parallel trendlines that slope slightly downward or move sideways. This formation represents a brief consolidation before the market resumes its upward trajectory.
While the falling wedge indicates a potential shift in a downtrend, the bullish flag suggests a continuation of an uptrend.
Falling Wedge vs Bearish Pennant
The falling wedge features two converging trendlines that slope downward, indicating decreasing selling pressure and often signalling a bullish reversal when the price breaks above the upper trendline.
Conversely, the bearish pennant forms after a significant downward movement and is characterised by converging trendlines that create a small symmetrical triangle. This pattern represents a consolidation phase before the market continues its downward trend upon breaking below the lower trendline.
While the falling wedge suggests a potential bullish move, the bearish pennant indicates a continuation of the bearish trend.
Falling Wedge vs Descending Triangle
The falling wedge consists of two downward-sloping converging trendlines, indicating decreasing selling pressure and often signalling a bullish reversal when the price breaks above the upper trendline. In contrast, the descending triangle features a flat lower trendline and a downward-sloping upper trendline, suggesting a buildup of selling pressure and typically signalling a bearish continuation when the price breaks below the flat lower trendline.
While the falling wedge is associated with a potential bullish move, the descending triangle generally indicates a bearish trend.
Falling Wedge: Advantages and Limitations
Like any technical pattern, the falling wedge has both limitations and advantages.
Advantages
- High Probability of a Reversal. The falling wedge is often seen as a strong, bullish signal, especially when it occurs after a downtrend. It suggests that selling pressure is subsiding, and a reversal to the upside may be imminent.
- Clear Entry and Exit Points. The pattern provides clear points for entering and exiting trades. Traders often enter when the price breaks out above the upper trendline and set stop-loss orders below a recent low within the formation.
- Versatility. The wedge can be used in various market conditions. It is effective in both continuation and reversal scenarios, though it is more commonly associated with bullish reversals.
- Widely Recognised. Since the falling wedge is a well-known formation, it is often self-fulfilling to some extent, as many traders recognise and act on it, further driving the market.
Limitations
- False Breakouts. Like many chart patterns, the falling wedge is prone to false breakouts. Prices may briefly move above the resistance line but then fall back below, trapping traders.
- Dependence on Market Context. The effectiveness of the falling wedge can vary depending on broader market conditions. In a strong downtrend, it might fail to result in a significant reversal.
- Requires Confirmation. The wedge should be confirmed with other technical indicators or analysis tools, such as volumes or moving averages, to increase the likelihood of an effective trade. Relying solely on the falling wedge can be risky.
- Limited Use in Low-Volatility Markets. In markets with low volatility, the falling wedge may not be as reliable, as price movements might not be strong enough to confirm the falling wedge's breakout.
The Bottom Line
The falling wedge is a powerful chart pattern that can offer valuable insights into potential trend reversals or continuations, depending on its context within the broader market. By understanding and effectively utilising the falling wedge in your strategy, you can enhance your ability to identify many trading opportunities. As with all trading tools, combining it with a comprehensive trading plan and proper risk management is crucial.
FAQ
Is a Falling Wedge Bullish?
Yes, the falling wedge is a bullish continuation pattern in an uptrend, and it acts as a bullish reversal formation in a bearish market.
What Does a Falling Wedge Pattern Indicate?
It indicates that the buyers are absorbing the selling pressure, which is reflected in the narrower price range and finally results in an upside breakout.
What Is the Falling Wedge Pattern Rule?
The falling wedge is a technical analysis formation that occurs when the price forms lower highs and lower lows within converging trendlines, sloping downward. Its rule is that a breakout above the upper trendline signals a potential reversal to the upside, often indicating the end of a downtrend or the continuation of a strong uptrend.
How to Trade Descending Wedge Patterns?
To trade descending wedges, traders first identify them by ensuring that the price is making lower highs and lows within converging trendlines. Then, they wait for the price to break out above the upper trendline, ideally accompanied by increased trading volume, which confirms the breakout. After the breakout, a common approach is to enter a long position, aiming to take advantage of the anticipated upward movement.
What Is the Target of the Descending Wedge Pattern?
The target for a descending wedge is typically set by measuring the maximum width of the wedge at its widest part and projecting that distance upwards from the breakout point. This projection gives a potential price target.
What Is the Entry Point for a Falling Wedge?
The entry point for a falling wedge is ideally just after the breakout above the upper trendline. Some traders prefer to wait for a retest of the broken trendline, which may act as a new support level, before entering a trade to confirm the breakout.
*Important: At FXOpen UK, Cryptocurrency trading via CFDs is only available to our Professional clients. They are not available for trading by Retail clients. To find out more information about how this may affect you, please get in touch with our team.
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
Trend Analysis
Why you should WAIT for trades to come to YOU!In this video, we dive deep into one of the most underrated but powerful habits that separates consistently profitable traders from the rest: waiting for the trade to come to you.
It sounds simple, even obvious. But in reality, most traders—especially newer ones—feel the constant urge to do something. They scan for setups all day, jump in at the first sign of movement, and confuse activity with progress. That mindset usually leads to emotional trading, overtrading, and eventually burnout.
If you've ever felt the pressure to chase price, force trades, or trade just because you're bored… this video is for you.
I’ll walk you through:
1. Why chasing trades destroys your edge—even when the setup “kind of” looks right
2. How waiting allows you to trade from a position of strength, not desperation
3. The psychological shift that happens when you stop trading to feel busy and start trading to feel precise
4. How the pros use waiting as a weapon, not a weakness
The truth is, trading is a game of probabilities and precision. And that means you don’t need 10 trades a day—you need a few good ones a week that truly align with your plan.
Patience doesn’t mean doing nothing, it means doing the right thing at the right time. And when you develop the skill to sit back, trust your process, and wait for price to come to your level… everything changes. Your confidence grows. Your equity curve smooths out. And most importantly, your decision-making gets sharper.
So if you're tired of overtrading, feeling frustrated, or constantly second-guessing your entries—take a breath, slow it down, and start thinking like a sniper instead of a machine gun.
Let the market come to you. That’s where the real edge is.
Trump's Tariff Wars : Why It Is Critical To Address Global TradeThis video, a continuation of the Trump's Tariff Wars video I created last week, tries to show you why it is critically important that we, as a nation, address the gross imbalances related to US trade to global markets that are resulting in a $1.5-$1.8 TRILLION deficit every fiscal year.
There has been almost NOTHING done about this since Trump's last term as President.
Our politicians are happy to spend - spend - spend - but none of them are worries about the long-term fiscal health of the US. (Well, some of them are worried about it - but the others seem to be completely ignorant of the risks related to the US).
Trump is raising this issue very early into his second term as president to protect ALL AMERICANS. He is trying to bring the issue into the news to highlight the imbalances related to US trade throughout the world.
When some other nation is taking $300B a year from the us with an unfair tariff rate - guess what, we need to make that known to the American consumer because we are the ones that continue to pay that nation the EXTRA every year.
Do you want to keep paying these other nations a grossly inefficient amount for cheap trinkets, or do you want our politicians and leaders to take steps to balance the trade deficits more efficiently so we don't pass on incredible debt levels to our children and grandchildren?
So many people simply don't understand what is at risk.
Short-term - the pain may seem excessive, but it may only last 30, 60, 90 days.
Long-term - if we don't address this issue and resolve it by negotiating better trade rates, this issue will destroy the strength of the US economy, US Dollar, and your children's future.
Simply put, we can't keep going into debt without a plan to attempt to grow our GDP.
The solution to this imbalance is to grow our economy and to raise taxes on the uber-wealthy.
We have to grow our revenues and rebalance our global trade in an effort to support the growth of the US economy.
And, our politicians (till now) have been more than happy to ignore this issue and hide it from the American people. They simply didn't care to discuss it or deal with it.
Trump brought this to the table because it is important.
I hope you now see HOW important it really is.
Get some.
#trading #research #investing #tradingalgos #tradingsignals #cycles #fibonacci #elliotwave #modelingsystems #stocks #bitcoin #btcusd #cryptos #spy #gold #nq #investing #trading #spytrading #spymarket #tradingmarket #stockmarket #silver
Learn 3 Best Time Frames for Day Trading Forex & Gold
If you want to day trade Forex & Gold, but you don't know what time frames you should use for chart analysis and trade execution, don't worry.
In this article, I prepared for you the list of best time frames for intraday trading and proven combinations for multiple time frame analysis.
For day trading forex with multiple time frame analysis, I recommend using these 3 time frames: daily, 1 hour, 30 minutes.
Daily Time Frame Analysis
The main time frame for day trading Forex is the daily.
It will be applied for the identification of significant support and resistance levels and the market trend.
You should find at least 2 supports that are below current prices and 2 resistances above.
In a bullish trend, supports will be applied for trend-following trading, the resistances - for trading against the trend.
That's the example of a proper daily time frame analysis on GBPCHF for day trading.
The pair is in an uptrend and 4 significant historic structures are underlined.
In a downtrend, a short from resistance will be a daytrade with the trend while a long from support will be against.
Look at GBPAUD. The market is bearish, and a structure analysis is executed.
Identified supports and resistances will provide the zones to trade from. You should let the price reach one of these areas and start analyzing lower time frames then.
Remember that counter trend trading setups always have lower accuracy and a profit potential. Your ability to properly recognize the market direction and the point that you are planning to open a position from will help you to correctly assess the winning chances and risks.
1H/30M Time Frames Analysis
These 2 time frames will be used for confirmations and entries.
What exactly should you look for?
It strictly depends on the rules of your strategy and trading style.
After a test of a resistance, one should wait for a clear sign of strength of the sellers : it can be based on technical indicators, candlestick, chart pattern, or something else.
For my day trading strategy, I prefer a price action based confirmation.
I wait for a formation of a bearish price action pattern on a resistance.
Look at GBPJPY on a daily. Being in an uptrend, the price is approaching a key resistance. From that, one can look for a day trade .
In that case, a price action signal is a double top pattern on 1H t.f and a violation of its neckline. That provides a nice confirmation to open a counter trend short trade.
Look at this retracement that followed then.
In this situation, there was no need to open 30 minutes chart because a signal was spotted on 1H.
I will show you when one should apply this t.f in another setup.
Once the price is on a key daily support, start looking for a bullish signal.
For me, it will be a bullish price action pattern.
USDCAD is in a strong bullish trend. The price tests a key support.
It can be a nice area for a day trade.
Opening an hourly chart, we can see no bullish pattern.
If so, open even lower time frame, quite often it will reveal hidden confirmations.
A bullish formation appeared on 30 minutes chart - a cup & handle.
Violation of its neckline is a strong day trading long signal.
Look how rapidly the price started to grow then.
In order to profitably day trade Forex, a single time frame analysis is not enough . Incorporation of 3 time frames: one daily and two intraday will help you to identify trading opportunities from safe places with the maximum reward potential.
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
Swing Trading: Unique Features and StrategiesSwing Trading: Unique Features and Strategies
Swing trading stands out as a dynamic approach in the trading world, blending elements of both short-term and long-term strategies. In this article, we will explore the unique features of swing trading, including its reliance on technical analysis, the use of chart patterns, and the strategic timing of entries and exits. Whether you're new to trading or seeking to refine your approach, understanding the nuances of swing trading can provide valuable insights into navigating the financial markets.
The Basics of Swing Trading
Swing trading meaning refers to a style that involves holding short- and medium-term positions - usually from a couple of days to a few weeks - with the aim of capitalising on the “swings” in the market.
What is a swing trader? A swing trader’s definition is simple: swing traders are those who typically enter and exit markets at significant support and resistance levels, hoping to capture the bulk of expected moves.
These traders tend to look at hourly to weekly charts to guide their entries, although the timeframe used will depend on the swing trader’s individual approach and the asset being traded. Swing trading can be used across all asset classes, from stocks and forex to cryptocurrencies* and commodities. In the stock market, swing trading can be especially effective, as stocks tend to experience high volatility and are subject to frequent news and events that can drive prices.
Swing traders predominantly use technical analysis to determine their entries and exits, but fundamental analysis, like comparing the interest rates of two economies, can also play a significant role. It can help determine a price direction over the course of days or weeks.
Swing Trading vs Other Styles
To better understand the unique features of swing trading, let’s compare it with our styles.
Position trading involves holding trades for weeks and months, focusing on capturing long-term trends. Position traders are less concerned with short-term fluctuations and are more likely to use fundamental analysis, such as economic data and company earnings, to make their decisions. This style requires patience and a long-term perspective, with fewer trades but potentially larger returns per trade.
Swing trading involves holding trades for several days to a few weeks, aiming to capture short- and medium-term price movements within a larger trend. This style balances the need for active market participation with the flexibility to not monitor trades constantly. Swing traders primarily rely on technical analysis to identify entry and exit points, focusing on chart patterns and indicators.
Day trading requires traders to buy and sell assets within the same trading day, often holding positions for just minutes or hours. The goal is to capitalise on intraday price movements, and traders close all positions before the market closes to avoid overnight risk. This style demands constant market monitoring and quick decision-making, with a strong reliance on real-time technical analysis.
Scalping is an ultra-short-term trading style where positions are held for seconds to minutes, aiming to make small profits on numerous trades throughout the day. Scalpers rely almost entirely on technical analysis and need to act quickly, often executing dozens or hundreds of trades daily. The focus is on high-frequency trading with very tight stop-losses, requiring intense concentration.
Swing Trading: Benefits and Challenges
Although swing trading provides numerous opportunities which makes it popular among traders, it comes with a few challenges traders should be aware of.
Benefits:
- Lower Time Commitment. One of the most significant benefits for swing traders is the reduced time commitment. This style can be adapted to suit a trader’s individual schedule.
- Flexibility. It is often more flexible than other styles. Not only does it offer time flexibility, but it allows for a wider range of tools to be used to determine price swings. Also, it can be applied to many assets. The most common is swing trading in forex and swing trading in stocks.
- Technical Analysis Focus: Utilises technical indicators and chart patterns to identify entry and exit points, providing clear criteria for decision-making.
- More Opportunities Compared to Long-Term Techniques. Because swing traders usually hold positions for a few days to a few weeks, they have the ability to take advantage of shorter-term market movements that might not be reflected in longer-term price trends.
Challenges:
- Exposure to Overnight Risk. Positions held overnight or over weekends can be affected by unexpected news or events, leading to potential gaps or adverse price movements.
- Requires Patience: Effective swing trading requires waiting for trades to develop over days or weeks, which may test a trader's patience.
- Market Volatility: Performance can be impacted by periods of low volatility or choppy markets, where price movements may not align with your expectations.
Popular Tools to Use When Swing Trading
The effectiveness of a swing traders’ strategies will ultimately depend on their ability to correctly identify price movements. For this, traders use different chart patterns and technical indicators. Here are three common tools that can be used as part of a swing trading strategy.
Channels
Traders can use channels to take advantage of well-identified price trends that play out over days and weeks. To plot a channel, you first need to identify a trending asset that’s moving in a relative zig-zag pattern rather than one with large jumps in price. Traders will often use the channel to open a swing trade in the direction of the trend; in the example above, they might look to buy when the price tests the lower line and take profit when the price touches the upper line of the channel.
Moving Averages
Moving averages (MAs) are one of the commonly used indicators and they can help swing traders determine the direction of the trend at a glance. The options here are endless:
- You could pair fast and slow moving averages and wait for the two to cross; this is known as a moving average crossover. When a shorter MA crosses above a longer one, the price is expected to rise. Conversely, when a shorter MA breaks below a longer one, the price is supposed to decline.
- You could stick with one and observe whether the price is above or below its average to gauge the trend. When the price is above the MA, it’s an uptrend; when it’s below the MA, it’s a downtrend.
- You could use an MA as a support or resistance level, placing a buy order when the price falls to the MA in an uptrend and a sell order when it rises to the MA in a downtrend.
Fibonacci Retracements
Lastly, many swing traders look to enter pullbacks in a larger trend. One of the most popular ways to identify entry levels during these pullbacks is the Fibonacci Retracement tool. Traders typically wait for a shift in price direction, then apply the tool to a swing high and swing low. Then, they enter at a pullback, usually to the 0.5 or 0.618 levels, to take advantage of the continuation of the trend. As seen above, this strategy can offer entry points for those looking to get in early before a trend continues.
The Bottom Line
Swing trading stands out for its ability to balance the demands of active trading with the flexibility of longer-term investing. The unique features of swing trading, such as its moderate holding periods and strategic use of technical indicators, allow traders to potentially manage risk and adapt to various market conditions. Embracing swing trading strategies can help traders refine their approach. As with any trading style, continued learning and disciplined execution are key to achieving consistent results.
FAQ
What Is Swing Trading?
Swing trading is a style that involves holding positions over a period of several days to weeks to take advantage of price movements within a trend. Swing traders use technical analysis, including chart patterns and indicators, to identify potential entry and exit points, balancing the need for active participation with a longer-term perspective.
What Is Swing Trading vs Day Trading?
Swing trading and day trading are distinct methods. The former focuses on capturing price movements over several days to weeks, allowing for less frequent trading and requiring less constant market monitoring. In contrast, the latter involves buying and selling assets within the same trading day, often holding positions for minutes or hours, and requires continuous market observation and quick decision-making.
What Is the Downside of Swing Trading?
The downsides of swing trading include exposure to overnight and weekend risks, as positions held outside market hours can be affected by unexpected news or events. Additionally, this method requires patience and discipline, as trades may take time to develop, and performance can be impacted by periods of low volatility or choppy markets.
*Important: At FXOpen UK, Cryptocurrency trading via CFDs is only available to our Professional clients. They are not available for trading by Retail clients. To find out more information about how this may affect you, please get in touch with our team.
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
Ultimate Guide to Smart Money ConceptsWhat Are Smart Money Concepts?
Introduction:
If you’ve been trading for a while, you’ve probably noticed that sometimes the market moves in ways that just don’t make sense. You’ve got your technical analysis all set, but the market seems to go in the opposite direction. That’s where Smart Money Concepts (SMC) come in.
At its core, SMC is all about understanding how big players in the market (think hedge funds, institutions, and banks) move prices. These players have massive amounts of capital and information, and they don’t trade like the average retail trader. Understanding their behavior can help you see where the market is going next before it happens.
What is Smart Money?
In the world of trading, smart money refers to the institutional investors who move markets with their huge orders. Unlike retail traders, who might be relying on indicators or patterns, smart money trades based on liquidity, market structure, and order flow.
While retail traders are typically reacting to price movements, smart money is the one causing those moves. They’re out there seeking out places where they can accumulate positions or distribute them. The tricky part is that they’ll often make the market go in one direction just to trap retail traders and get them to take positions before flipping it back to where they wanted it to go in the first place.
Key Concepts in Smart Money Trading
1. Market Structure
Market structure refers to the way price moves in a trend. It’s essentially a pattern of higher highs and higher lows for an uptrend, or lower highs and lower lows for a downtrend.
Smart money uses these patterns to their advantage. When they see the market creating a series of higher highs and higher lows, they’ll take advantage of that momentum to push prices further, knowing retail traders will follow along.
But when they want to reverse the market, they’ll push it in the opposite direction, creating a market structure shift or a break of structure, which signals that the trend is over and a new one is starting.
2. Liquidity
Liquidity refers to the amount of orders available to be filled at different price levels. Smart money knows exactly where retail traders are likely to place their stops or buy orders.
They’ll often push the price to these levels, triggering those stops and collecting the liquidity. Once that liquidity is grabbed, they’ll reverse the price and move it in the intended direction.
A common way to spot liquidity is by looking for equal highs or equal lows, where traders often place their stop-loss orders. These are often areas smart money will target.
3. Order Blocks
Order blocks are areas on the chart where institutions have placed big orders. These are key levels that represent where price might return to later, and they can act as areas of support or resistance.
Order blocks are usually found after big price moves. Institutions place these orders to either accumulate positions or offload them, and price often comes back to these levels to fill orders that were left behind.
4. Fair Value Gaps (FVG)
Fair value gaps, or imbalances, are price areas where the market moves quickly, leaving gaps between candlesticks. These gaps represent areas where the market has moved too fast for regular orders to fill, and price tends to return to these levels to fill the gaps.
Smart money knows that these imbalances are critical areas for future price action, and they’ll use them to re-enter the market after a move has been completed.
Why Does Smart Money Matter?
Understanding smart money concepts is like learning to think like an institution. Instead of chasing after price based on typical retail indicators, you start looking for the big moves that smart money is making. You begin to notice when the market is setting traps for retail traders, and how these large players accumulate positions before pushing price in a big way.
With SMC, you stop guessing and start anticipating. By looking for liquidity zones, order blocks, and market structure shifts, you can get in sync with the big players and follow their moves, not fight them.
Conclusion
Smart Money Concepts are all about shifting your perspective. Instead of thinking like a retail trader looking for quick breakouts, oversold/overbought conditions, or chasing trends — start looking at the market as the big players do. Pay attention to where the liquidity is, identify key order blocks, and use market structure shifts to guide your trades.
By learning to spot these key signs, you’ll stop being the one who’s trapped and start being the one who’s in sync with the smart money.
Ready to trade smarter? Keep an eye on those order blocks and liquidity zones — they’re where the real money is made.
Next Steps
- Start practicing by reviewing charts through the SMC lens.
- Keep refining your understanding of market structure, liquidity, and order blocks.
- Stay patient, smart money trades aren’t about quick wins, but about positioning yourself for big moves.
__________________________________________
Thanks for your support!
If you found this guide helpful or learned something new, drop a like 👍 and leave a comment, I’d love to hear your thoughts! 🚀
Make sure to follow me for more price action insights, free indicators, and trading strategies. Let’s grow and trade smarter together! 📈
Why Support and Resistance are Made to Be Broken ?Hello fellow traders! Hope you're navigating the markets smoothly. As we go through the daily dance of price action, one thing becomes clear support and resistance are just moments, not walls. They're temporary. Momentum and trend strength? Now that’s where the real story lies.
This publication dives into how these so-called key levels break and more importantly, how to position yourself smartly when they do. Stay flexible, trade with confidence, and let the market lead. Let’s get into it.
Why Support and Resistance Levels Break
Support and resistance are some of the most talked-about tools in technical analysis. But here's the truth they’re not meant to last forever.
No matter how strong a level may appear on your chart, it eventually gets tested, challenged, and often broken. Why? Because the market is dynamic. The real edge for a trader lies not in hoping a level holds, but in reading when it’s about to fail and being ready for it.
No Resistance in a Bull, No Support in a Bear
Ever seen a strong bull market pause just because of a resistance line? It doesn’t. Price keeps pushing higher as buyers keep stepping in. Same goes for a strong bear market support levels collapse as fear takes over and selling snowballs.
Instead of clinging to lines on a chart, think bigger: Where is the momentum? What’s the trend saying? That’s where your trading decisions should come from.
Support and Resistance: Not Fixed, Always Shifting
Yes, these levels matter but only as zones, not exact prices. They’re areas where price has reacted in the past, where traders might expect something to happen again. But they’re not magic numbers.
When traders treat these levels as absolute, they fall into traps false confidence, poor entries, tighter than-needed stop losses. Always remember: market sentiment, liquidity, and institutional activity are constantly changing. So should your interpretation of the chart.
The Temporary Nature of These Levels
Markets move on supply and demand. A level that acted as resistance last week could easily become support next week. Or break completely.
Take the classic example support turning into resistance. When support breaks, former buyers might now be sellers, trying to get out on a bounce. That flip happens because behavior and sentiment have shifted. And as traders, that’s the real pattern we need to track not just price levels, but the psychology behind them.
“Strong” Support? It’s Mostly an Illusion
We all love the idea of a strong level something we can lean on. But large players? They don’t think like that.
Institutions don’t place massive orders at a single price point. They spread across a zone building positions slowly without moving the market too much. What looks like a strong level to us might just be an accumulation or distribution range for them. Always think beyond what’s visible on the surface.
How to Spot Breakouts Before They Hit
Here’s what separates seasoned traders from the rest the ability to spot potential breakouts before they explode.
🔹 Volume Confirmation: If a resistance level is tested repeatedly on rising volume, that’s a big clue buyers are serious.
🔹 Structure Shifts: Higher highs in an uptrend or lower lows in a downtrend signal that the old levels are being challenged.
🔹 Liquidity Traps: Watch out for fakeouts. These are designed to trap impatient traders just before the real move.
🔹 News & Events: Never ignore macro triggers. Earnings, economic data, or geopolitical surprises can fuel breakouts that crush technical levels.
🔹 Break & Retest: A solid strategy — wait for the level to break, then get in on the retest.
🔹 Momentum Tools: Indicators like RSI, MACD, or even EMAs can offer extra confidence that a move has legs.
3 Practical Trading Setups
1. Breakout Trading
Mark key levels on daily or weekly charts.
Watch for volume and momentum confirmation.
Enter after a clear breakout or retest.
Stop-loss: Just below resistance (for longs) or above support (for shorts).
2. Range Trading
If price is stuck between support and resistance, trade the range.
Look for price rejection (wicks, pin bars, etc.).
Use RSI or Stochastics to time entries.
3. Trend Following
Identify the dominant trend using moving averages or price structure.
Avoid going against the trend unless reversal signs are very clear.
Let profits run use trailing stops instead of fixed targets.
Mind Over Market: Psychology of S&R
One of the biggest traps in trading? Overtrusting support and resistance.
We get emotionally attached. We want the support to hold or the resistance to reject. And that bias clouds our judgment. How many times have you seen price break a level — and you freeze because it “wasn’t supposed to”?
To break free of that:
✅ Trade with a plan.
✅ Set your risk before the trade, not after.
✅ Don’t treat any level as sacred.
✅ Stay open to what the market is telling you not what you want it to say.
Final Thoughts
Support and resistance are great tools but they’re just one part of the puzzle. The real power lies in reading price action, watching volume, and understanding market sentiment. Don’t ask, “Will this level hold?” Ask instead, “What happens if it breaks?”
That shift in thinking? It can make all the difference.
Stay sharp, stay adaptive, and keep evolving with the market.
Wishing you green trades and growing accounts!
Best Regards- Amit Rajan.
Why I Only Buy Dips / Sell Rallies When I Trade GoldWhen it comes to trading Gold (XAUUSD), I’ve learned one key truth: breakouts lie, but dips/rallies tell the truth.
That’s why I stick to one rule that has kept me consistently profitable:
I only buy dips in an uptrend and only sell rallies in a downtrend.
Let me explain exactly why this approach works so well—especially on Gold, a notoriously tricky market.
________________________________________
1. 🔥 Gold is famous for fake breakouts
Breakouts on Gold often look amazing… until they trap you.
You enter just as price breaks a key level—then suddenly it reverses and stops you out.
This happens because Gold loves to tease liquidity. It breaks highs or lows just enough to activate stop losses or attract breakout traders, only to reverse.
Buying dips or selling rallies protects you from these traps by entering from value, not hype.
________________________________________
2. ✅ I get better stop-loss placement and risk:reward
When I buy a dip, I can place my stop below a strong level (like a support zone or swing low).
That gives me tight risk and allows for big reward potential—often 1:2, 1:3 or more.
Breakout trades, on the other hand, often require wider stops or result in poor entries due to emotional execution.
________________________________________
3. ⏳ I get time to assess the market
False breakouts happen fast. But dips usually form more gradually.
That gives me time to analyze price action, spot confirmation signals, and even scratch the trade at breakeven if it starts to fail.
This reduces emotional decisions and increases my accuracy.
________________________________________
4. 🎯 Gold respects key levels more than it respects momentum
Even in strong trends, Gold often retraces deeply and retests zones before continuing.
That means entries near key levels—on a dip or rally—are more reliable than chasing price.
I’d rather wait for the zone than jump in mid-air.
________________________________________
5. 🔁 Even in aggressive trends, Gold often reverts to the mean
Lately, Gold has been trending hard—no doubt.
But even during explosive moves, it frequently pulls back to key moving averages or demand zones.
That’s why mean reversion entries on dips or rallies continue to offer excellent setups, even in fast-moving markets.
________________________________________
6. 🧠 I benefit from retail trader mistakes
Most traders get excited on breakouts.
But what usually happens? The breakout fails, and the price returns to structure.
By waiting for the dip/rally (when others are panicking or taking losses), I can enter at a discount and ride the move in the right direction.
________________________________________
7. 🧘♂️ This strategy forces patience and discipline
Waiting for dips or rallies requires patience.
You don’t jump in randomly. You plan your entry, your stop, your take profit—calmly.
That mental discipline is a trading edge on its own.
________________________________________
8. 📊 I align myself with probability, not emotion
In an uptrend, buying a dip is logical.
In a downtrend, selling a rally is natural.
Trying to “chase the breakout” is emotional—trying to get in on the action, fearing you'll miss the move.
I trade with the trend, from the right zone, and with a clear plan.
________________________________________
9. 🕒 I can use pending limit orders and walk away
One of the most underrated benefits of trading dips and rallies?
I don’t need to chase the market or be glued to the screen.
When I see a clean level forming, I simply place a buy limit (or sell limit) with my stop and target predefined.
This saves time, reduces overtrading, and keeps my emotions in check.
It’s a set-and-forget approach that fits perfectly with Gold’s tendency to return to key zones—even during high volatility.
________________________________________
🔚 Final thoughts
There’s no perfect trading strategy. But when it comes to Gold, buying dips and selling rallies consistently keeps me on the right side of probability.
I avoid the emotional traps. I get better entries. And most importantly, I protect my capital while maximizing reward.
Next time you see Gold breaking out, ask yourself:
“Is this real… or should I just wait for the dip/rally?”
That question might save you a lot of pain.
How Can You Use the STRAT Method in Trading?How Can You Use the STRAT Method in Trading?
The STRAT method is a unique trading approach that is supposed to simplify market analysis by breaking price action into clear, actionable scenarios. Developed by Rob Smith, it focuses on candlestick patterns, scenarios, and timeframe alignment to help traders better understand market structure. This article explores the key components of the STRAT method, its practical application, and how it can potentially refine trading strategies.
What Is the STRAT Trading Method?
The STRAT method is a trading strategy created by Rob Smith. It’s designed to simplify technical analysis by focusing on price action and breaking down market movements into clear, actionable steps. At its core, the STRAT strategy categorises price behaviour into three scenarios—inside bars (1), directional bars (2), and outside bars (3)—helping traders identify potential opportunities and understand the market structure.
One of the STRAT’s standout features is its emphasis on timeframe continuity, where traders examine how price movements align across different timeframes, such as daily, weekly, and monthly charts. This alignment helps traders gauge the broader market direction, potentially improving their analysis.
The STRAT trading method also uses specific candlestick patterns to signal potential reversals or continuations. For example, an inside bar (Scenario 1) indicates price consolidation, often preceding a breakout. A directional bar (Scenario 2) suggests trending movement, while an outside bar (Scenario 3) reflects heightened volatility by capturing both higher and lower price ranges.
Unlike some trading approaches that rely heavily on indicators, the STRAT focuses on raw price action, giving traders a clearer, no-nonsense view of market dynamics. It’s an accessible and structured way to analyse charts and make decisions based on what the market is doing right now.
Key Components of the STRAT Trading Strategy
The STRAT trading strategy stands out because of its straightforward approach to breaking down price action. As mentioned above, inside bars, directional bars, and outside bars are central scenarios. These scenarios categorise how the price behaves within a given timeframe, providing a framework for traders to interpret the market. Let’s delve into each component in detail.
Scenario 1: Inside Bar
An inside bar forms when the current candlestick's high and low remain within the range of the previous candlestick. In other words, the market is consolidating, showing no breakout beyond the prior candle’s extremes. Traders often interpret this as a pause or a moment of indecision in the market.
What makes inside bars significant is their potential to precede larger price movements. For example, after a series of inside bars, a breakout often occurs when the price breaks above or below the consolidation range. While this pattern alone doesn’t confirm direction, it signals the market is storing energy for a potential move.
Scenario 2: Directional Bar
A directional bar, also called a “2” in STRAT terminology, occurs when the price breaks either the high or low of the previous candle but not both. This creates a clear directional move—either upward (2 up) or downward (2 down).
These bars are essential because they indicate that the market has picked a direction. A “2 up” shows bullish momentum, while a “2 down” signals bearish activity. These movements are especially useful when aligned with other factors, such as larger trends or support and resistance levels.
Scenario 3: Outside Bar
The outside bar is the most volatile of the three. It forms when the current candlestick's high exceeds the previous candle’s high, and its low breaks below the previous low. Essentially, the price covers both sides of the prior range, capturing significant market activity.
Outside bars often suggest a battle between buyers and sellers, leading to volatility. These bars can provide insights into reversals or continuing trends, depending on their context within the broader market structure.
Expanding and Contracting Markets
The STRAT method also places significant emphasis on understanding the expanding and contracting market phases, which offer critical insights into market dynamics. These phases reflect shifts in volatility and price behaviour, helping traders interpret broader market conditions.
Expanding markets occur when price action creates both higher highs and lower lows compared to previous bars or ranges. This phase often signals heightened volatility as buyers and sellers battle for control, creating larger swings. Scenario 3 (outside bars) typically appears during this phase, capturing the market’s attempt to push in both directions. Expanding markets can provide potential opportunities for traders who are prepared to navigate rapid price movements.
Contracting markets, on the other hand, are characterised by shrinking ranges, with lower highs and higher lows. This consolidation phase often results in inside bars (Scenario 1) and suggests indecision or reduced momentum. Traders frequently watch for potential breakouts as the market transitions out of contraction.
Combining Scenarios and Context
Ultimately, there are many combinations of these bars under the STRAT method, each with names like the 3-2-2 Bearish Reversal, 2-2 Bearish Continuation, 1-2-2 Bullish Reversal, and so on. For traders new to this system, it might be easier to start with a handful of patterns and practice them before adding others to their arsenal.
Some of the basic starting patterns include:
2-1-2 Reversal
3-1-2 Reversal
2-1-2 Continuation
2-2 Continuation
However, each of these scenarios becomes even more meaningful when paired with other market data, such as higher timeframes or candlestick structures. For instance, patterns like hammers or shooting starts often emerge within these scenarios, offering specific signals to traders.
Timeframe Continuity: A Core Pillar
Timeframe continuity is a fundamental aspect when interpreting the STRAT candle patterns, offering traders a way to align their analysis across multiple timeframes. It’s about ensuring that the price action on smaller timeframes complements what’s happening on larger ones. When all timeframes “agree,” it can provide a clearer picture of market direction and potentially improve the decision-making process.
In practice, traders using the STRAT in stocks, forex, commodities, and other assets often look at three primary timeframes: the daily, weekly, and monthly charts. Each represents a piece of the puzzle. For example, if a trader sees a bullish “Scenario 2” (directional bar) on the daily chart, but the weekly chart shows a bearish pattern, this misalignment might signal caution. However, when the daily, weekly, and monthly timeframes all show bullish directional movement, it creates a stronger case for a trend continuation.
Timeframe continuity also helps traders filter out noise. Shorter timeframes, like the 15-minute or hourly charts, can produce conflicting signals, leading to overtrading or confusion. By focusing on the larger timeframes first, traders can ground their analysis in broader market trends and avoid reacting impulsively to minor fluctuations.
Practical Application of the STRAT Method
Applying the STRAT method involves a systematic approach to analysing charts and identifying potential opportunities. While every trader may adapt the method to their own style, the process generally follows a logical flow. Here’s how it can be broken down:
Step 1: Understanding the Current Scenario
Traders typically start by identifying the active scenario (1, 2, or 3) on their chosen timeframe. This initial classification helps to set the context. For instance, in the EUR/USD daily chart above, we initially see an outside bar (Scenario 3), followed by two inside bars (Scenario 1)—a 3-1-1 Bullish Reversal pattern; this transitions into a 1-2 Bullish Reversal before a 2-2 Bullish Continuation. In other words, the market is seen as entering a bullish phase.
Step 2: Aligning Multiple Timeframes
The next step involves assessing how the current scenario fits within the larger market structure by checking higher timeframes. In the EUR/USD example, the monthly chart shows three consecutive bullish directional bars (Scenario 2), also known as a 2-2 Bullish Continuation. This is supported by the weekly chart. Initially, there are two bearish directional bars before a bullish outside bar (Scenario 3) and a bullish directional bar. This indicates an alignment of bullish momentum, indicating a higher probability for the daily chart setup.
Step 3: Identifying Supporting Patterns and Signals
Within the scenario, specific candlestick patterns, like hammers or shooting stars, alongside key support and resistance levels, often provide additional context. These signals are believed to be more effective when they align with the broader market direction and timeframe continuity.
In the EUR/USD example, the weekly chart shows a candle resembling a hammer (the outside bar), while the daily chart shows a pattern resembling a Three Stars in the South formation (the 3, 1, 1 candles). While rare, the three stars in the south pattern can signal sellers are losing momentum, when:
The first candle features a long body and long lower wick.
The second candle has a shorter body and closes above the first candle’s low.
The third candle has another short body with minimal wicks and a range inside the second candle.
While both formations don’t meet the technical criteria for their respective patterns, a trader might consider them to add weight to the bullish idea. The weekly chart also shows the price breaking past a previous resistance level, which adds confluence.
Step 4: Entering and Exiting
A trader would typically enter as the candle on their chosen timeframe closes. A stop loss could be set beyond the entry candle or a nearby swing high/low. Some traders prefer to close the position depending on the next candle close and corresponding scenario, while others might target a particular support/resistance level or use multi-timeframe analysis to find a suitable exit point.
Advantages and Challenges of the STRAT Method
The STRAT method offers a unique, structured approach to trading, but like any strategy, it comes with both advantages and challenges. Understanding these can help traders decide how to integrate it into their approach.
Advantages
- Clarity in Analysis: By categorising price action into simple scenarios, the STRAT’s patterns simplify market behaviour, reducing ambiguity.
- Focus on Price Action: The method relies on raw price data rather than indicators, offering a direct view of market dynamics.
- Adaptability Across Markets: Whether trading equities, forex, or commodities, the STRAT applies universally to any market with candlestick data.
- Improved Consistency: Its rules-based framework helps traders avoid impulsive decisions and stay aligned with their analysis.
Challenges
- Learning Curve: Understanding the nuances of scenarios and timeframe continuity requires time and practice.
- Patience Required: Waiting for alignment across multiple timeframes may lead to fewer trade opportunities, which may frustrate active traders.
- Context Dependency: While structured, the STRAT still requires interpretation, and outcomes depend on how well traders incorporate broader market factors.
The Bottom Line
The STRAT method offers traders a structured way to analyse price action, combining scenarios, candlestick patterns, and timeframe continuity to navigate markets with confidence. While it requires discipline to master, its clear framework can potentially improve decision-making.
FAQ
What Is the STRAT Strategy by Rob Smith?
Rob Smith developed the STRAT strategy, a trading method that simplifies technical analysis by categorising price action into three STRAT candle scenarios: inside bars, directional bars, and outside bars. It focuses on understanding market structure, using timeframe continuity and actionable signals to interpret trends and reversals.
What Is the STRAT Method of Trading?
The STRAT method is a rules-based approach to trading that prioritises price action over indicators. It uses specific candlestick patterns and scenarios to identify potential trading opportunities and aligns multiple timeframes to provide a cohesive market view.
What Is a Rev Strat?
According to Rob Smith, a “rev strat” refers to particular setups. First is a 1-2-2, initially with an inside bar, then a directional bar in one direction, and finally a directional bar in the opposite direction, marking a possible reversal. The second is a 1-3 setup, with an inside bar followed by an outside bar. This signals an expanding market in the STRAT, meaning a period of heightened volatility, and is considered bullish or bearish based on the outside bar’s direction.
This article represents the opinion of the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand only. It is not to be construed as an offer, solicitation, or recommendation with respect to products and services provided by the Companies operating under the FXOpen brand, nor is it to be considered financial advice.
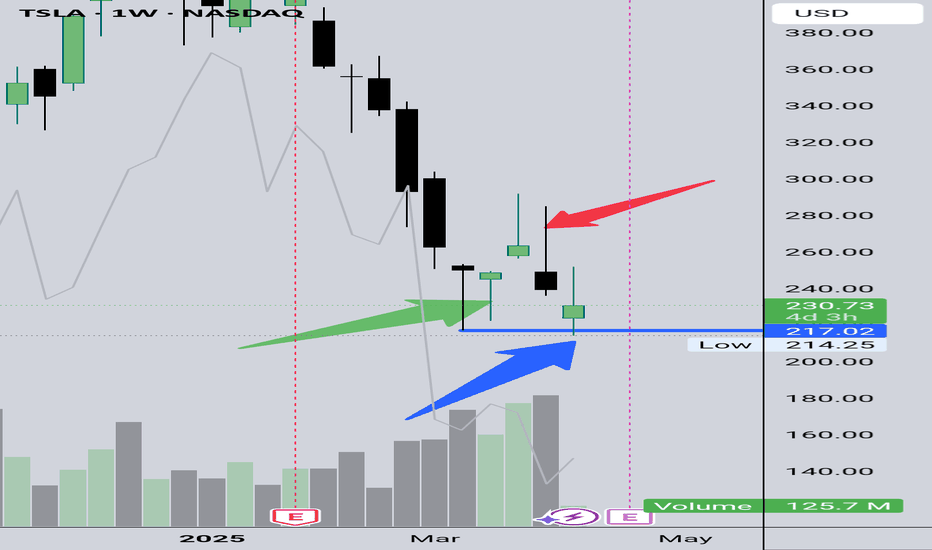
TESLA Always Pay YOURSELF! Tsla Stock were you PAID? GOLD Lesson
⭐️I want to go into depth regarding the this topic but it is a long one with PROS & CONS for doing and not doing it.
Every trader must choose what's best for them but you will SEE when I finally get to the write up that MANY OF THE PROS are NOT FINANCIAL but PSYCHOLOGICAL❗️
Another of 🟢SeekingPips🟢 KEY RULES!
⚠️ Always Pay YOURSELF.⚠️
I know some of you chose to HOLD ONTO EVERYTHING and place your STOP at the base of the WEEKLY CANDLE we entered on or the week priors base.
If you did that and it was in your plan GREAT but... if it was NOT that is a TRADING MISTAKE and You need to UPDATE YOUR JOURNAL NOW.
You need to note EVERYTHING. What you wanted to see before your exit, explain why not taking anything was justified to you, were there EARLY exit signals that you did not act on. EVERYTHING.
🟢SeekingPips🟢 ALWAYS SAYS THE BEST TRADING BOOK YOU WILL EVER READ WILL BE YOUR COMPLETE & HONEST TRADING JOURNAL ⚠️
📉When you read it in black amd white you will have YOUR OWN RECORD of your BEST trades and TRADING TRIUMPHS and your WORST TRADES and TRADING ERRORS.📈
✅️ KEEPING an UPTO DATE JOURNAL is STEP ONE.
STUDYING IT IS JUST AS IMPORTANT👍
⭐️🌟⭐️🌟⭐️A sneak peek of the LESSON after will be HOW & WHEN TO ENTER WHEN THE OPEN BAR IS GOING THE OPPOSITE WAY OF YOUR IDEA.👌
🚥Looking at the TESLA CHART ABOVE you will see that we were interested in being a BUYER when the weekly bar was BEARISH (GREEN ARROW) and we started to consider TAKE PROFITS and EXITS when the (RED ARROW) Weekly bar was still BULLISH.🚥
RSI + BB strategy - the strong duo you will ever need to win Hello traders!
This article shares with you a strategy employing two famous indicators that have stood the test of time and used by professionals and amateurs alike. A solid trading plan needs at least one solid strategy which will be your bread and butter. You can always add more strategies or game plans to your repertoire but you need to master one. Trading can be as complicated or simple as you make it. To make sense of it all, you should always try to be realistic and stick to a trading plan which is "simple and stupid" so that you free your mind from overthinking and focus on the market movements instead. A good strategy, along with constant market trend analysis, good risk management, news awareness and emotion control can ultimately transition you to being a consistent profitable trader. Indeed, there are times where the odds will not be in your favour and you will have losing trades. However, the key to success is to think of trading as a game of probability and developing a winning edge that ensures you are profiting more than losing. A 1:2 RRR is the least you have to accept when entering a trade, else sit tight and wait for the next opportunity. As Jesse Livermore quoted, "It never was my thinking that made the big money for me. It always was my sitting. Got that? My sitting tight!".
RSI
Developed by J. Welles Wilder Jr. In 1978, the relative strength index is a momentum indicator that measures the speed and magnitude of price changes. At 70+, RSI is considered overbought and a retracement in price may occur. At 30-, RSI is considered oversold and price may go up. The middle line is the mean of recent prices, usually during a 14 days period.
BB
Developed by John Bollinger much later in the 1980s, BB is a volatility indicator which measures the speed and extent of price changes. A wider band signals high volatility and a narrow band signals low volatility. When price reaches the upper band, the asset is considered overbought and price may retract. When price reaches the lower band, the asset is considered oversold, meaning there are less and less sellers in the market and price may go up. The middle line is usually a simple moving average, showing the mean price across a time period.
RSI + BB strategy
The combination relies, and truthfully so, on the fact that the price of an asset usually hovers around its mean. Unless there are significant macroeconomic changes and news are strong (ultimately forming a new trend), price does not deviate much from its mean. It continues and builds its existing trend and moves up and down the moving average. By meauring both the momentum and volatility of the price, while keeping an eye on the direction of the trend, a trader can place small trades with a minimum 1:2 RRR as the asset moves in a range, an uptrend or a downtrend. The indicators give you insight on where to buy and place your SL and TP.
Trading set ups
- RSI 70+, BB touching upper band, no news, BB horizontal (showing a ranging market), price at major resistance zone - sell because price is likely to move through the moving average towards to lower band
- RSI 30-, BB touching lower band, no news, BB horizontal (showing a ranging market), price at major support zone- buy because price is likely to move through the moving average towards to upper band
- RSI 70+, BB touching upper band (price climbing up the BB ladder), BB moving upwards (uptrend), strong good news - buy because price is in uptrend and trend is likely to continue
- RSI 30-, BB touching lower band (price falling off the BB cliff), strong bad news - sell because price is in downtrend and trend is likely to continue
Sitting tight
-Playing on a 1hr timeframe, there won't be many instances when all these stars align. That is when you sit tight and wait.
- When price is hovering in between the RSI grid and BB band - sit tight and wait because the odds are not in your favour and it is impossible to predict which way price will move. Let the market do its thing, protect your capital and wait for the market to show you what to do next.
Note
- When the conditions are met, always enter the trade as soon as you get confirmation. If you are late in entry, skip the trade and wait
- Place your SL just above the upper BB if selling or just below the lower BB if buying
- TP is essential so you can lock in profits, especially in ranging markets where price quickly touches the BB band and bounces back. If you are in a trade and not able to monitor it, a TP ensures you have closed your trade at your desired and predicted price. TP is placed close to the lower band if selling or close to the upper band if buying
-Ensure that all your other criteria such as news, RRR and emotion control are met to enter a trade. If one is not met, this trade is not for you.
- Familiarise yourself using alerts. You have to be able to be present when the opportunity presents itself. Tradingview's lowest paid plan gives you 20 alerts, which is more than sufficient if you are focusing on 4-5 assets only. Alerts add to your winning edge and enable you to be trading the best set ups when they form.
Please do not hesitate to share your thoughts if you do use RSI and/or BB and have had positive outcomes. :)
GL to all!
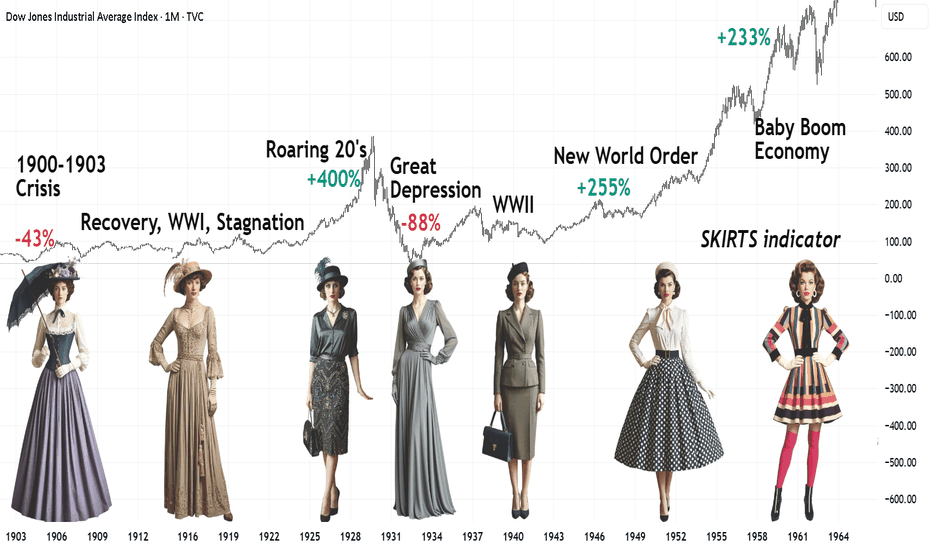
Skirt Lengths as Market Indicators: A Socionomics PerspectivePart of the #Socionomics series.
How fashion and societal moods shifted in the first half of the 20th century.
1900–1910
Economy: The rise of industrialization in the U.S. — Ford’s assembly line (1908), booming cities, and a growing wealth gap between the elite and the working class. In Europe, colonial powers raced for survival, fueling military spending (sound familiar?).
Mood: Faith in technological progress clashed with protests against exploitation. Suffragettes smashed London storefronts (1908), while New York’s Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire (1911) galvanized labor rights movements.
Fashion: Rigid corsets and floor-length skirts symbolized Victorian morality. Yet rebels like designer Paul Poiret introduced hobble skirts — a tentative step toward freedom of movement.
1910–1920
Economy: World War I (1914–1918) reshaped the globe: Europe lay in ruins, while the U.S. profited from arms sales. Postwar hyperinflation crippled Germany, and the Spanish Flu (1918–1920) claimed millions.
Mood: Women replaced men in factories, only to be pushed back into domestic roles after the war. A feminist explosion: American women won voting rights in 1920.
Fashion: Skirts rose to ankle-length for practicality. By the decade’s end, the flapper emerged — straight-cut dresses, beaded necklaces, and cigarettes in hand, defying tradition. A sign of the stock market’s brewing boom.
1920–1929
Economy: The "Roaring Twenties" — jazz, speculation, and Prohibition. The stock market quadrupled; ordinary Americans borrowed heavily to invest, then borrowed again against rising shares.
Mood: Hedonism reigned. Speakeasies and Gatsby-esque parties masked pre-crash euphoria.
Fashion: Knees on display! Fringed dresses, bobbed haircuts, and gartered stockings. By 1929, subdued silhouettes crept in — an omen of crisis.
1930–1940
Economy: The 1929 bubble burst: Wall Street crashed, triggering the Great Depression (1929–1939). U.S. unemployment hit 25%. Europe veered toward fascism and war.
Mood: Despair from Dust Bowl migrations and hunger marches. Yet Hollywood’s Golden Age offered escapism.
Fashion: Skirts lengthened — modesty returned. Long dresses dominated, while cheap fabrics and turbans (to hide unwashed hair) became staples.
1940–1950
Economy: World War II (1939–1945). Postwar Europe rebuilt via the Marshall Plan; the U.S. embraced consumerism.
Mood: Patriotism ("Rosie the Riveter") and postwar hope. The baby boom idealized domesticity.
Fashion: War mandated minimalism: knee-length skirts and padded shoulders. In 1947, Christian Dior’s New Look rebelled — voluminous ankle-length skirts symbolized postwar opulence.
1950–1960
Economy: America’s "Golden Fifties" — middle-class expansion, cars, and TV. Europe recovered, but colonial wars (Algeria, Vietnam) exposed crises.
Mood: Conformity (suburban perfection) vs. teenage rebellion (James Dean, Elvis’s rock ‘n’ roll).
Fashion: Sheath dresses and midi skirts emphasized femininity. By the late 1950s, Mary Quant experimented with mini-skirts — a harbinger of the sexual revolution.
1960s: Peak of Postwar Prosperity
Economy: U.S. GDP grew 4-5% annually; unemployment dipped below 4%. Baby boomers (1946–1964) fueled suburban housing and education demand.
Fashion: The mini-skirt became an era-defining manifesto of freedom, paired with bold go-go boots. Economic optimism bred experimentation: neon synthetics (nylon, Lycra) and psychedelic hues.
Conclusion
Women’s fashion mirrors its era. Crises (1930s) hide knees; liberating times (1920s, 1960s) bare them. Even war skirts (1940s’ knee-length pragmatism) carried hope.
💡 Like and subscribe for insights your economics textbook won’t reveal!
#beginners #learning_in_pulse #interesting
#socionomics #history #fashiontrends
RSI 101: Scalping Strategy with RSI DivergenceFX:XAUUSD
I'm an intraday trader, so I use the H1 timeframe to identify the main trend and the M5 timeframe for entry confirmation.
How to Determine the Trend
To determine the trend on a specific timeframe, I rely on one or more of the following factors:
1. Market Structure
We can determine the trend by analyzing price structure:
Uptrend: Identified when the market consistently forms higher highs and higher lows. This means price reaches new highs in successive cycles.
Downtrend: Identified when the market consistently forms lower highs and lower lows. Price gradually declines over time.
2. Moving Average
I typically use the EMA200 as the moving average to determine the trend. If price stays above the EMA200 and the EMA200 is sloping upwards, it's considered an uptrend. Conversely, if price is below the EMA200 and it’s sloping downwards, it signals a downtrend.
3. RSI
I'm almost use RSI in my trading system. RSI can also indicate the phase of the market:
If RSI in the 40–80 range, it's considered an uptrend.
If RSI in 20 -60 range, it's considered a downtrend.
In addition, the WMA45 of the RSI gives us additional trend confirmation:
Uptrend: WMA45 slopes upward or remains above the 50 level.
Downtrend: WMA45 slopes downward or stays below the 50 level.
Trading Strategy
With this RSI divergence trading strategy, we first identify the trend on the H1 timeframe:
Here, we can see that the H1 timeframe shows clear signs of a new uptrend:
Price is above the EMA200.
RSI is above 50.
WMA45 of RSI is sloping upward.
To confirm entries, move to the M5 timeframe and look for bullish RSI divergence, which aligns with the higher timeframe (H1) trend.
RSI Divergence, in case you're unfamiliar, happens when:
Price forms a higher high while RSI forms a lower high, or
Price forms a lower low while RSI forms a higher low.
RSI divergence is more reliable when the higher timeframe trend remains intact (as per the methods above), indicating that it’s only a pullback in the bigger trend, and we’re expecting the smaller timeframe to reverse back in line with the main trend.
Stop-loss:
Set your stop-loss 20–30 pips beyond the M5 swing high/low.
Or if H1 ends its uptrend and reverses.
Take-profit:
At a minimum 1R (risk:reward).
Or when M5 ends its trend.
You can take partial profits to optimize your gains:
Take partial profit at 1R.
Another part when M5 ends its trend.
The final part when H1 ends its trend.
My trading system is entirely based on RSI, feel free to follow me for technical analysis and discussions using RSI.
How to Use the TradingView Search Bar Efficiently 01. Introduction to the TradingView Search Bar
The TradingView Search Bar is one of the most essential tools in your charting journey. Located at the top-left corner of the interface, this feature allows you to instantly switch between stocks, indices, crypto assets, forex pairs, futures, and more — without leaving your current chart tab.
Whether you're a day trader looking for high-volume movers or an investor monitoring global indices, the search bar makes it effortless to pull up symbols with lightning speed.
One of the best parts? You don’t even need to click anything — just start typing on your keyboard while a chart is open, and the search bar automatically activates.
Pro Tip: The TradingView Search Bar supports symbol auto-suggestions with exchange suffixes (like .NS for NSE stocks), making it ultra-fast for Indian markets too.
02. How to Open the Symbol Search Bar
Opening the symbol search bar in TradingView is incredibly intuitive — and can be done in multiple ways depending on how fast you want to move.
Here are the top 3 ways to launch the search bar:
• 🔘 Click the Symbol: Go to the top-left corner of your chart and click the current symbol (e.g., NIFTY or BTCUSD) to open the search panel.
• ⌨️ Start Typing: When your chart is focused, just begin typing any symbol directly — the search window pops up instantly.
• 📚 Use the Watchlist: Open a saved symbol from your Watchlist using a simple click, and it automatically replaces the current chart.
Shortcut Key:
Just press your keyboard and type RELIANCE or NIFTY without clicking anywhere — TradingView immediately opens the search popup.
Works on both Windows and Mac.
03. Extended: Exploring the Search Interface (Tab-by-Tab Breakdown)
The TradingView Symbol Search Interface is more than just a place to look up stock names. It’s a powerful filtering system designed to help traders and investors access any instrument—globally and across asset classes—in just a few clicks. Let’s break down each tab and filter in detail:
🔍 1. Asset Type Tabs
Located at the top of the search panel, these tabs let you narrow down by instrument type:
• All – View all available instruments.
• Stocks – Equity shares from global exchanges (e.g., NSE, NASDAQ, BSE, etc.).
• Funds – Includes ETFs, mutual funds, and index funds.
• Futures – Derivative contracts across commodities, indices, etc.
• Forex – Currency pairs like USDINR, EURUSD, GBPJPY, etc.
• Crypto – Popular cryptocurrencies like BTC, ETH, and exchange pairs.
• Indices – Market indices like NIFTY50, S&P 500, NASDAQ100.
• Bonds – Government and corporate bond listings.
• Economy – Macro-economic indicators like GDP, unemployment, CPI.
• Options – Derivative instruments based on options chain availability.
💡 Pro Tip: Use these tabs before typing a symbol to narrow down your focus instantly.
🌍 2. All Countries Filter
You can choose to see instruments only from specific countries. Selecting this opens a country-wise list showing all supported exchanges under each country.
• USA: NASDAQ, NYSE, CBOE, OTC
• India: NSE, BSE
• UK: LSE
• Germany: XETRA, FWB
🔎 Use Case: If you only want Indian stocks, choose India to limit the results to NSE/BSE only.
🧾 3. All Types Filter (Only under Stocks Tab)
This filter lets you refine your equity instrument type, such as:
• Common Stock
• Preferred Stock
• Depository Receipt (like ADR/GDR)
• Warrant
🔍 Use Case: Great for global investors looking specifically for ADRs or warrants.
🧭 4. All Sectors Filter (Only under Stocks Tab)
This is one of the most powerful tools for equity screening. You can filter stocks based on their sector like:
• Finance
• Technology Services
• Health Technology
• Consumer Durables
• Electronic Technology
• ... and 20+ more industry segments
💼 Use Case: Perfect for sector-based trading or thematic investing.
⚙️ Power Feature: All filters can be used in combination. Example: You can search only Technology sector stocks from India, of Common Stock type — all in seconds.
05: Using the Flag to Add Symbols to Watchlist
The 🚩 flag icon in TradingView allows you to tag symbols with color-coded labels for easy watchlist management. You can organize your stocks by strategy, sector, volatility, or timeframe using these flags.
🎯 What Does the Flag Icon Do?
• Click the 🚩 icon next to any symbol in the search panel.
• Choose from 7 different colors to group stocks by theme.
• Flagged stocks immediately appear under that color in your Watchlist.
You can create multiple groups — like F&O, Crypto, Sectors, Swing Picks — all visually organized.
🔍 06: Smart Search Tricks (Symbol Syntax, Exchanges, Shortcuts)
The TradingView Symbol Search bar supports intelligent filters, shortcuts, and exchange-based syntax to save time and improve accuracy. Mastering these tricks will allow you to switch charts and find instruments faster than ever.
🧠 1. Use Exchange Prefixes
You can directly use exchange prefixes to narrow your search:
NSE: – National Stock Exchange of India
BSE: – Bombay Stock Exchange
NASDAQ: – U.S. Nasdaq-listed stocks
NYSE: – New York Stock Exchange
👉 Example: NSE:RELIANCE shows Reliance on NSE instantly.
💡 2. Partial Name Works Too
You can type partial symbols after the exchange code and TradingView will auto-suggest:
🔎 Example: Typing NSE:REL shows Reliance Industries and others.
⚡ 3. Avoid Full Company Names
Typing full company names like “Reliance Industries Ltd” might not show accurate results quickly. Instead, use ticker codes or shortcuts with exchange prefixes for better precision.
🎯 4. Type Directly to Open Search
No need to click the 🔍 icon! Just start typing on the chart:
Windows/Mac: Type any symbol (e.g. INFY)
Use Arrows: ⬆️ ⬇️ to move between results
Press Enter: to select symbol instantly
🌐 5. Use Filter Tabs Above Search
TradingView lets you filter across:
Markets: All / India / US / Global
Types: Stocks / Crypto / Forex / Futures
Sectors: Banks / Tech / Pharma / Energy
💡 Pro Tip: Combine NSE: + partial ticker + filters to drill down fast without leaving the chart screen
Could Bitcoin Crash 60%—But Only 20% of Traders Lose?Analyzing the current BTC/USDT chart, we see that Bitcoin is hanging just above a critical support zone—what many traders recognize as “the most important support level” from a volume perspective on Binance. The chart illustrates a potential 60.37% drop, which would pull BTC down nearly $49,000, back toward the high-volume range near $30K.
This sounds catastrophic, right? But here’s the twist...
🔍 Why Only 20% of Traders Might Actually Lose
According to Binance's volume profile data:
The majority of buying activity and position accumulation happened below $35,000.
Most long-term holders and smart money entered during the 2022-2023 accumulation range.
The Volume Profile Visible Range (VPVR) shows significant support below the current price, with minimal trading volume at higher levels.
💡 That means only a minority (approx. 20%) of traders bought BTC during its late-stage bull run above $70K. These are the traders most at risk if a drop occurs.
In contrast, the majority are still sitting in profit—or near break-even—even if Bitcoin retraces back to its base.
📊 So while the price could drop 60%, 80% of holders might remain safe, having entered at lower levels.
🧠 What This Means for You:
If you're a late bull, it’s time to assess risk.
If you're a smart accumulator, the pullback could offer another golden entry.
If you're a bear, this chart supports your thesis—but don't forget the whales are watching this zone closely.
Stay sharp. Stay informed.
Example of how to draw a trend line using the StochRSI indicator
Hello, traders.
If you "Follow", you can always get new information quickly.
Please click "Boost" as well.
Have a nice day today.
-------------------------------------
I have explained how to draw a trend line before, but I will take the time to explain it again so that it is easier to understand.
-
When drawing a trend line, it must be drawn on the 1M, 1W, and 1D charts.
However, since I focused on understanding the concept of drawing a trend line and the volatility period that can be seen with a trend line, I will explain it only with a trend line drawn on the 1D chart.
Please note that in order to calculate a somewhat accurate volatility period, support and resistance points drawn on the 1M, 1W, and 1D charts are required.
I hope this was helpful for understanding my thoughts on the concept of drawing trend lines and how to interpret them.
The main reason for drawing trend lines like this is so that anyone who sees it can immediately understand why such a trend line was drawn.
Then, there will be no unnecessary disagreements about the drawing, and each person will be able to share their opinions on the interpretation.
--------------------------
When drawing trend lines, the StochRSI indicator is used.
The reason is to secure objectivity.
When the StochRSI indicator touches the oversold zone and rises, the low corresponding to the peak is connected to draw a trend line between low points.
And, when the StochRSI indicator touches the overbought zone and falls, the Open of the downward candle corresponding to the peak is connected to draw a trend line between high points.
If the peak is not a downward candle, it moves to the right and is drawn with the Open of the first downward candle.
If you refer to the candlesticks of the arrows in the chart above, you will understand.
The trend line drawn as a dot is a high-point trend line, but it is a proper trend line because it does not touch the overbought zone between highs.
Therefore, you can draw a trend line corresponding to trend line 1.
Accordingly, around March 25-29, around April 8, and around April 14 correspond to the volatility period.
-
You can see how important the low-point trend line (2) is.
If the high-point trend line is properly created this time and the low-point trend line and the high-point trend line are displayed in the same direction, the trend is likely to continue along that channel.
If the StochRSI indicator rises and a peak is created in the overbought zone, you will draw a high-point trend line that connects to point A.
-
Thank you for reading to the end. I hope your transaction will be successful.
--------------------------------------------------
Mastering Market Trends: Your Guide to Clearer Trading DecisionsTrends shape every decision you make in the markets, even if you’re unaware of it. Understanding how to identify and adapt to these market phases is your foundational skill - one that separates successful traders from the rest.
Today, let’s simplify and clarify the three essential types of market trends. By mastering this, you’ll approach trading decisions with more confidence and clarity.
⸻
📈 1. Uptrend – Riding the Bull
• What is it?
An uptrend is like climbing stairs upward. Each step (low) is higher than the previous one, and every leap (high) sets a new peak.
• What drives it?
Buyers dominate, optimism rules, and demand pushes prices upward.
• Trading tip:
Identify support levels and look for retracements as potential entry points. Be cautious about chasing prices that have moved too far without a pullback.
⸻
📉 2. Downtrend – Navigating the Bearish Territory
• What is it?
Visualize going down a staircase. Each step down (low) surpasses the previous one, and every upward bounce (high) falls short of the prior peak.
• What drives it?
Sellers control the market, bearish sentiment takes over, and supply outweighs demand.
• Trading tip:
Look for resistance areas to identify potential short entries or wait patiently for signs of a reversal if you’re bullish.
⸻
➡️ 3. Sideways Market – The Calm Before the Storm
• What is it?
Imagine a tug-of-war with evenly matched teams. The price moves back and forth in a narrow range without breaking decisively higher or lower.
• What drives it?
Uncertainty, indecision, or equilibrium between buyers and sellers.
• Trading tip:
Stay patient! Either look to trade range extremes (buying support and selling resistance) or wait for clear breakout signals to catch the next big move.
⸻
🔍 Pro Tip for Trend Analysis:
• Multi-timeframe analysis is key: Always check higher timeframes (weekly, daily, or hourly) to confirm the primary trend. Don’t let short-term noise mislead your trading decisions.
⸻
🚀 Why It Matters:
Aligning your strategies with the correct market trend significantly improves your odds. It’s like sailing with the wind at your back instead of battling against it.
Now, tell us in the comments: Which trend type do you find most challenging to trade?
Trade smarter. Trade clearer.
Clear DayTrading strategy video. The "Inside Bar"🔉Sound on!🔉
📣Make sure to watch fullscreen!📣
Thank you as always for watching my videos. I hope that you learned something very educational! Please feel free to like, share, and comment on this post. Remember only risk what you are willing to lose. Trading is very risky but it can change your life!
Understanding the ICT Venom ModelIn this video I break down the ICT Venom Model as recently described by the man himself on his YouTube channel. I am sure he has more details on the model he has not released, but I basically attempt to give my two cents on NQ and the model itself.
I hope you find the video useful in your endeavours regarding learning ICT concepts as well as trading in general.
- R2F Trading
Using Fibonacci/Measured Moves To Understand Price TargetThis video is really an answer to a question from a subscriber.
Can the SPY/QQQ move downward to touch COVID levels (pre-COVID High or COVID Low).
The answer is YES, it could move down far enough to touch the pre-COVID highs or COVID lows, but that would represent a very big BREAKDOWN of Fibonacci/ElliotWave price structure.
In other words, a breakdown of that magnitude would mean the markets have moved into a decidedly BEARISH trend and have broken the opportunity to potentially move substantially higher in 2025-2026 and beyond (at least for a while).
Price structure if very important to understand.
Measured moves happen all the time. They are part of Fibonacci Price Theory, Elliot Wave, and many of my proprietary price patterns.
Think of Measured Moves like waves on a beach. There are bigger waves, middle waves, smaller waves, and minute waves. They are all waves. But their size, magnitude, strength vary.
That is kind of what we are trying to measure using Fibonacci and Measured Move structures.
Watch this video. Tell me if you can see how these Measured Moves work and how to apply Fibonacci structure to them.
This is really the BASICS of price structure.
Get Some.
#trading #research #investing #tradingalgos #tradingsignals #cycles #fibonacci #elliotwave #modelingsystems #stocks #bitcoin #btcusd #cryptos #spy #gold #nq #investing #trading #spytrading #spymarket #tradingmarket #stockmarket #silver
The Power of Technical Indicators: ETH 4H Chart Breakdown📈 In this analysis, I demonstrate how a combination of key technical indicators can provide high-probability trade setups. By using Auto Fibonacci Gauge, Quantum Moving Average, Momentum Charge Theory, and Smart Money Concept, we can decode market movements with precision.
🔹 Auto Fibonacci Gauge: The Perfect Retracement
The Auto Fib Gauge shows a textbook retracement, respecting key levels like 23.6% & 61.8%.
These levels act as potential reversal zones where price reacts based on trader sentiment.
🔹 Quantum Moving Average & Momentum Charge Theory: Trend Confirmation
The Quantum Moving Average aligns perfectly with the momentum shift, confirming trend direction.
The Momentum Charge Theory further validates entry & exit signals, showing confluence with the Fib levels.
🔹 Smart Money Concept: Tracking Institutional Moves
The SMC method helps identify where large institutional orders (aka smart money) are likely placed.
Key structure points like BOS (Break of Structure) & CHoCH (Change of Character) signal potential trend shifts.
📊 Why is this important?
Combining these indicators enhances probability of successful trades.
Understanding retracements, momentum, and institutional order flows helps traders avoid weak setups and trade with confidence.
🚀 What’s your take? Do you use similar confluences in your trading? Let me know in the comments!