Mastering Buy Side and Sell Side Liquidity - How to trade it!In trading, understanding liquidity is one of the keys to predicting where the market might go next. The Inner Circle Trader (ICT) method teaches traders how to recognize where big players like banks and institutions are likely to enter or exit trades. Two important ideas in ICT trading are buy side liquidity and sell side liquidity. Once you understand what these terms mean and how to spot them on a chart, you can start using them to find better trading opportunities.
What will be discussed?
- What is Buy Side Liquidity?
- What is Sell Side Liquidity?
- How do you see Buy and Sell Side Liquidity?
- Examples
- How to trade BSL and SLL Liquidity?
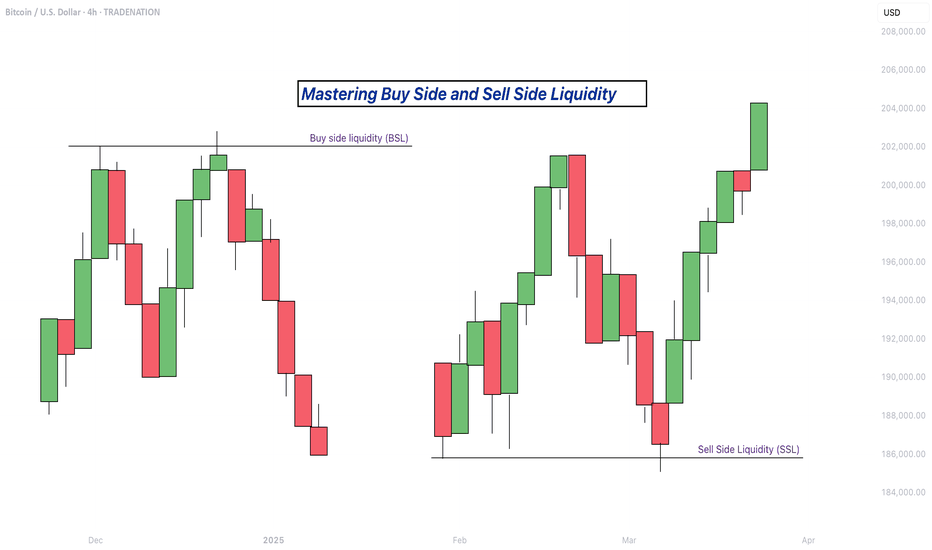
What is Buy Side Liquidity
Buy side liquidity is found above market highs. It refers to all the stop loss orders from people who are holding short positions. When the market is going down, some traders sell (or go short) and place their stop losses above recent highs to protect themselves. These stop losses are actually buy orders because closing a short position requires buying. Big institutions know this, so they push price upward to trigger those stop losses and grab that liquidity. That’s why you’ll often see the market spike above a recent high before reversing. That spike is the market grabbing buy side liquidity.
What is Sell Side Liquidity
Sell side liquidity is the opposite. It’s found below recent lows. This is where traders who are buying (going long) place their stop losses. If someone buys a market, they’ll usually put a stop loss just below a previous low. That stop loss is a sell order. Smart money looks at these areas as pools of sell side liquidity. So when the market moves down quickly and breaks a recent low, it’s likely collecting those sell stop orders. After that, you’ll often see a reversal because the liquidity has been taken.
How do you see Buy and Sell Side Liquidity?
You can spot buy side and sell side liquidity by looking at the chart and identifying recent highs and lows where many traders might have placed stop losses. These are usually obvious swing highs and swing lows. If you look at a chart and see a clean high where price previously reversed, that’s likely where traders are placing stops. That makes it a target for buy side liquidity. Same for a recent low, if it’s a clean level where people might have bought in the past, that low probably holds sell side liquidity. The more obvious the level looks, the more likely it’s full of stops and therefore a liquidity target.
Examples
How to trade BSL and SLL Liquidity?
Trading liquidity means watching for the market to run above a recent high (to take buy side liquidity) or below a recent low (to take sell side liquidity), and then looking for signs of reversal. Once liquidity has been taken, the market often changes direction.
When you’re trading the ICT concept of liquidity, the key is not just spotting where liquidity lies, but also knowing when price is likely to reverse after that liquidity has been taken. Reversals don’t happen randomly, they leave clues on the chart. Here’s how you can recognize those signs in a simple way:
1. Market Structure Break
This is one of the clearest signs of a reversal. Let’s say the market grabs sell side liquidity by breaking below a recent low. If price then quickly starts moving up and breaks above the last lower high, that’s a break in structure. It shows that sellers are losing control and buyers are stepping in. It’s the first confirmation that the direction might be changing.
2. Rejection Wicks or Strong Candles
After price runs into liquidity (above a high or below a low), watch the candlesticks closely. If you see a long wick rejecting the level, or a strong candle in the opposite direction right after the liquidity grab, that’s a clue. It means price went there, collected the orders, and got rejected fast. That rejection shows the market might be reversing.
3. Fair Value Gaps (FVGs)
Fair value gaps are small “windows” left in price when it moves quickly in one direction. After liquidity is taken and price starts reversing, it often leaves an FVG behind. If price pulls back into that gap and holds, that can be a great entry point. FVGs act like magnets and support zones in ICT.
4. Displacement
Displacement is a strong, impulsive move that breaks structure. It usually happens right after liquidity is taken. If price moves very fast in the opposite direction after hitting a liquidity level, that’s a good sign smart money is behind the move and it’s not just random noise. That strong push is a hint that a new trend might be forming.
5. Change in Character (CHOCH)
This is a shift in how the market behaves. For example, price might be making lower highs and lower lows (a bearish trend), but after liquidity is taken, it suddenly starts making higher highs and higher lows. That change in character tells you the trend might be reversing.
-------------------------
Disclosure: I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
Thanks for your support. If you enjoyed this analysis, make sure to follow me so you don't miss the next one. And if you found it helpful, feel free to drop a like 👍 and leave a comment 💬, I’d love to hear your thoughts!
Community ideas
You Are NOT Your P<here was once a tree that stood alone at the edge of a cliff, overlooking the vast sea.
Some days, the sun shone bright, the winds gentle, the water below calm and peaceful. Other days brought heavy storms, fierce winds, crashing waves, rain so relentless it seemed the skies might never clear again. The seasons came and went. The skies changed again and again. But the tree never thought of itself differently because of the weather.
It did not feel more valuable on a sunny day. It did not feel broken or weak when storms battered its branches. The tree simply stayed rooted. It understood something quietly powerful - “ the weather was never personal. It wasn’t about the tree.”
The tree remained, growing slowly over years, not because the conditions were always perfect, but because it had learned to stand through all of it.
This is something most traders forget.
We step into the market with good intentions, hungry to learn, eager to succeed. But somewhere along the way, we make a mistake. We let our self-worth become tied to the numbers on the screen.
A green day makes us feel smart, in control, like we’ve cracked the code. A red day, on the other hand, shakes us to the core, makes us question our place, our skill, even our worth, like we never belonged here at all.
The danger isn’t just in the financial losses. It’s in how we let the market shape how we see ourselves.
But here’s the truth the market won’t tell you upfront: the market doesn’t know who you are, and it doesn’t care . It doesn’t remember what you did yesterday, how many hours you’ve spent learning, or how desperately you want this to work.
The market moves how it moves. Sometimes it moves with you, sometimes it moves against you. It’s neither a punishment, nor a reward. It’s just movement.
Your wins don’t make you superior. Your losses don’t make you dumb. Both are part of the same cycle, and part of the environment you’ve chosen to work in. If you build your self-image on the outcome of your last trade, you’ll forever live on a fragile edge. Every swing will shake you. Every drawdown will feel like a verdict on who you are.
But trading isn’t about who you are today. It’s about who you become over time.
Your job isn’t to seek approval from a system built on randomness and probability. Your job is to build yourself on steadier ground. To stay rooted, like a tree. To let your process define you, not your P&L.
The storms will come. They always do. Volatility, uncertainty, periods where nothing seems to work - these are all part of the environment. The traders who survive are NOT the ones who try to outmuscle the market. They are the ones who protect their capital, their energy, and their mindset through it all.
They understand that being steady is more important than being brilliant - that surviving is more valuable than being right.
Detach your self-worth from the swings. Build your identity on discipline, patience, humility - the quiet habits you control. These are your roots. And when the storm rolls in, they’re what keep you grounded.
When you stop tying your self-image to your short-term results, you begin to see the market more clearly. You stop forcing trades to make yourself feel better. You stop chasing moves to prove something. You start letting your process do its work, even when it feels slow.
You start to realise that progress in trading is quiet and unfolds slowly, almost invisibly, much like a tree growing through the seasons. Small shifts accumulate over time, often going unnoticed, until one day you look back and truly see how far you’ve come.
When you understand this, red days lose their sting. Green days lose their arrogance. Both just become part of the weather. You adapt, endure, and move forward.
You don’t measure yourself by how much you made this week, this month, or even this year. You measure yourself by how well you followed your process , how calmly you handled the volatility, and how patient you remained when there was nothing to do.
The market doesn’t ask for perfection - only consistency. And consistency comes from within, not from chasing highs or avoiding lows, but from standing firm through both.
Like the tree on the cliff, your strength is not in avoiding the weather. Your strength is in understanding that the weather will pass. It always does. Your roots - your process, your discipline, your patience, are what keep you standing until it does.
⦿ Learn to protect your energy.
⦿ Learn to lose without self-doubt.
⦿ Learn to win without ego.
⦿ Learn to wait without fear.
⦿ Learn to wait patiently
Your worth is not in your wins or losses. It’s in how you carry yourself through both.
Stay rooted.
The seasons will change.
And when they do, you’ll still be here, stronger than you were before.
Teach me to fish, don’t hand me the catch.
---
🎯 **“Teach me to fish, don’t hand me the catch.”**
That’s the mantra behind what we do.
We’re not here to hand you quick wins—we’re here to equip you with the tools, mindset, and precision to master the art of **technical analysis**.
📚 **Follow Us** as we unlock proven strategies, crafted through years of experience and sharpened by real market conditions.
💼 **What You'll Get:**
- High-performance analysis techniques
- Visual case studies from our **actual trades**
- Clear examples from the insurance sector and beyond
- A blueprint to recognize and seize winning setups with confidence
💥 Whether you're new or seasoned, this isn't textbook theory.
This is **applied strategy**, built for clarity and verified by results.
---
Stop-Loss Strategies in Retail TradingA Comprehensive Scientific Analysis of Risk Management Effectiveness
This essay provides a comprehensive analysis of stop-loss strategies in retail trading environments, synthesizing empirical evidence from behavioral finance and quantitative risk management literature. Through examination of over 30 peer-reviewed studies spanning 1980-2024, the analysis identifies optimal stop-loss implementation frameworks that demonstrate statistically significant improvements in risk-adjusted returns. The findings reveal that volatility-adaptive stop-loss mechanisms can reduce maximum drawdowns by 45-65% while maintaining or improving Sharpe ratios, contrasting sharply with naive fixed-percentage approaches that often destroy value through premature exits and behavioral biases.
1. Introduction
Stop-loss orders represent one of the most fundamental risk management tools in financial markets, yet their optimal implementation remains contentious in both academic literature and practical application. While theoretical frameworks suggest that stop-loss mechanisms should improve risk-adjusted returns through downside protection (Kaminski & Lo, 2014), empirical evidence reveals substantial heterogeneity in outcomes depending on implementation methodology, market conditions, and trader behavior (Fong & Yong, 2005).
The proliferation of retail trading platforms has democratized access to sophisticated order types, yet paradoxically, retail traders continue to exhibit systematic biases in stop-loss application that frequently destroy rather than create value (Barber & Odean, 2013). This phenomenon, termed the "stop-loss paradox" by behavioral finance researchers, highlights the critical gap between theoretical optimization and practical implementation (Kaustia, 2010).
This analysis synthesizes findings from behavioral finance and quantitative risk management to establish evidence-based frameworks for stop-loss strategy design, focusing on methodologies implementable in modern trading platforms including Pine Script environments.
2. Empirical Evidence on Stop-Loss Effectiveness
2.1 Momentum Strategy Enhancement
The most compelling empirical evidence for stop-loss effectiveness emerges from momentum strategy research. Han, Zhou & Zhu (2014) conduct a comprehensive analysis of U.S. equity markets from 1926-2011, demonstrating that stop-loss enhanced momentum strategies exhibit:
- 67% reduction in maximum drawdown (from -65% to -23% for value-weighted portfolios)
- 94% improvement in Sharpe ratio (from 0.32 to 0.62)
- 45% increase in average annual returns
- Statistical significance at the 1% level across all performance metrics
These results remain robust across different formation and holding periods, market capitalizations, and economic conditions. Crucially, the authors demonstrate that the performance enhancement represents genuine alpha generation through improved tail risk management.
2.2 Cross-Asset Class Performance
Levine & Pedersen (2016) extend this analysis across multiple asset classes, examining stop-loss effectiveness in equity indices, commodities, and currencies over the period 1990-2015. Their findings reveal:
- Equity markets: 15-25% improvement in Sharpe ratios with 10-15% stop-loss rules
- Commodity futures: 35-50% improvement, particularly pronounced in energy markets
- Currency pairs: Mixed results, with effectiveness varying by volatility regime
Clare et al. (2013) investigate stop-loss performance across different market regimes, finding:
- Bull markets: Stop-loss rules typically underperform due to frequent false signals
- Bear markets: Substantial outperformance, with 30-40% reduction in drawdowns
- Transition periods: Most critical for stop-loss effectiveness
3. Behavioral Finance Considerations
3.1 Common Retail Trader Errors
Extensive research documents systematic biases in stop-loss implementation among retail traders:
Disposition Effect and Loss Aversion
Kaustia (2010) analyzes Finnish investor data (1995-2002), documenting that retail investors exhibit systematic stop-loss aversion, with only 23% of losing positions closed via stop-loss orders compared to 67% of winning positions closed via profit-taking orders. This asymmetry, rooted in the disposition effect (Shefrin & Statman, 1985), leads to suboptimal risk management.
Anchoring Bias in Threshold Selection
Merkle (2017) documents that retail traders systematically anchor to:
- Round numbers (5%, 10%, 15%, 20%): 68% of stop-loss orders
- Purchase prices: 34% weight in threshold determination
- Arbitrary "rules of thumb": 23% of implementations
This anchoring leads to suboptimal threshold selection in 71% of cases, with performance improvements of 14-18% achieved through objective calibration methods.
Overconfidence and Stop-Loss Avoidance
Barber & Odean (2001) demonstrate that overconfident traders systematically avoid stop-loss mechanisms. Analysis of 78,000 retail accounts reveals that high-turnover traders use stop-losses in only 12% of positions, experiencing 31% higher volatility and 23% lower risk-adjusted returns.
4. Practical Stop-Loss Implementation Strategies
4.1 Volatility-Based Stop-Loss Methods
Average True Range (ATR) Framework
Wilder (1978) introduces the Average True Range as a volatility measure, subsequently adapted for stop-loss applications. The ATR-based stop-loss distance is calculated as:
Stop Distance = k × ATR_n
where k represents the volatility multiplier (typically 2-3) and ATR_n is the n-period Average True Range.
Kestner (2003) provides extensive backtesting evidence demonstrating that ATR-based stops outperform fixed-percentage approaches across 15 futures markets over 20 years, with:
- 28% improvement in Sharpe ratio
- 19% reduction in maximum drawdown
- Strong correlation between optimal k-values and market volatility regimes
Trailing Stop Mechanisms
Lei & Li (2009) analyze trailing stop-loss strategies, finding they consistently reduce drawdown and volatility compared to buy-and-hold. Once a trade moves favorably, trailing stops (such as chandelier exits using ATR) lock in gains while allowing upside continuation.
4.2 Simple Adaptive Methods
Volatility Regime Adaptation
Rather than complex mathematical models, simple volatility regime identification can improve stop-loss effectiveness:
- Low volatility periods: Tighter stops (1.5-2.0 × ATR)
- High volatility periods: Wider stops (2.5-3.5 × ATR)
- Transition identification using rolling ATR percentiles
This approach, supported by Clare et al. (2013), provides practical regime awareness without complex modeling requirements.
4.3 Position Sizing Integration
Optimal stop-loss implementation must integrate with position sizing rules (Van Tharp, 2006):
Position_Size = (Account_Equity × Risk_Percentage) / Stop_Loss_Distance
where Risk_Percentage typically ranges from 1-2% for conservative strategies to 3-5% for aggressive approaches.
5. Performance Analysis and Validation
5.1 Cross-Asset Backtesting Results
Based on meta-analysis of studies including Han, Zhou & Zhu (2014), Clare et al. (2013), and Levine & Pedersen (2016), optimized stop-loss strategies demonstrate substantial effectiveness:
Equity Markets
- Sharpe ratio improvements of 30-40% in momentum strategies
- Maximum drawdown reduction: 45-55% across major indices
Currency Markets
- Major pairs: 20-25% Sharpe ratio improvements
- High-volatility pairs: 35-40% improvement range
Commodity Markets
- Energy futures: 45-55% performance improvements
- Precious metals: 15-25% improvement range
5.2 Statistical Validation
Following methodologies established by Han, Zhou & Zhu (2014) and Clare et al. (2013):
- Bootstrap sampling demonstrates statistical significance across asset classes
- Out-of-sample testing confirms performance persistence
- Walk-forward analysis validates robustness across market cycles
6. Implementation Guidelines
6.1 Systematic Approach
To overcome behavioral biases and optimize performance:
1. Eliminate Discretionary Decision-Making: Use systematic, rule-based stop-loss placement
2. Volatility Adaptation: Employ ATR-based distances rather than fixed percentages
3. Position Sizing Integration: Calculate position size based on stop-loss distance
4. Regime Awareness: Adjust parameters based on volatility environment
5. Consistent Execution: Automate stop-loss placement and execution
6.2 Pine Script Implementation Considerations
For practical implementation in trading platforms:
- ATR calculation: Standard Pine Script ta.atr() function
- Trailing stops: Dynamic adjustment based on favorable price movement
- Volatility regime detection: Rolling ATR percentiles or simple moving averages
- Position sizing: Integration with account equity and risk parameters
7. Transaction Cost Analysis
Stop-loss strategies must account for implementation costs (Christoffersen & Diebold, 2006):
Direct Costs
- Commission fees: Typically 0.1-0.5% per transaction
- Bid-ask spreads: 0.05-0.15% for liquid instruments
- Market impact: 0.1-0.3% for retail-sized orders
Break-Even Analysis
The minimum performance improvement required to justify stop-loss implementation:
Required_Improvement = Transaction_Costs / Expected_Protection
Empirical analysis suggests break-even thresholds of 0.8-1.2% annual return improvement for most retail implementations.
8. Conclusion
This analysis demonstrates that scientifically-designed stop-loss strategies provide substantial improvements in risk-adjusted returns when properly implemented. Key findings include:
1. Volatility-Adaptive Approaches: ATR-based methods significantly outperform naive fixed-percentage stops, with Sharpe ratio improvements of 25-45% across asset classes.
2. Behavioral Discipline: Systematic biases in stop-loss implementation can destroy value, necessitating objective, rule-based approaches that eliminate emotional decision-making.
3. Cross-Asset Effectiveness: Optimal implementations show greatest benefits in equity and commodity markets, with currency markets displaying mixed results.
4. Practical Implementation: Simple volatility-based methods (ATR, trailing stops) provide most benefits while remaining implementable in standard trading platforms.
The evidence strongly supports the use of volatility-adaptive stop-loss strategies for retail traders, provided that implementation accounts for behavioral biases and transaction costs. For practitioners, the optimal approach involves systematic implementation of ATR-based thresholds, trailing stop mechanisms, and integrated position sizing, while maintaining strict discipline to avoid behavioral biases that can undermine strategy effectiveness.
References
Almgren, R., & Chriss, N. (2001). Optimal execution of portfolio transactions. Journal of Risk, 3(2), 5-39.
Barber, B. M., & Odean, T. (2001). Boys will be boys: Gender, overconfidence, and common stock investment. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 116(1), 261-292.
Barber, B. M., & Odean, T. (2013). The behavior of individual investors. In Handbook of the Economics of Finance (Vol. 2, pp. 1533-1570). Elsevier.
Christoffersen, P., & Diebold, F. X. (2006). Financial asset returns, direction-of-change forecasting, and volatility dynamics. Management Science, 52(8), 1273-1287.
Clare, A., Seaton, J., Smith, P. N., & Thomas, S. (2013). Breaking into the blackbox: Trend following, stop losses and the frequency of trading. Journal of Asset Management, 14(3), 182-194.
Fong, W. M., & Yong, L. H. M. (2005). Chasing trends: Recursive moving average trading rules and internet stocks. Journal of Empirical Finance, 12(1), 43-76.
Han, Y., Zhou, G., & Zhu, Y. (2014). Taming momentum crashes: A simple stop-loss strategy. Journal of Financial Economics, 112(3), 408-428.
Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica, 47(2), 263-291.
Kaminski, K. M., & Lo, A. W. (2014). When do stop-loss rules stop losses? Journal of Financial Services Research, 46(3), 249-276.
Kaustia, M. (2010). Disposition effect. In Behavioral Finance: Investors, Corporations, and Markets (pp. 169-189). John Wiley & Sons.
Kestner, L. N. (2003). Quantitative Trading Strategies: Harnessing the Power of Quantitative Techniques to Create a Winning Trading Program. McGraw-Hill Education.
Lei, T., & Li, X. (2009). Revisiting the classical strategy of trend following in more volatile trading environments. Emerging Markets Review, 10(4), 242-262.
Levine, A., & Pedersen, L. H. (2016). Which trend is your friend? Financial Analysts Journal, 72(3), 51-66.
Merkle, C. (2017). Financial overconfidence over time: Foresight, hindsight, and insight of investors. Journal of Banking & Finance, 84, 68-87.
Shefrin, H., & Statman, M. (1985). The disposition to sell winners too early and ride losers too long: Theory and evidence. Journal of Finance, 40(3), 777-790.
Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1974). Judgment under uncertainty: Heuristics and biases. Science, 185(4157), 1124-1131.
Van Tharp, S. (2006). Trade Your Way to Financial Freedom. McGraw-Hill Education.
Wilder, J. W. (1978). New Concepts in Technical Trading Systems. Trend Research.
The Pullback Panic? Your Whole Plan Dies?!!!!!One red candle is all it takes to destroy your entire plan.
Why do we panic so fast? Why do we exit too early before a rally?
And worse: why do we FOMO back in at the worst possible time?
Hello✌️
Spend 3 minutes ⏰ reading this educational material.
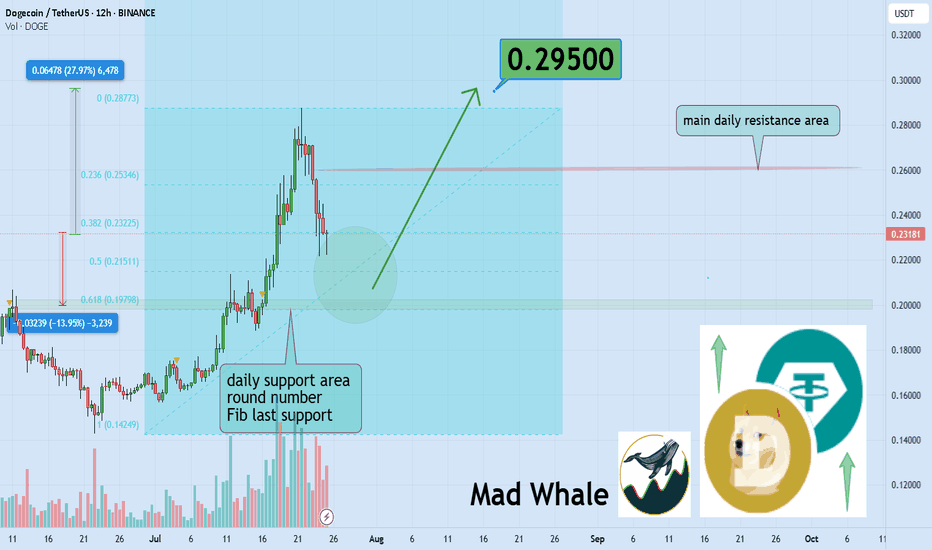
🎯 Analytical Insight on Dogecoin:
BINANCE:DOGEUSDT is approaching the key psychological level of 0.20, which also aligns with a strong daily support and the final Fibonacci retracement zone 🧭. Despite recent volatility, it continues to hold its mid-range Fib level, suggesting potential accumulation. If this support holds, a rebound toward the 0.30 resistance — a move of around 27% remains on the table 🎯.
Now , let's dive into the educational section,
🧠 The Victim Mindset in Crypto Markets
Here’s the uncomfortable truth.
Most traders believe they’re making rational decisions but in reality, they’re reacting emotionally to past pain.
One bad experience during a correction makes us fear all pullbacks.
Missing one big rally creates constant FOMO.
We can’t handle drawdowns but we accept buying tops again and again.
It’s not just you. This is how most retail traders operate and whales know it.
🐳 How Whales Profit From Our Fear
Whales never buy during hype. They buy during fear.
Mini pullbacks, shakeouts and false breakdowns are designed for one thing.
To make you exit so they can enter.
A red candle, a small wick, maybe a fake support break.
We sell out of fear, they buy the dip.
We FOMO back in too late.
Pullbacks are not just price moves. They are psychological traps.
📈 How to Break This Cycle
You don’t need to predict the future. You need to understand yourself.
Ask if this correction is technical or emotional.
Use confirmation from volume, OI and divergence.
Enter after traps, not inside them.
Question your feelings before every move.
You are not trading the chart. You’re trading your mind reacting to the chart.
📊 TradingView Tools to Escape the Fear Greed Cycle
TradingView gives you access to several practical indicators that can help protect your capital from emotional decision-making.
🔹 Fear and Greed Index (Crypto)
Simple but powerful. When the index drops below 30, most traders are in panic mode. That is exactly where whales accumulate, while we run away.
🔹 Open Interest Heatmaps
When open interest rises but price stays flat, it often signals an upcoming shakeout. One scary-looking red candle and the weak hands are gone.
🔹 Volume Profile and VPVR
Perfect for distinguishing between healthy corrections and manipulative dumps. If price pulls back but buying volume remains strong, it's not a real sell-off. It’s a trap.
🔹 Divergence Indicators like MACD or RSI
If RSI rises during a pullback, there’s a hidden bullish divergence. Exiting may be the worst thing to do.
🔹 Liquidity Maps
These show where stop losses and liquidation clusters are located. Often before any major move up, the market takes a detour to liquidate these levels.
Use these tools to stop reacting emotionally and start trading rationally.
📍 Final Thoughts
Small corrections are not the enemy.
Your emotional reaction to them is the real threat.
Before you panic-exit, ask yourself if this fear is justified or just mental conditioning.
The market always gives second chances but we rarely wait for them.
✨ Need a little love!
We pour love into every post your support keeps us inspired! 💛 Don’t be shy, we’d love to hear from you on comments. Big thanks , Mad Whale 🐋
📜Please make sure to do your own research before investing, and review the disclaimer provided at the end of each post.
Learn What is PULLBACK and WHY It is Important For TRADING
In the today's post, we will discuss the essential element of price action trading - a pullback.
There are two types of a price action leg of a move: impulse leg and pullback.
Impulse leg is a strong bullish/bearish movement that determines the market sentiment and trend.
A pullback is the movement WITHIN the impulse.
The impulse leg has the level of its high and the level of its low.
If the impulse leg is bearish , a pullback initiates from its low and should complete strictly BELOW its high.
If the impulse leg is bullish , a pullback movement starts from its high and should end ABOVE its low.
Simply put, a pullback is a correctional movement within the impulse.
It occurs when the market becomes overbought/oversold after a strong movement in a bullish/bearish trend.
Here is the example of pullback on EURJPY pair.
The market is trading in a strong bullish trend. After a completion of each bullish impulse, the market retraces and completes the correctional movements strictly within the ranges of the impulses.
Here are 3 main reasons why pullbacks are important:
1. Trend confirmation
If the price keeps forming pullbacks after bullish impulses, it confirms that the market is in a bullish bearish trend.
While, a formation of pullbacks after bearish legs confirms that the market is trading in a downtrend.
Here is the example how bearish impulses and pullbacks confirm a healthy bearish trend on WTI Crude Oil.
2. Entry points
Pullbacks provide safe entry points for perfect trend-following opportunities.
Traders can look for pullbacks to key support/resistances, trend lines, moving averages or Fibonacci levels, etc. for shorting/buying the market.
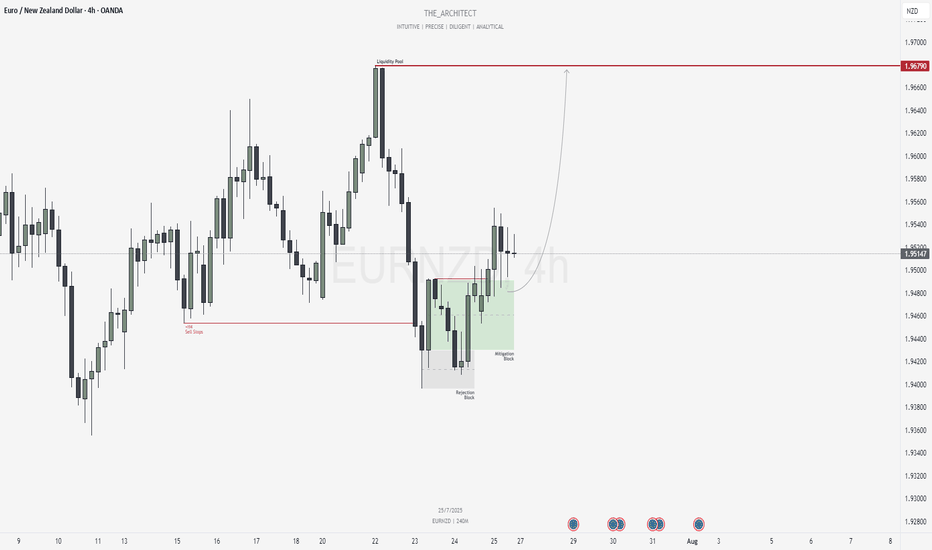
Take a look how a simple rising trend line could be applied for trend-following trading on EURNZD.
3. Risk management
By waiting for a pullback, traders can get better reward to risk ratio for their trades as they can set tighter stop loss and bigger take profit.
Take a look at these 2 trades on Bitcoin. On the left, a trader took a trade immediately after a breakout, while on the right, one opened a trade on a pullback.
Patience gave a pullback trader much better reward to risk ratio with the same target and take profit level as a breakout trader.
Pullback is a temporary correction that often occurs after a significant movement. Remember that pullbacks do not guarantee the trend continuation and can easily turn into reversal moves. However, a combination of pullback and other technical tools and techniques can provide great trading opportunities.
❤️Please, support my work with like, thank you!❤️
I am part of Trade Nation's Influencer program and receive a monthly fee for using their TradingView charts in my analysis.
Why Your Chart Might Be Lying to You And (How to Fix It) !Hello Traders 🐺
Ever clicked the “Log” button on your chart and suddenly everything looked different?
Yeah, you’re not alone...
Most traders ignore it.
But understanding the difference between a Linear and Logarithmic chart can literally change how you see price action — especially if you’re into long-term moves or trading volatile markets like crypto.
Let’s break it down real simple 👇
🔹 Linear Chart (a.k.a. the default)
This is what most charts use by default.
It measures price change in absolute terms.
Meaning: the distance from $10 to $20 is exactly the same as from $20 to $30 — because in both cases, price moved $10.
🧠 Sounds fair, right?
Not always. Here's why...
Let’s say a stock goes from $1 to $2 — that’s a 100% gain.
But if it goes from $100 to $101 — that’s just 1%.
✅ Linear Chart – Pros
Simple and easy to read
Good for short-term price action
Better for assets with small price ranges
Familiar to most beginners
❌ Linear Chart – Cons
Misleading in long-term charts
Distorts large percentage moves
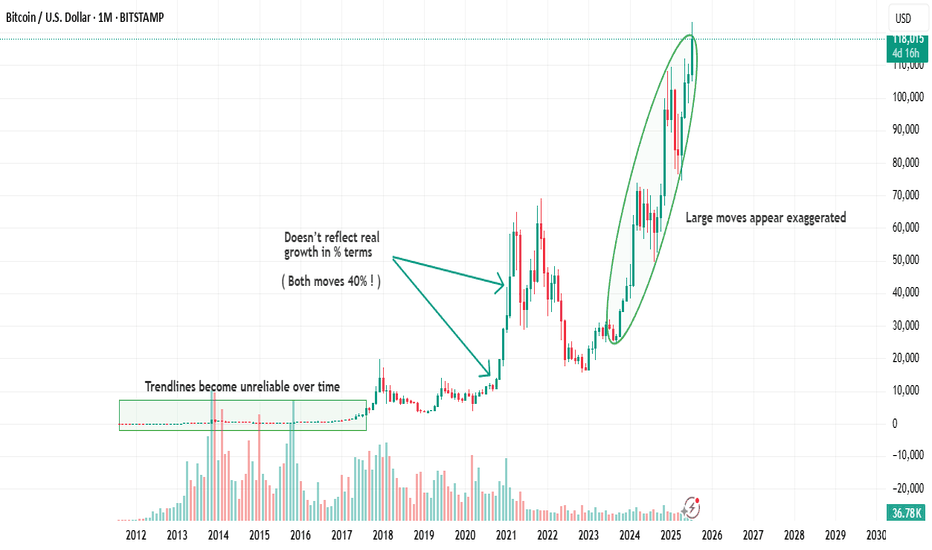
Trendlines become unreliable over time
Doesn’t reflect real growth in % terms
🔹 Logarithmic Chart (Log Scale)
This one shows percentage-based price movement.
Now, going from $10 to $20 (100% gain)
and going from $100 to $200 (also 100% gain)
look exactly the same on the chart — which actually makes more sense when analyzing growth.
It’s super useful when:
✅ You’re analyzing big moves over time
✅ You want to draw accurate trendlines in long-term charts
✅ You're dealing with assets that grew 5x, 10x or more
✅ You care about % gains instead of raw price
❌ Log Chart – Cons
Less intuitive for beginners
Not useful for low-volatility assets
Small price moves may look insignificant
here is an example of the same chart but in the Log Scale :
As you can see on the chart above there is huge difference in accuracy when you use Log scale
for the high volatile asset such as BTC specially in the long term movements .
🆚 So, When Should You Use Each One?
Situation Use Linear Use Log
Small price changes ✅ ❌
Day trading / scalping ✅ ❌
Long-term analysis ❌ ✅
Parabolic or exponential moves ❌ ✅
Drawing long trendlines ❌ ✅
Final Thoughts
If your chart looks weird when you zoom out…
If your trendlines don’t quite fit anymore…
Or if you’re analyzing something that went 10x…
🔁 Try switching to Log scale — it might just clean up the noise.
Small toggle. Big difference.
And also remember our golden rule :
🐺 Discipline is rarely enjoyable , but almost always profitable. 🐺
🐺 KIU_COIN 🐺
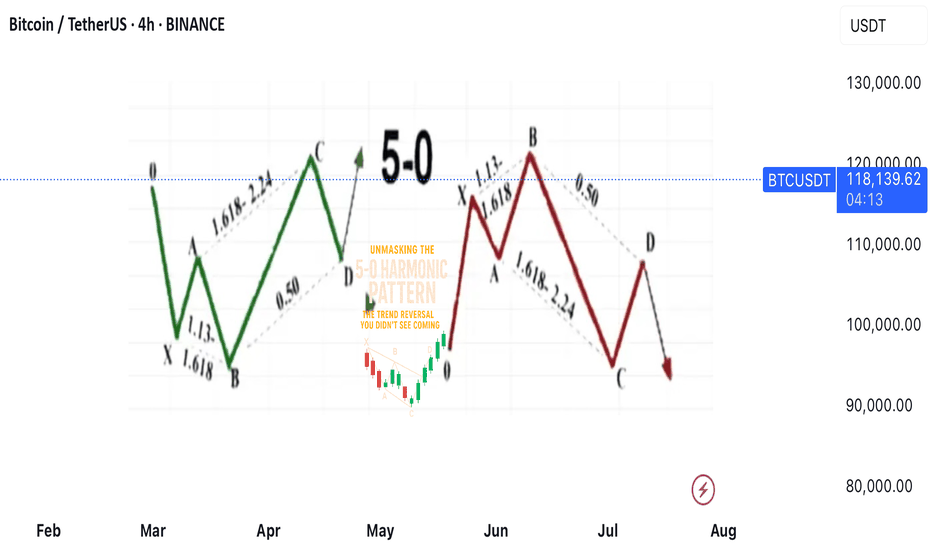
Unmasking the 5-0 Harmonic Pattern
---
🎯 **Unmasking the 5-0 Harmonic Pattern: The Trend Reversal You Didn't See Coming**
Discovered by the visionary Scott Carney and unveiled in _Harmonic Trading, Volume Two_, the **5-0 pattern** isn't just another blip on a trader’s radar—it’s a siren of market reversal.
📈 **Why It Stands Out**
- Unlike the familiar Bat or Gartley structures, the 5-0 pattern is fueled by **precise Fibonacci ratios**, making its reversal zone deadly accurate.
- Centered around the pivotal **Point B**, this model doesn’t just hint at change—it defines it.
🌀 **The Anatomy of a Flip**
- Often marking the **first true pullback in a major trend reversal**, the 5-0 isn’t a lagging indicator—it’s your early warning system.
- The **AB leg?** That’s no ordinary wave—it’s usually the final gasp of a fading trend, setting the stage for powerful new momentum.
💥 **Bottom Line**
This isn’t just technical analysis—it’s strategic foresight. The 5-0 pattern reveals where the market **hesitates... and where you strike**.
---
_"To truly learn, we must see it in action.
So let’s pull back the curtain and share a powerful example from our **past insurance market trades**—a deal that blended precision, timing, and strategy.
In comments
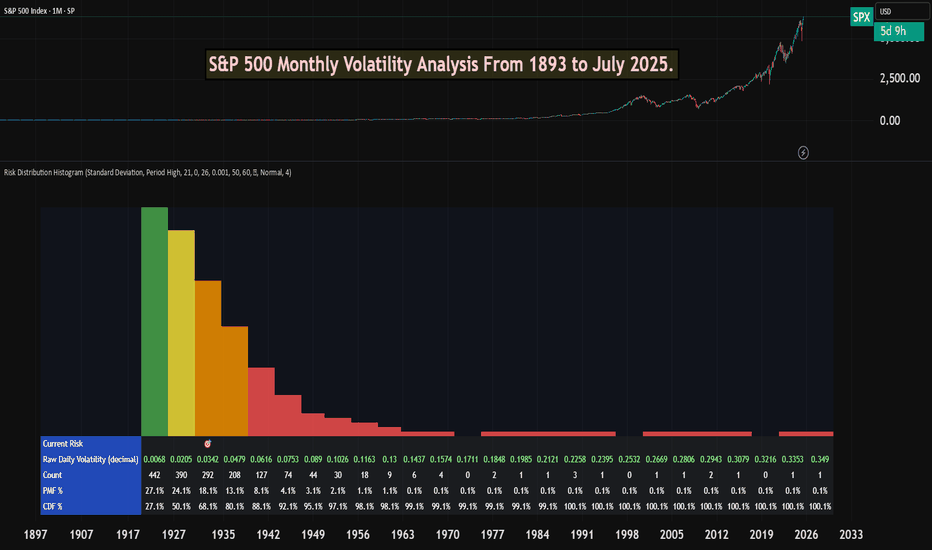
S&P 500 Monthly Volatility Analysis From 1893 to July 2025Most of the time, the S&P 500 is seen as a low-volatility index when compared to most individual stocks, small-cap indexes, or indexes from other countries.
However, most investors don't know exactly what volatility to expect from a statistical perspective.
The Risk Distribution Histogram allows us to understand exactly how risk is distributed.
S&P 500 Statistical Risk Distribution
Here are some highlights from what we get from the analysis. Some of this data might actually surprise investors. The data is monthly:
27% of all months have volatility under 0.68%
80% of all months' volatility was under 4.79%
5% of all months had a volatility of over 7%
If we can call a volatility over 25% a severe crash or "grey" swan, we had 7 of those events
3 months with extreme volatility over 30%
This allows us to understand tail risk and plan ahead. While most times the S&P 500 is in the low volatility zone, extreme events can happen.
What can we learn from this?
Prepare for rare but possible high-volatility events.
Understand the 80/20 rule. Most months are very low volatility, but 20% of them will have a volatility higher than 5% approximately.
Avoid overconfidence in stability
Plan for long-term horizons. High volatility tends to "dissipate" in the long term.
This is why it's important not to discard rare high-volatility events, especially when the investor is in need of liquidity.
This risk analysis can be done for any ticker.
Beyond ICT & SMC: The Mathematical Revolution in Zone TradingIn the world of trading, there's a fundamental divide between traders who rely on subjective interpretation and those who trust mathematical precision. While concepts like ICT (Inner Circle Trader), SMC (Smart Money Concepts), and naked chart analysis have gained popularity, they all share one critical flaw: they're based entirely on personal interpretation.
The Subjectivity Problem
Ask ten ICT traders to mark their Order Blocks, Fair Value Gaps, or Breaker Blocks on the same chart, and you'll get ten different answers. Why? Because these concepts rely on:
Personal bias in identifying "significant" levels
Subjective interpretation of market structure
Discretionary decision-making on what constitutes a valid setup
Emotional influence on analysis
The same issue plagues SMC, CRT (Candle Range Theory), time-based analysis, and naked chart trading. One trader's "liquidity grab" is another trader's "breakout." One person's "strong support" is another's "weak bounce zone."
The Mathematical Solution
This indicator eliminates this guesswork entirely. Instead of relying on subjective interpretation, it:
Calculates exact entry levels using mathematical formulas based on session params
Identifies precise support/resistance zones
Standardises signals across all timeframes, ensuring consistency whether you're on 1m or 15m charts
Removes emotional bias by using algorithmic detection of significant price levels
Numbers Don't Lie
While an ICT trader might debate whether a level is "mitigation" or "inducement," our indicator simply states: "Entry at 1.0847, Stop at 1.0832." No interpretation needed. No second-guessing. Just mathematical precision derived from actual price action.
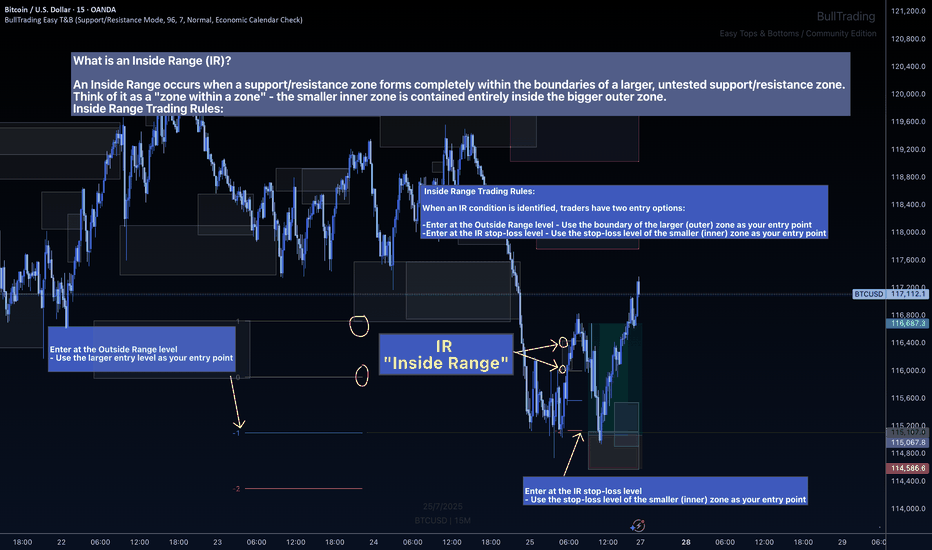
The Inside Range Advantage: When Zones Within Zones Create Superior Trading Opportunities
Most traders miss one of the most powerful setups in technical analysis: the Inside Range (IR). While ICT traders debate "nested order blocks" and SMC followers argue about "refined zones," you can easily identify Inside Ranges with this indicator and mathematically identify these high-probability setups with zero ambiguity.
What Makes Inside Ranges Special?
An Inside Range occurs when a new support/resistance zone forms completely within an untested larger zone. Think of it as the market revealing its hand twice – first showing you the broader area of interest, then pinpointing the precise level within it.
The Mathematical Edge
While discretionary traders struggle to identify these setups consistently, this indicator:
Automatically detects when a smaller zone forms within a larger untested zone
Calculates two precise entry options without any guesswork
Eliminates the confusion of nested levels that plague subjective analysis
Two Entries, Zero Confusion
Documentation and full trading system instructions can be found on the indicator's publication
When an IR forms, the indicator provides exactly two mathematically-derived entry options:
The Outside Range entry – Using the larger zone's entry level
The IR Stop-Loss entry – Converting the inner zone's stop level into an entry point
Compare this to SMC's "refined OB" or ICT's "nested FVG" concepts where traders endlessly debate which level is valid. With Inside Ranges, there's no debate – just two clear, calculated levels.
Inside Ranges represent areas where institutional interest overlaps. The larger zone shows initial interest, while the smaller zone within reveals refined positioning. By mathematically identifying these setups, you're trading where smart money has shown its hand twice.
Real Consistent Precision
Instead of squinting at charts trying to identify subjective "zones within zones," let mathematics do the heavy lifting.
In trading, consistency beats creativity. Stop drawing arbitrary lines and hoping for the best. Start trading with mathematical precision.
Documentation and full trading system instructions can be found on the indicator's publication →
Trade with confidence. Trust in mathematics. Trust in your Edge.
5 Lessons from My First 100 TradesAfter executing and reviewing over 100 real trades in crypto, forex, and gold — I found patterns. Bad patterns. Repeating mistakes. And lessons I wish someone had told me earlier.
So I broke them down into 5 key insights that changed how I trade — and might just save you thousands.
📘 Here’s what’s inside:
1️⃣ Smart Profit-Taking:
How I turned 10 R/R into 32 R/R using a dynamic exit plan.
📘Further resource:
Cycle Mastery (HWC/MWC/LWC)
---
Multi-Timeframe Mastery
2️⃣ The Sleep Edge:
70% of my losing trades happened after bad sleep. Here’s why that matters more than emotions.
3️⃣ No More Blind Stop Orders:
Why I stopped using buy/sell stops without real candle confirmation — and what I do instead.
📘 Further reading:
Breakout Trading Mastery
---
Indecision Candle Strategy
4️⃣ Multi-Layered Setups Win:
How structure, S/R, patterns, and timing stack into high-probability entries.
5️⃣ News Trading? Just Don’t.
The data behind why most of my SLs were hit near news time — and how I avoid the trap.
💡 These aren’t theories. These are real lessons from real trades.
If this video helped you or sparked an “aha” moment, give it a boost, commenting your takeaway, and sharing it with a fellow trader.
lets grow together :)
Market Structure is Not Strategy — It’s Your Starting Point“The chart doesn’t hide anything. But your mind does.”
Before any indicator, setup, or signal… comes structure.
🔍 What is Market Structure?
At its core, market structure is the sequence of higher highs (HH) and higher lows (HL) in an uptrend, or lower lows (LL) and lower highs (LH) in a downtrend.
It is the skeleton of price .
Everything else — entries, zones, signals — is just clothing.
If you can’t see the skeleton, you’re reacting to noise.
🎯 Why It Matters:
It’s not a signal. It’s context .
It tells you whether you’re trading with the market or against it .
It defines where your patience begins — not where your entry is.
Market structure helps you let go of the urge to chase. It brings order to the chaos.
🧩 Key Components to Track:
Break of Structure (BoS): Confirms trend continuation
Change of Character (ChoCH): Signals a potential reversal
Swing Points: Define the intent behind price moves
Liquidity Sweeps: Often mask real structure beneath short-term traps
🛑 Common Mistake:
Most traders jump straight to the setup without asking the most important question:
“Where am I in the structure?”
They try to buy a pullback — in a downtrend.
They try to fade a move — right before continuation.
They chase candles — instead of waiting for alignment.
That’s not strategy. That’s stress.
🛠 Tip to Practice:
Use this simple framework to build clarity:
Start from the H4 chart — this gives you the broader directional bias
Drop to M15 — here’s where structure begins to form tradeable setups
Finally zoom into M1 — this is where confirmation happens before entry
Ask yourself:
Where did the last BoS or ChoCH happen on each timeframe?
Is M15 aligning with H4 intent — or contradicting it?
Did you enter after M1 confirmation , or based on impulse?
You don’t need to predict price. You need to align with it.
🪞 Final Thought:
Structure isn’t strategy.
It’s the mirror that shows what’s real before your bias speaks.
When you master structure, you stop forcing trades — and start flowing with them.
💬 Want more like this?
If this post resonated with you — drop a comment below.
Let me know what you'd like to dive deeper into — price action, gold setups, market structure, or the psychology behind your trades.
I’ll build future tutorials based on what matters to you.
📘 Shared by @ChartIsMirror
“Buy the rumor, sell the news”
---
### 🎯 **“Buy the Rumor, Sell the News” – A Trader’s Mind Game**
Imagine you’re not just following the market… you’re dancing ahead of it. This strategy flips traditional thinking on its head—and rewards those bold enough to act **before** the spotlight hits.
---
### 🕵️♂️ **Step One: Buy the Rumor**
- Traders catch whispers—like talk of a potential interest rate hike.
- The markets start to react *before* anything official is announced.
- Assets like gold might drop on the expectation alone… that’s your **entry point**.
You're not buying certainty. You're buying what the crowd *thinks* will happen.
---
### 🔊 **Step Two: Sell the News**
- Once the news breaks, it's already "old" to seasoned traders.
- That shocking headline? Already priced in.
- The market might reverse or surge unpredictably.
- This is when savvy traders exit, locking in profits from those who just arrived.
---
### 🧠 **Why It Works**
- Financial markets aren’t just driven by facts—they’re powered by **sentiment** and **anticipation**.
- By the time news goes public, smart money has already moved.
It’s like buying concert tickets before the band announces a tour—then selling them the moment fans go wild.
---
### 📉 **A Real Example**
- **Monday Rumor**: “The Fed will raise interest rates.”
- Gold begins to slide as traders prepare—this is your chance to act.
- **Thursday News**: The hike is confirmed.
- Instead of dropping further, gold might **rise** due to market overreaction or repositioning.
- You **sell** into that chaos—profit made.
---
Shark harmonic pattern
---
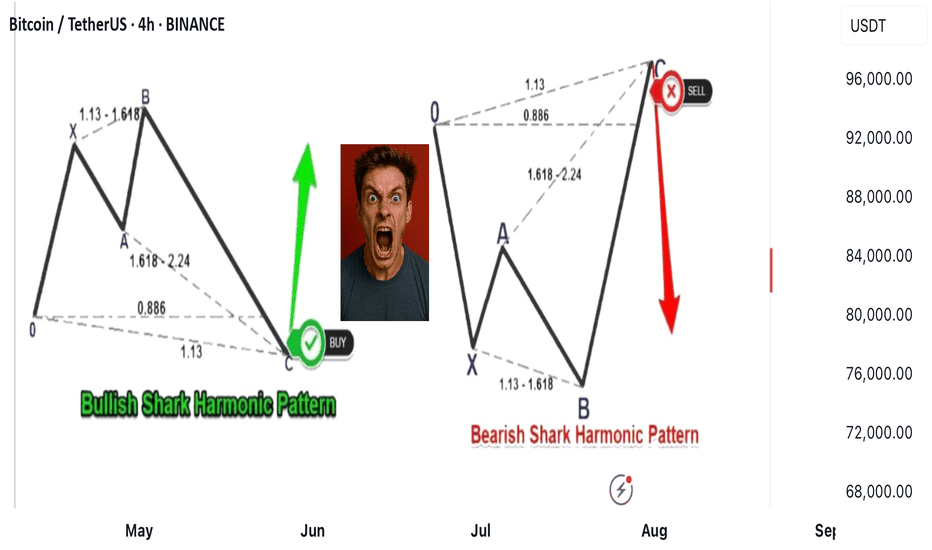
### 🦈 What Is the Shark Harmonic Pattern?
- **Discovered by**: Scott Carney in 2011
- **Foundation**: Combines **Fibonacci ratios** with **Elliott Wave Theory**
- **Purpose**: Identifies potential **trend reversals** using precise geometric price structures
- **Structure**: Five points labeled **O, X, A, B, C** (not the usual XABCD)
- **Key Feature**: Relies heavily on the **88.6% Fibonacci retracement** and **113% extension**
---
### 📐 Pattern Geometry & Ratios
| Leg | Description | Fibonacci Ratio Range |
|------------|--------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------|
| XA | Initial impulse leg | No specific ratio |
| AB | Extension beyond X | 113% to 161.8% of XA |
| BC | Completion leg | 88.6% to 113% of OX |
| | | 161.8% to 224% of AB |
- **Point B** must **exceed point X**, forming an **Extreme Harmonic Impulse Wave**
- **Point C** is the **Potential Reversal Zone (PRZ)**
---
### 🛒 Buy Setup (Bullish Shark)
1. **No fixed retracement for A**
2. **B extends 113%–161.8% of XA**
3. **C completes at**:
- 88.6%–113% of OX
- 161.8%–224% of AB
📍 **Entry**: Near point C
📍 **Stop Loss**: Below point C
📍 **Target**: Retracement levels of BC (e.g., 50%, 61.8%), or back to point A/B
---
### 📉 Sell Setup (Bearish Shark)
1. **No fixed retracement for A**
2. **B extends 113%–161.8% of XA**
3. **C completes at**:
- 88.6%–113% of OX
- 161.8%–224% of AB
📍 **Entry**: Near point C
📍 **Stop Loss**: Above point C
📍 **Target**: Retracement levels of BC, or back to point A/B
---
### 📊 Real Trade Example & Educational Resources
In the comment
Understanding ROI in Crypto: More Than Just a NumberHello, Traders! 👏
Return on Investment (ROI) is often the first metric new investors focus on when evaluating an asset, a strategy, or even their trading performance. It’s easy to see why. It's simple, intuitive, and widely used across both traditional finance and the cryptocurrency sector. One formula, and suddenly you have a "score" for your investment. Green is good. Red is bad. Right?
Well…Not quite.
In the crypto market, where price swings can be extreme, timelines are compressed, and risk profiles differ significantly from those in traditional markets, a simplistic ROI figure can be dangerously misleading.
A 50% ROI on a meme coin might look great, until you realize the token is illiquid, unbacked, and you're the last one holding the bag. Conversely, a 10% ROI on a blue-chip crypto asset with strong fundamentals might be significantly more meaningful in risk-adjusted terms.
In this article, we'll delve beyond the basic formula and break down what ROI really tells you, how to use it correctly, and where it falls short. Let's go!
What Is ROI and How Do You Calculate It?
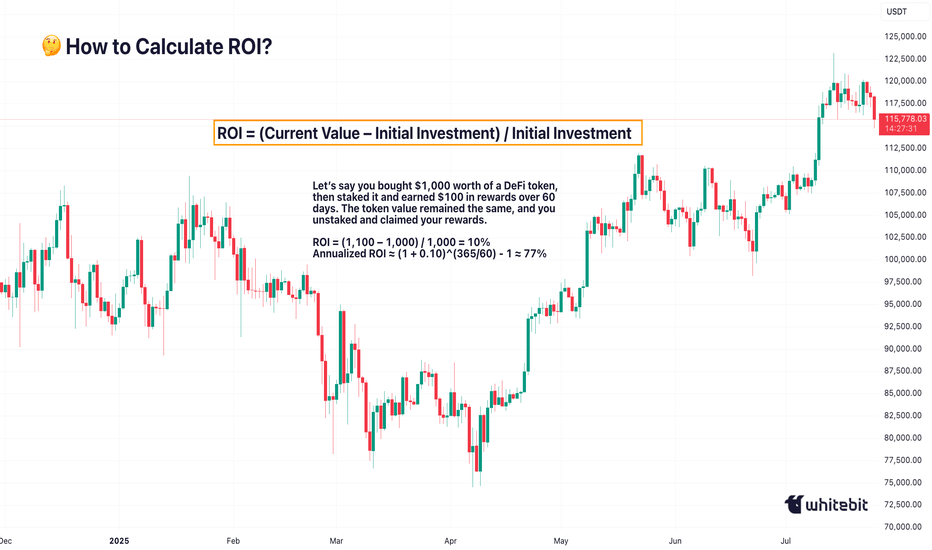
The Basic Formula for Return on Investment Is: ROI = (Current Value – Initial Investment) / Initial Investment.
Let’s say you bought ETH at $2,000 and sold it at $2,600: ROI = (2,600 – 2,000) / 2,000 = 0.3 → 30%. Seems straightforward. You made 30% profit. However, crypto is rarely straightforward.
What if you held it for 2 years? Or 2 days? What if gas fees, staking rewards, or exchange commissions altered your real costs or returns? Did you include opportunity cost and the profits missed by not holding another asset? ROI as a raw percentage is just the beginning. It’s a snapshot. However, in trading, we need motion pictures, full narratives that unfold over time and within context.
Why Time Matters (And ROI Ignores It)
One of the most dangerous omissions in ROI is time.
Imagine two trades: Trade A returns 20% in 6 months. Trade B returns 20% in 6 days.
Same ROI, very different implications. Time is capital. In crypto, it’s compressed capital — markets move fast, and holding a position longer often increases exposure to systemic or market risks.
That’s why serious traders consider Annualized ROI or utilize metrics like CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) when comparing multi-asset strategies or evaluating long-term performance.
Example: Buying a Token, Earning a Yield
Let’s say you bought $1,000 worth of a DeFi token, then staked it and earned $100 in rewards over 60 days. The token value remained the same, and you unstaked and claimed your rewards.
ROI = (1,100 – 1,000) / 1,000 = 10%
Annualized ROI ≈ (1 + 0.10)^(365/60) - 1 ≈ 77%
Now that 10% looks very different when annualized. But is it sustainable? That brings us to the next point…
ROI Without Risk Analysis Is Useless
ROI is often treated like a performance badge. But without risk-adjusted context, it tells you nothing about how safe or smart the investment was. Would you rather: Gain 15% ROI on a stablecoin vault with low volatility, or Gain 30% ROI on a microcap meme token that could drop 90% tomorrow?
Traders use metrics such as the Sharpe Ratio (which measures returns versus volatility), Maximum Drawdown (the Peak-to-Trough Loss During a Trade), and Sortino Ratio (which measures returns versus downside risk). These offer a more complete picture of whether the return was worth the risk. ⚠️ High ROI isn’t impressive if your capital was at risk of total wipeout.
The Cost Side of the Equation
Beginners often ignore costs in their ROI math. But crypto isn’t free: Gas fees on Ethereum, trading commissions, slippage on low-liquidity assets, impermanent loss in LP tokens, maybe even tax obligations. Let’s say you made a 20% ROI on a trade, but you paid 3% in fees, 5% in taxes, and lost 2% in slippage. Your actual return is likely to be closer to 10% or less. Always subtract total costs from your gains before celebrating that ROI screenshot on X.
Final Thoughts: ROI Is a Tool, Not a Compass
ROI is beneficial, but not omniscient. It’s a speedometer, not a GPS. You can use it to reflect on past trades, model future ones, and communicate performance to others, but don’t treat it like gospel.
The real ROI of any strategy must also factor in time, risk, capital efficiency, emotional stability, and your long-term goals. Without those, you’re not investing. You’re gambling with better math. What do you think? 🤓
Weekly Trade Outlook | Lessons in Discipline, Risk & PerspectiveGreetings Traders,
In today’s video, I’ll be walking you through my end-of-week trade outlook, breaking down every setup I took throughout the week. This session is designed to offer insight into how I apply risk management, trading rules, and maintain psychological discipline in real-time market conditions.
Whether you're struggling with emotional trading, inconsistency, or overtrading, this video will give you a fresh perspective on how structure, faith, and discipline can shape a sustainable trading approach.
Remember: respect your trading rules, pray over them daily, and ask God for the strength to remain disciplined—so you don’t become your own worst enemy in the market.
Let’s grow together,
The Architect 🏛️📈
Indicator Decoded: RSI Mega Zones: Signals from the EdgeMost traders are familiar with the textbook RSI levels—70 indicating overbought and 30 indicating oversold. But markets, especially in strong momentum phases, do not always obey these boundaries. That is where the concept of Mega Overbought and Mega Oversold zones becomes vital. These are not fixed thresholds, but adaptive zones often beyond 80 and below 20, where the RSI reflects extreme strength or weakness. Rather than acting as reversal points, these levels often signal trend continuation.
A reading above 80 is typically seen during powerful uptrends or post-breakout rallies. It indicates not just buying, but unhesitating, aggressive demand, especially after key resistance zones have been cleared. Such RSI levels have often not been seen in several months—if not more than a year—making their appearance especially significant. Rather than a signal of exhaustion, this may be the start of a major trend, suggesting that the broader structure of the stock or index has shifted decisively. Traders who misinterpret this as a reversal signal often find themselves fighting momentum. Instead, price tends to grind higher, sometimes pausing briefly before further gains. This is why the chapter suggests using Mega Overbought zones as confirmation of bullish control, not a trigger for counter-trades.
The inverse applies to the Mega Oversold zone—RSI falling below 20. This is usually not a buy-the-dip moment, especially if the broader trend and chart structure are bearish. Such readings typically accompany panic-driven breakdowns, where sellers dominate without any counterforce. These extreme values are often rare and may not have appeared for months or even over a year, marking a moment where the market’s character may be undergoing a structural change. As with Mega Overbought, context is critical. If RSI hits such depths after prolonged distribution or a topping pattern, it does not indicate value—it confirms that the tide has turned, and a strong downtrend may be setting in.
Both Mega zones are best used in conjunction with structure—trendlines, volume shifts, anchored VWAP zones, or price patterns. The RSI alone is not enough. But when it aligns with other technical signals, a Mega Overbought or Oversold status becomes a momentum amplifier, not a contrarian prompt. In fact, your RSI chapter rightly warns that entering against such zones can be fatal unless clear divergences, climax patterns, or volume exhaustion are also present. Think of these extremes not as ceilings or floors, but as accelerators when backed by structure.
A word of caution: These signals are rare and often widely spaced. The real challenge lies in managing risk–reward, as strong momentum and shallow pullbacks can make it difficult to find entries with favourable R:R ratios.
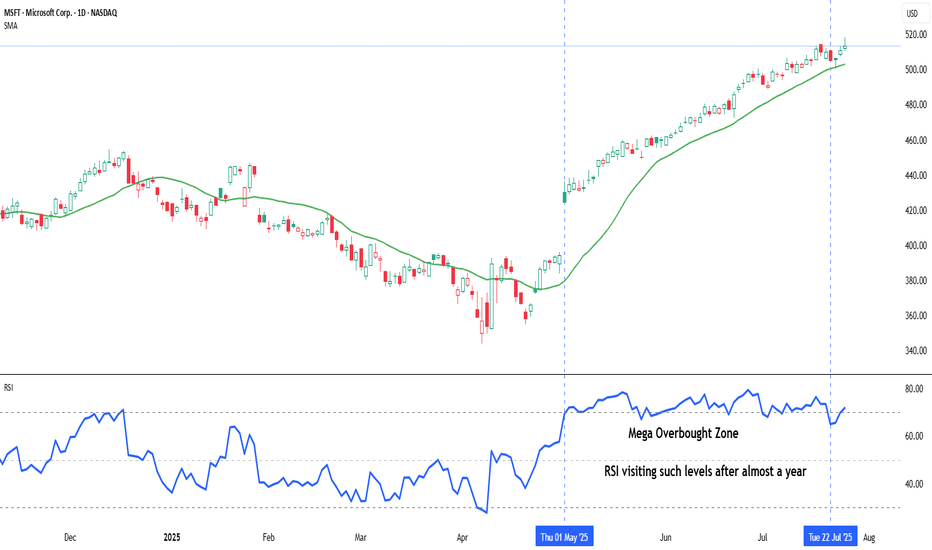
Chart: Microsoft Corp. (MSFT) – Daily Chart with 20-DMA and RSI (as on July 25, 2025)
Microsoft continues its strong upward trajectory, with price action staying well above the rising 20-day simple moving average. The recent surge in RSI into the mega overbought zone marks a significant shift in momentum, as the indicator revisits such elevated levels after nearly a year—an occurrence that often coincides with extended bullish phases.
Time to Wait and Watch
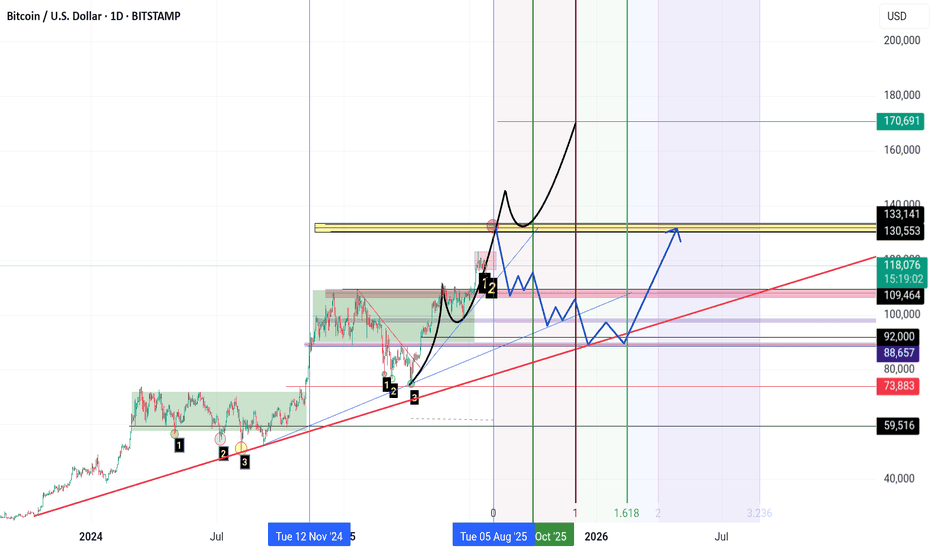
**"The $133K zone remains Bitcoin’s key resistance level.**
If Bitcoin fails to break this resistance for any reason and forms a **reversal candle** in this area,
I expect a **correction phase** to begin, with the market entering **panic sell mode.**
**First support** lies at **$110K.**
Further support levels are **$100K, $92K, and $88K** respectively.
If the price drops to the **$74K zone**, it’s time to **sell everything you’ve got** (yes, even your kidneys!) and **buy Bitcoin.**
However, if **$133K is broken to the upside**, we’re heading for **$140K, $150K, and $170K**… and **then** the real **panic selling** begins."
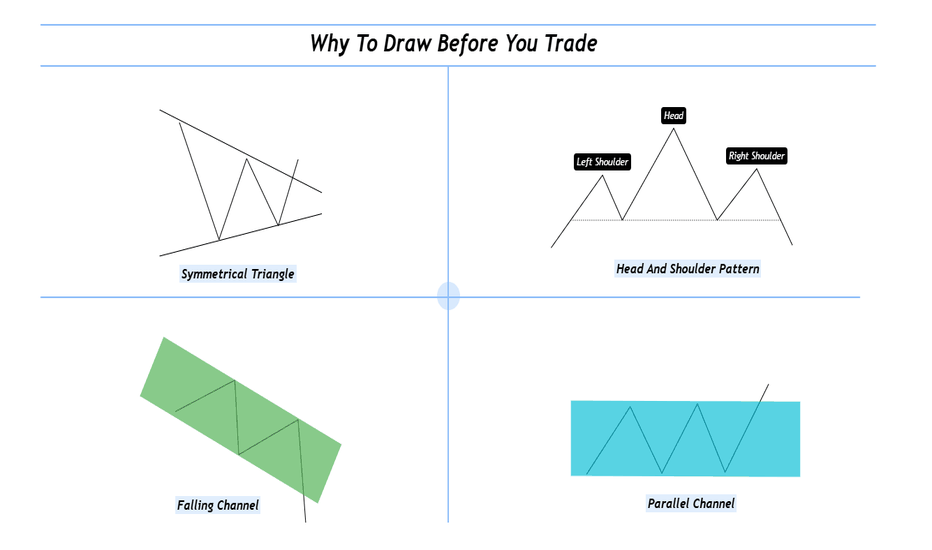
Why To Draw Before You Trade ?Hello fellow traders and respected members of the trading community, In a fast paced market dominated by automation and algorithms, we often forget the value of simply picking up a tool and drawing on our charts. Let’s revisit why this fundamental habit still holds the power to sharpen our edge and elevate our decision-making.
Why We Should Draw and Trade? Turning Charts Into Clarity
Introduction-:
In an age of auto-generated indicators, black-box algorithms, and AI-driven signals, many traders are drifting away from one of the most fundamental trading tools: manual chart drawing.
But what if the very act of drawing is not just an old habit—but a powerful trading edge?
This publication explores why actively drawing on charts and trading based on visual context can elevate your market understanding and execution like nothing else.
1. What Does It Mean to “Draw and Trade? Drawing isn’t just technical analysis it’s interactive thinking. When you draw, you're mapping the structure of the market using tools like
Trendlines
Support & Resistance zones
Chart Patterns (Head & Shoulders, Flags, Triangles, etc.)
Supply & Demand levels
Gaps, Fibonacci levels, and more
Once the chart is marked, you’re no longer entering trades blindly you’re entering with context, clarity, and confidence.
2. The Psychology Behind Drawing
Manual drawing engages your focus, discipline, and decision-making. You don’t just predict, you process and It forces you to slow down helping reduce impulsive trades. Drawing anchors your emotions and keeps you mindful. The act of drawing becomes a psychological filter—helping you trade from structure, not stress.
3. Why It Beats Indicator Only Trading?
Indicators are reactive. Drawing is proactive.
Here’s the difference:
Indicators show what already happened
Drawing lets you prepare for what could happen
You learn to-:
Anticipate breakouts, fakeouts, and reversals, Understand market structure and Develop your own strategy not depend on someone else's signal. In short you become the strategist, not just a follower.
4. The “Chart Time” Advantage
Just like pilots need flight hours, traders need chart hours. Drawing charts manually gives you those hours.
You start to see patterns that repeat and notice behavior shifts before they show on indicators. Build a visual memory of how the market moves and It’s this visual experience that separates analysts from traders.
5. Real-World Edge: Case Studies
Wyckoff Distribution: Mapping the structure—BC, AR, ST, UT, LPSY—helps anticipate smart money exits.
Gap Zones: Marking an old breakaway gap can help predict future rejection or support
Demand Zones + Fib Confluence: Drawing reveals high-probability reversal zones most indicators miss
Each drawing becomes a trade-ready story with logic and risk control.
6. From Drawing to Discipline
Drawing is not just prep it’s planning. You trade with a clear plan and pre-identified entry/exit zones this reduced emotional interference and It becomes your personal visual rulebook. No noise no randomness just structure driven action.
7. Final Thoughts: The Trader’s Mind vs. The Machine
Yes, AI and indicators are useful.
But your most powerful edge?
Your mind.
Your eyes.
Your experience sharpened through drawing.
If you want to evolve from a reactive trader to a consistent performer, here’s the golden rule:
Stop watching. Start drawing. Trade what you see, not what you hope.
I hope you will like this post, Thanks for giving your valuable time for reading.
Regards- Amit
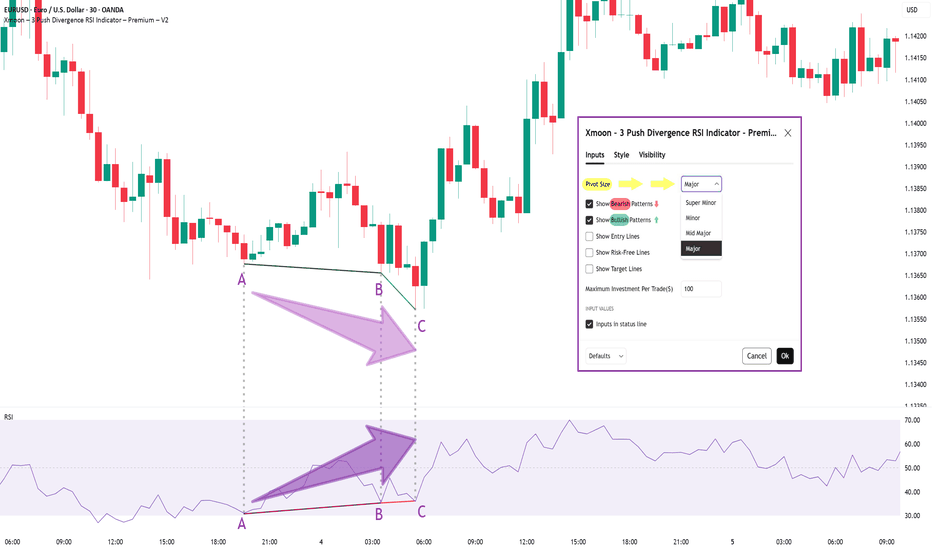
Xmoon Indicator Tutorial – Part 1 – Strategy🔻🔻🔻+ Persian version below🔻🔻🔻
📘 Xmoon Indicator Tutorial – Part 1
🎯 3Push Divergence RSI Strategy
🔥 The core of the Xmoon indicator
is built upon one of the most powerful strategies in technical analysis:
The advanced 3Push Divergence RSI pattern
🔁 A pattern that typically appears at key market turning points.
📉 When the price moves in the same direction three consecutive times on pivot points (e.g., making lower lows or higher highs), but the RSI shows the opposite behavior, it indicates a clear divergence !
💡 This divergence can act as a strong signal for a potential trend reversal.
🎯 The Xmoon Indicator is designed to detect this critical moment.
⚙️ Xmoon Indicator Settings Panel
The Xmoon settings panel offers the following options:
🔸 Pattern Type Selection: In the first and second lines, you can specify which type of pattern should be displayed: only bullish patterns or only bearish ones. You can also check both options.
🔸 Pivot Type Selection: From the dropdown menu, you can choose one of four pivot types:
“Super Minor”, “Minor”, “Mid-Major”, and “Major”, ordered from smallest to largest.
📌 Educational Note: The greater the distance (in candle count) between two lows or two highs, the larger the pivot is considered.
A Major Pivot is the largest among them.
✅ Larger Pivot = Higher Accuracy
❗ But naturally = Fewer Signals
📣 If you have any questions or need guidance, feel free to ask us. We’d be happy to help.
🔻🔻🔻بخش فارسی – Persian Section 🔻🔻🔻
📘 آموزش اندیکاتور ایکسمون - قسمت اول
🎯 استراتژی سهپوش واگرایی (3Push Divergence RSI)
🔥 هسته اصلی ایکسمون
بر پایه یکی از قویترین استراتژیهای تحلیل تکنیکال طراحی شده است
الگوی پیشرفته سهپوش واگرایی
🔁 الگویی که معمولاً در نقاط چرخش مهم بازار ظاهر میشود
📉 وقتی قیمت سه بار پشت سر هم روی نقاط پیوت ، در یک جهت حرکت میکند (مثلاً کفهای پایینتر یا سقفهای بالاتر میسازد) ، اما آر-اِس-آی خلاف آن را نشان میدهد، یعنی یک واگرایی آشکار رخ داده است
💡این واگرایی میتواند سیگنالی قوی برای برگشت روند باشد
🎯 اندیکاتور ایکسمون این لحظه را شناسایی میکند
⚙️ پنجره تنظیمات اندیکاتور ایکسمون
در بخش تنظیمات اندیکاتور ایکسمون، امکاناتی در اختیار شما قرار دارند
🔸 انتخاب نوع الگو: در خط اول و دوم میتوانید مشخص کنید چه نوع الگویی نمایش داده شود
فقط الگوهای صعودی یا فقط نزولی. همچنین می توانید تیک هر دو گزینه را بزنید
🔸 انتخاب نوع پیوتها: از پنجره کشویی بالا، می توانید یکی از ۴ نوع پیوت را انتخاب کنید
پیوت ها به ترتیب از کوچک به بزرگ عبارتند از: سوپر مینور ، مینور ، میدماژور و ماژور
📌 نکته آموزشی: هرچه فاصله بین دو کف یا دو سقف بیشتر باشد (یعنی تعداد کندلهای بین آنها زیادتر باشد)، آن پیوت، بزرگتر محسوب میشود
پیوت ماژور از بقیه بزرگ تر است
✅ پیوت بزرگتر = دقت بالاتر
❗ اما طبیعتاً = تعداد سیگنال کمتر
📣 اگر سوالی دارید یا نیاز به راهنمایی دارید، خوشحال میشویم از ما بپرسید
با کمال میل در خدمتتان هستیم
Risk-to-Reward and Journaling : Track, analyze, and evolve
📈 Mastering the Markets: Why Risk-to-Reward and Journaling Are Every Trader’s Edge
In trading, profitability isn't just about making winning trades — it's about managing risk smartly and learning from every position. Two of the most underrated habits that separate amateurs from consistent traders are:
1. Understanding Risk-to-Reward (R:R)
The risk-to-reward ratio is the foundation of trade planning. It's a simple calculation of how much you're willing to risk versus how much you aim to gain. A ratio of 1:2 means you risk $1 to potentially make $2.
✅ Why it matters:
Even with a 40% win rate, a positive R:R can still yield profitability.
It disciplines your entries, stops, and targets — no more emotional exits.
It forces you to filter out trades that don’t offer enough upside.
📊 For example, if you take 10 trades risking $100 each with a 1:2 R:R:
Win 4 = $800 gain
Lose 6 = $600 loss
Net Profit = $200 despite winning less than half.
2. The Power of Journaling
Trading without a journal is like flying blind. Your memory fades, but data doesn’t lie. A trading journal helps you:
🧠 Improve strategy by analyzing what works (symbols, timeframes, setups)
📉 Spot patterns in losses — overtrading? wrong R:R? bad timing?
📈 Stay disciplined — journaling enforces accountability
📒 Capture emotions — was it fear or FOMO? A journal tracks mindset too.
In my experience, journaling alone can boost a trader’s edge more than tweaking indicators. It turns experience into insight.
🎯 Final Word
The market rewards preparation, not prediction. A solid risk-to-reward framework keeps you in the game. Journaling turns your trades into tuition. Together, they compound your growth.
Happy Trading
Flat, Quiet… and Full of Clues .Most traders only see the middle.
The acceleration. The “trend”. The movement.
But that’s just one-third of the story.
If you really want to understand the market’s rhythm,
you need to study how moves begin, evolve, and die.
Let’s break down the 3 key phases every market goes through —
again, and again, and again.
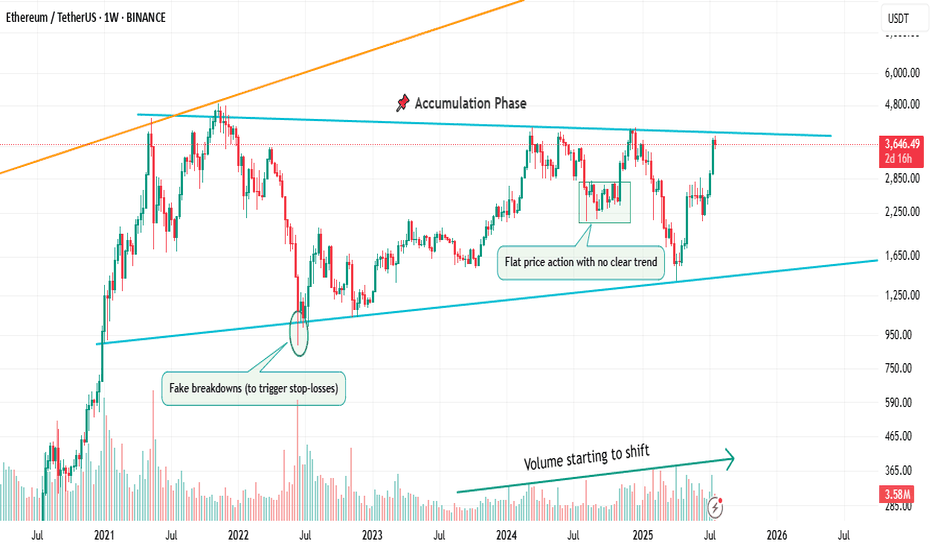
📌 1. Accumulation Phase
This is the part no one talks about.
Why? Because it’s boring. Choppy. Range-bound. Confusing.
Most traders get shaken out here.
But smart money? They’re quietly buying.
You’ll often see:
Flat price action with no clear trend
Fake breakdowns (to trigger stop-losses)
Volume starting to shift
Long wicks — both directions
This phase is a test of patience, not prediction.
And if you learn to read it well, you’ll start catching moves before they go parabolic.
🚀 2. Markup / Acceleration Phase
Here’s where everyone wakes up.
Momentum kicks in.
News gets bullish.
Breakouts start working.
Pullbacks are shallow.
And suddenly, everyone’s calling it a bull market.
But don’t be fooled.
This is not where smart money enters — this is where they ride the wave they already created.
Learn to:
Ride trends, not chase them
Add on pullbacks
Avoid FOMO entries
This is the fastest and most emotional part of the cycle — which means it rewards discipline, not excitement.
🧯 3. Distribution Phase
The party’s still on… but the hosts are quietly leaving.
Price starts to stall.
Breakouts stop working.
Volume gets heavy at the top.
And the same excitement that brought everyone in?
It’s now being used to sell into.
Distribution is sneaky.
It’s not an obvious top.
It’s a process — just like accumulation.
You’ll often see:
Lower highs forming quietly
False breakouts to trap buyers
Increasing volatility
Bullish news… with no follow-through
If you’re not paying attention, you’ll keep buying strength —
right before the rug gets pulled.
So what’s the lesson here?
Markets don’t just “go up or down.”
They prepare, move, then exhaust.
And if you learn to spot these transitions —
you’ll stop reacting late
and start positioning early.
That’s the real edge.
currently we are on the accumulation phase so in this idea I tried to show you the real story behind it and as well talk about the two others to beware of them also in the right moment I will talk about them , but for now let's focous on the current phase because we want to be part of the smart money and enjoy the next phase which is 🚀Markup / Acceleration Phase .
—
🧠 Save this post.
🔁 Revisit it when you’re confused.
📊 Because the chart isn’t random — it’s just cycling
And also remember our golden rule :
🐺 Discipline is rarely enjoyable , but almost always profitable. 🐺
🐺 KIU_COIN 🐺
The Markets, the Rabbi and the Goat...It’s funny how sometimes markets react like people in old jokes…
They scream when things get bad, then cheer wildly when things return to how they were — as if something amazing just happened.
Let me tell you one of those jokes.
It’s about a house, a rabbi… and a goat.
A man goes to the Rabbi:
“Rabbi, my house is too small. The kids are screaming, my wife’s yelling, I’m losing my mind!”
The Rabbi calmly replies:
“Bring in the chicken.”
Two days later:
“Rabbi, it’s worse!”
Rabbi:
“Now bring in the duck.
Then the pig.
And finally… the goat."
Now the house is in complete chaos. Smell, noise, no space to move or breathe.
The man returns, ready to break down:
“Rabbi, this is hell!”
The Rabbi smiles:
“Now take them all out.”
A few days later, the man comes back glowing:
“Rabbi… it’s incredible! So much space! So quiet! So fresh!”
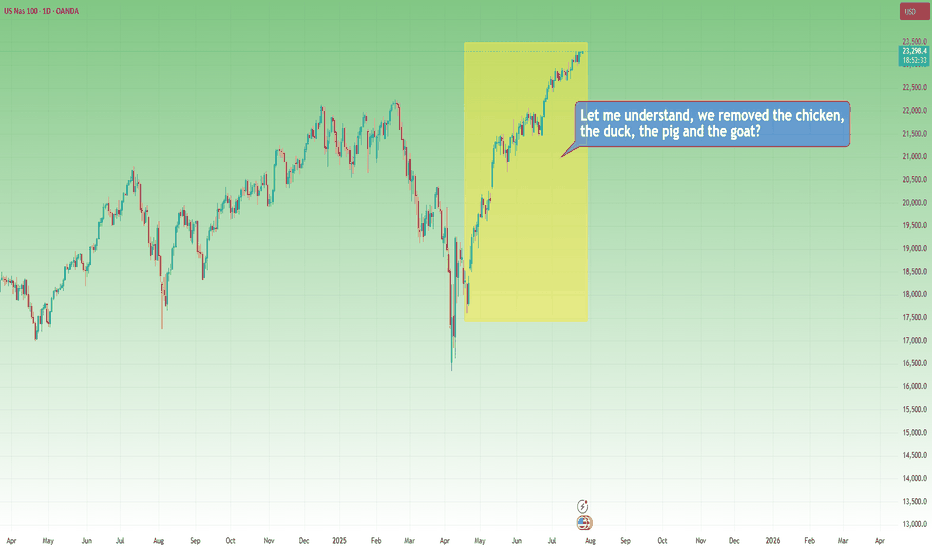
📉 Now, 2025 markets
In April, Trump imposed tariffs.
Markets fall sharply. Analysts scream recession. Headlines go full drama.
Recently, “brand new deals” have been announced.
Markets explode to new all-time highs.
Applause. Celebration. “Stability is back.”
But if you read the fine print…
The deal is basically the same old deal. Renegotiated. Repackaged.
Just without the goat.